Question: 3 3 5 Given A and b to the right, write the augmented matrix for the linear system that corresponds to the matrix equation Ax

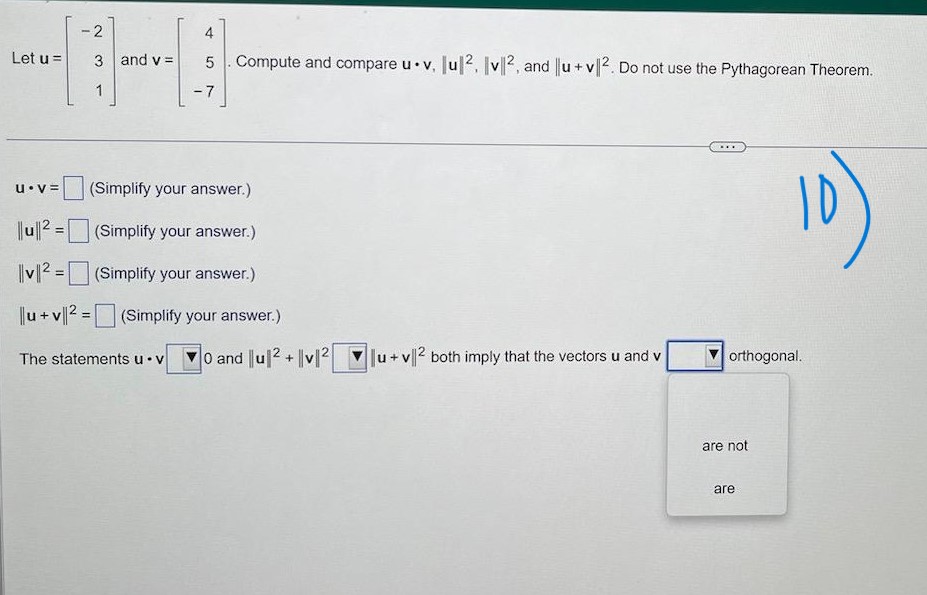

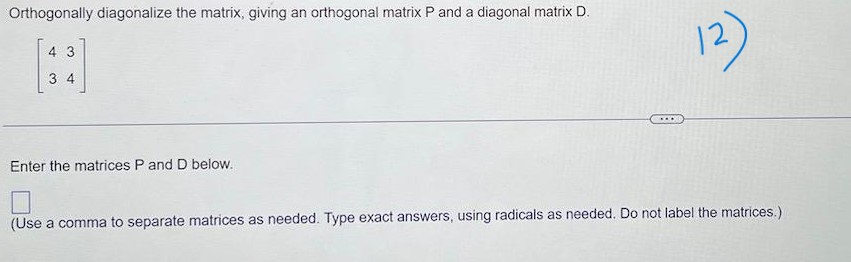


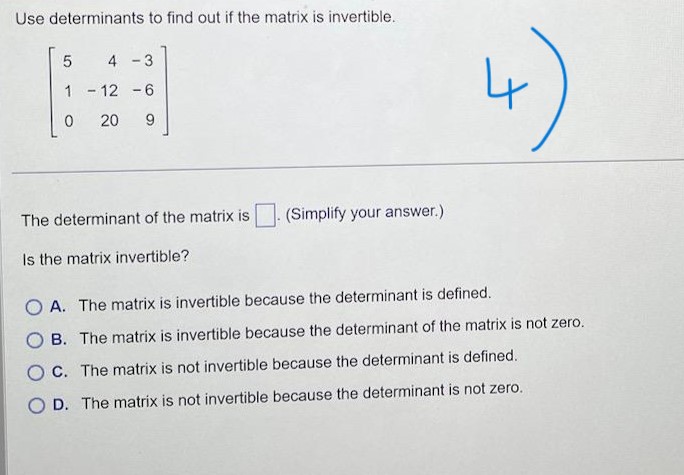


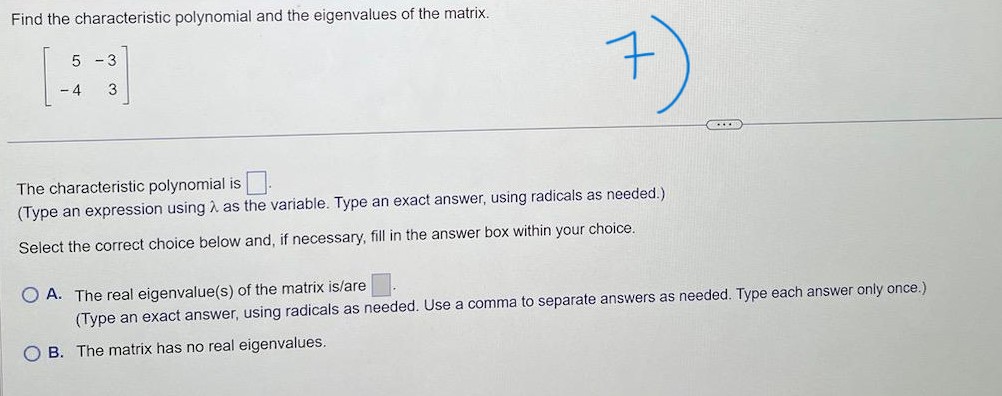
3 3 5 Given A and b to the right, write the augmented matrix for the linear system that corresponds to the matrix equation Ax = b. A= -4 -2 2 b= 10 Then solve the system and write the solution as a vector. 4 3 Write the augmented matrix for the linear system that corresponds to the matrix equation Ax = b Solve the system and write the solution as a vector. X24 Let u = 3 and V = 5 . Compute and compare u . v. Ju|2, |v|2, and |u + v|2. Do not use the Pythagorean Theorem. U . V = (Simplify your answer.) 10 lu|2 =(Simplify your answer.) I/v /2 =(Simplify your answer.) lu + v|2 = (Simplify your answer.) The statements u - v| 0 and u|2 + |v|2| |u + v|2 both imply that the vectors u and v orthogonal. are not areThe set is a basis for a subspace W. Use the Gram-Schmidt process to produce an orthogonal basis for W. Assume the vectors are in the order x, and x,. 4 6 5 The orthogonal basis produced using the Gram-Schmidt process for W is (Use a comma to separate vectors as needed.)Orthogonally diagonalize the matrix, giving an orthogonal matrix P and a diagonal matrix D. 4 3 12 4 Enter the matrices P and D below. (Use a comma to separate matrices as needed. Type exact answers, using radicals as needed. Do not label the matrices.)Find the inverse of the matrix, if it exists. - 2 0 A= 2 3 - 5 O A. O B. 0 2 3 3 10 10 O C. O D. A is not invertible. O 2 3 10Find the inverse of the matrix, if it exists. 6 4 3 A = 3 - 2 O A. O B. 6 O D. A is not invertible. O C. W- ONUse determinants to find out if the matrix is invertible. 5 4 3 1 - 12 -6 4 0 20 9 The determinant of the matrix is (Simplify your answer.) Is the matrix invertible? O A. The matrix is invertible because the determinant is defined. O B. The matrix is invertible because the determinant of the matrix is not zero. O C. The matrix is not invertible because the determinant is defined. O D. The matrix is not invertible because the determinant is not zero.0 - 5 6 Find a basis for the null space of the matrix 0 1 - 2 4 5 5 - 13 1 -22 A basis for the null space is (Use a comma to separate vectors as needed.)Find a basis for the eigenspace corresponding to the eigenvalue. 4 -2 A= - 3 9 -3 ,1=3 3 -6 6 A basis for the eigenspace corresponding to > = 3 is {} (Type a vector or list of vectors. Type an integer or simplified fraction for each matrix element. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)Find the characteristic polynomial and the eigenvalues of the matrix. 5 -3 7 4 3 The characteristic polynomial is| (Type an expression using ) as the variable. Type an exact answer, using radicals as needed.) Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice. O A. The real eigenvalue(s) of the matrix is/are (Type an exact answer, using radicals as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed. Type each answer only once.) O B. The matrix has no real eigenvalues.Diagonalize the following matrix. The real eigenvalues are given to the right of the matrix. 0 3 -1 - 3 2 3 :2=2,3,5 -3 -3 8 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. O A. 20 0 For P = D = 030 0 0 5 (Simplify your answer.) O B. The matrix cannot be diagonalized.Construct the general solution of x"= Ax involving complex eigenfunctions and then obtain the general real solution. Describe the shapes of typical trajectories. A = -9 14 What is the general solution involving complex eigenfunctions? ( A. X(1) = C1 - - 8+ cz _ is * (1 ) = c , 2 + i @ ( - 8 + 3ill + c 2 2 - i ( - 8 - 30 x B C. x(1) = C, [D D. X(1) = C, 5 ( - 8 - 31 - 9 - 2+1 (-8+ 30)1 + 62 - 14 - What is the general real solution? Re(x(1)) = Describe the shapes of typical trajectories of Re(x(1)). Choose the correct answer below. O The trajectories spiral outward from from the origin. O The trajectories form ellipses around the origin. O The trajectories spiral inward toward the origin
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


