Question: 3 . 1 Logical variables While most values in a MATLAB ? program are numbers, sometimes logical values are useful. A logical value, also known
Logical variables
While most values in a MATLAB program are numbers, sometimes logical values are useful. A logical value, also known as a Boolean
value, can be only true any nonzero number, typically or false printed by MATLAB as a In contrast, a numerical value can be any
value, ex: etc. Assigning a logical value to a variable creates a logical variable that can hold only logical values.
Logical variables can be used to test a logical state, namely whether something is either true or false, or to hold the outcome of a logical
or a relational operation, which is discussed elsewhere.
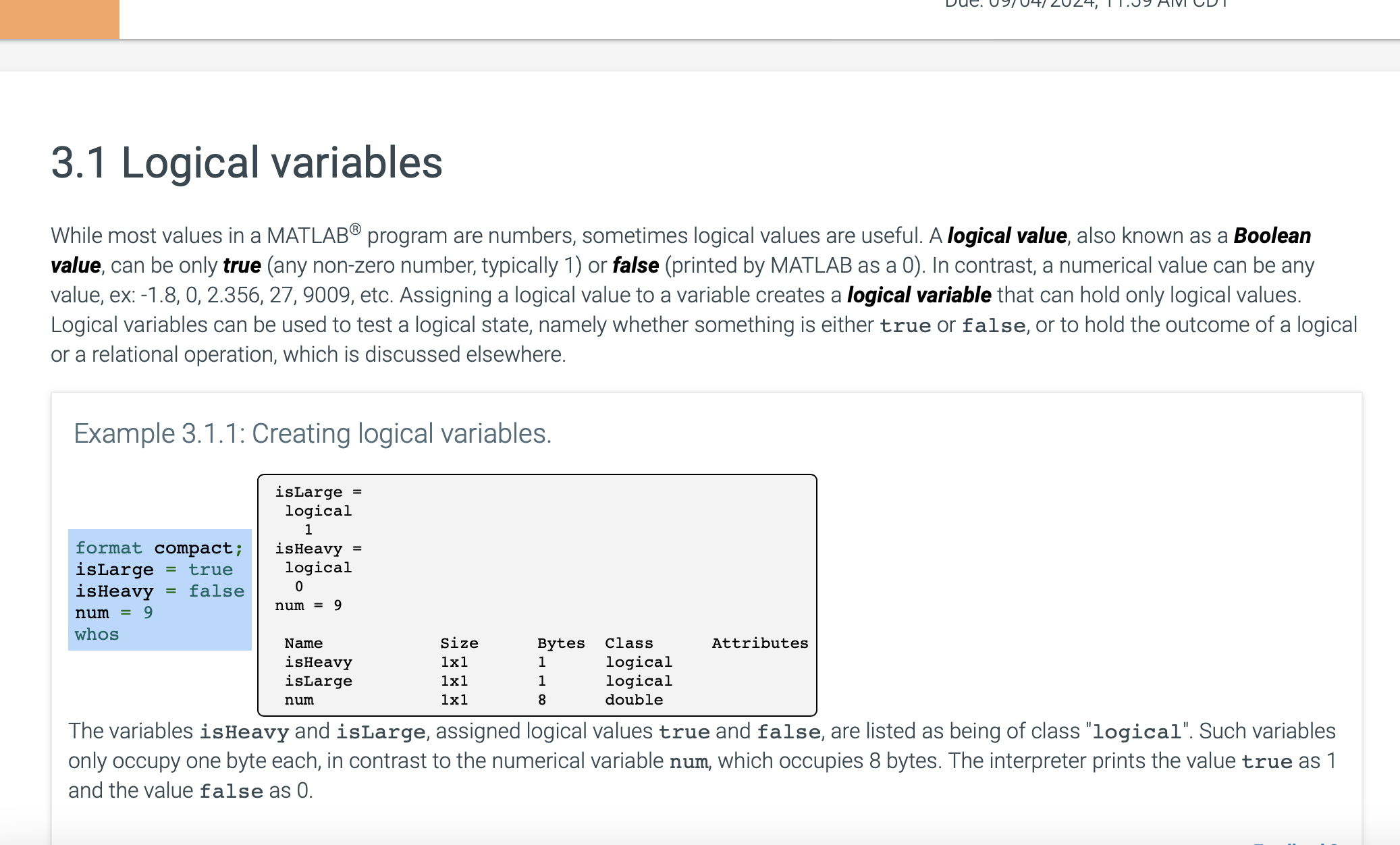
Example : Creating logical variables.
isLarge
logical
format compact;
isLarge true
isHeavy
logical
isHeavy false
num
whos
num
The variables isHeavy and isLarge, assigned logical values true and false, are listed as being of class "logical". Such variables
only occupy one byte each, in contrast to the numerical variable num, which occupies bytes. The interpreter prints the value true as
and the value false as
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


