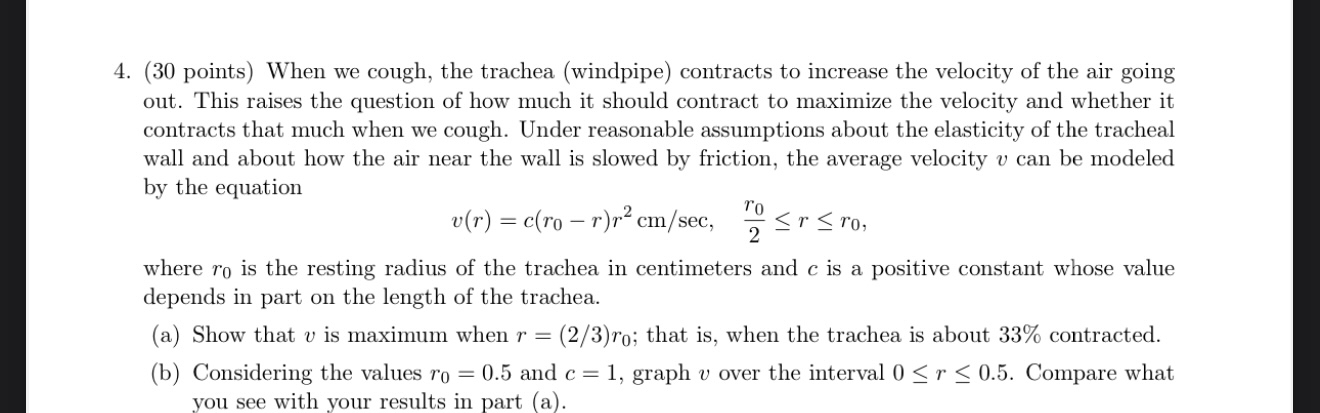
Question: ( 3 0 points ) When we cough, the trachea ( windpipe ) contracts to increase the velocity of the air going out. This raises
points When we cough, the trachea windpipe contracts to increase the velocity of the air going out. This raises the question of how much it should contract to maximize the velocity and whether it contracts that much when we cough. Under reasonable assumptions about the elasticity of the tracheal wall and about how the air near the wall is slowed by friction, the average velocity can be modeled by the equation
where is the resting radius of the trachea in centimeters and is a positive constant whose value depends in part on the length of the trachea.
a Show that is maximum when ; that is when the trachea is about contracted.
b Considering the values and graph over the interval Compare what you see with your results in part a
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


