Question: 3. [20] In our example Y86-64 programs, such as the Sum function shown in Figure 4.6, we encounter many cases (e.g., lines 2 and 10)
3. [20] In our example Y86-64 programs, such as the Sum function shown in Figure 4.6, we encounter many cases (e.g., lines 2 and 10) in which we want to add a constant value to a register. This requires first using an irmovq instruction to set a register to the constant, and then an addq instruction to add this value to the destination register. Using Figure 4.18 as a guide, draw a diagram expressing how the existing Y86-64 architecture could implement a new iaddq V, rB instruction to accomplish this functionality: Write your answer in your solutions document.
![3. [20] In our example Y86-64 programs, such as the Sum function](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f4e5054f3aa_44466f4e504eaa1f.jpg)
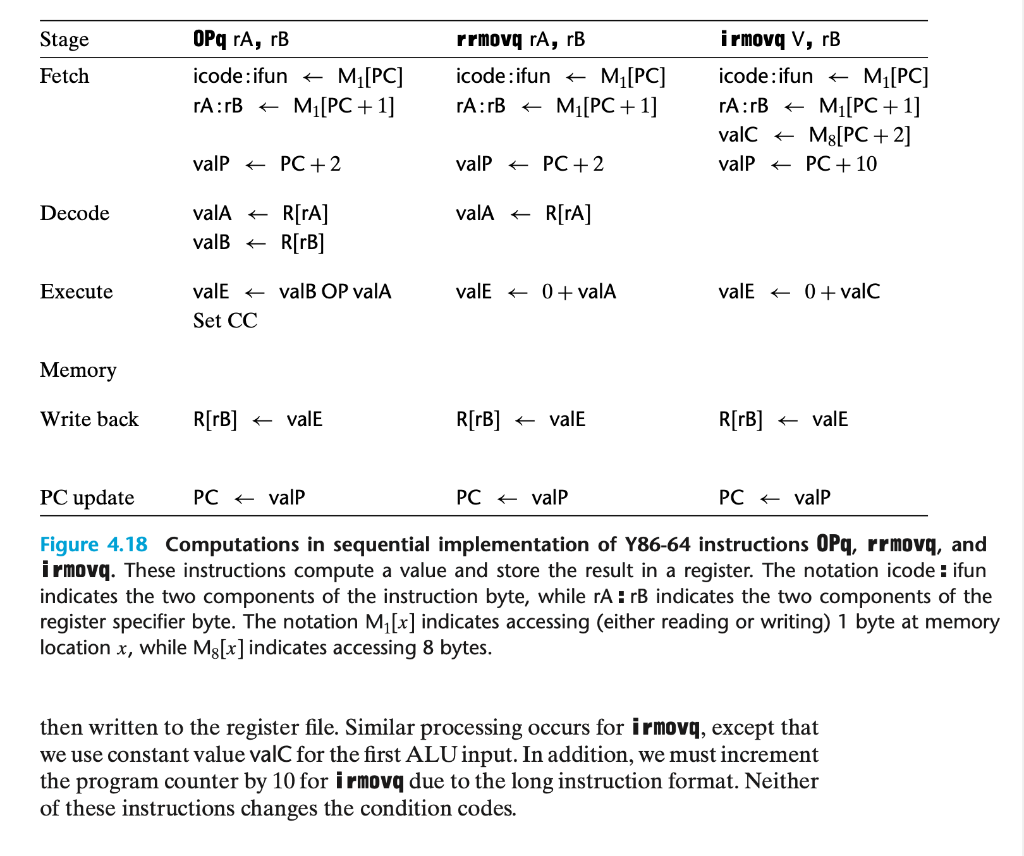
3. [20] In our example Y86-64 programs, such as the Sum function shown in Figure 4.6, we encounter many cases (e.g., lines 2 and 10) in which we want to add a constant value to a register. This requires first using an irmovq instruction to set a register to the constant, and then an addq instruction to add this value to the destination register. Using Figure 4.18 as a guide, draw a diagram expressing how the existing Y86-64 architecture could implement a new iaddq V, rB instruction to accomplish this functionality: Write your answer in your solutions document. Stage Fetch OPq ra, rB icode:ifun M[PC] rA:rB+ M[PC +1] rrmovq ra, rB icode:ifun M[PC] rA:rB M[PC + 1] i rmovq V, rB icode:ifun M[PC] rA:rB+ M[PC + 1] valc M8[PC + 2] valP + PC + 10 valp + PC + 2 valp + PC + 2 Decode vala R[rA] vala + R[ra] valB R[TB] Execute vale + 0 + valA valE+ 0 + valc vale valB OP valA Set CC Memory Write back R[rB] valE R[TB] + valE R[rB] + valE PC update PC + valp PC + valp PC + valp Figure 4.18 Computations in sequential implementation of Y86-64 instructions OPq, rrmovq, and irmovq. These instructions compute a value and store the result in a register. The notation icode : ifun indicates the two components of the instruction byte, while rA :rB indicates the two components of the register specifier byte. The notation M[x] indicates accessing (either reading or writing) 1 byte at memory location x, while M8[x] indicates accessing 8 bytes. then written to the register file. Similar processing occurs for irmovq, except that we use constant value valC for the first ALU input. In addition, we must increment the program counter by 10 for irmovq due to the long instruction format. Neither of these instructions changes the condition codes. 3. [20] In our example Y86-64 programs, such as the Sum function shown in Figure 4.6, we encounter many cases (e.g., lines 2 and 10) in which we want to add a constant value to a register. This requires first using an irmovq instruction to set a register to the constant, and then an addq instruction to add this value to the destination register. Using Figure 4.18 as a guide, draw a diagram expressing how the existing Y86-64 architecture could implement a new iaddq V, rB instruction to accomplish this functionality: Write your answer in your solutions document. Stage Fetch OPq ra, rB icode:ifun M[PC] rA:rB+ M[PC +1] rrmovq ra, rB icode:ifun M[PC] rA:rB M[PC + 1] i rmovq V, rB icode:ifun M[PC] rA:rB+ M[PC + 1] valc M8[PC + 2] valP + PC + 10 valp + PC + 2 valp + PC + 2 Decode vala R[rA] vala + R[ra] valB R[TB] Execute vale + 0 + valA valE+ 0 + valc vale valB OP valA Set CC Memory Write back R[rB] valE R[TB] + valE R[rB] + valE PC update PC + valp PC + valp PC + valp Figure 4.18 Computations in sequential implementation of Y86-64 instructions OPq, rrmovq, and irmovq. These instructions compute a value and store the result in a register. The notation icode : ifun indicates the two components of the instruction byte, while rA :rB indicates the two components of the register specifier byte. The notation M[x] indicates accessing (either reading or writing) 1 byte at memory location x, while M8[x] indicates accessing 8 bytes. then written to the register file. Similar processing occurs for irmovq, except that we use constant value valC for the first ALU input. In addition, we must increment the program counter by 10 for irmovq due to the long instruction format. Neither of these instructions changes the condition codes
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


