Question: 3. 4. Find the mean, X and the standard deviation, s for this data. Ans 3 X = S= Estimate the mean completion time


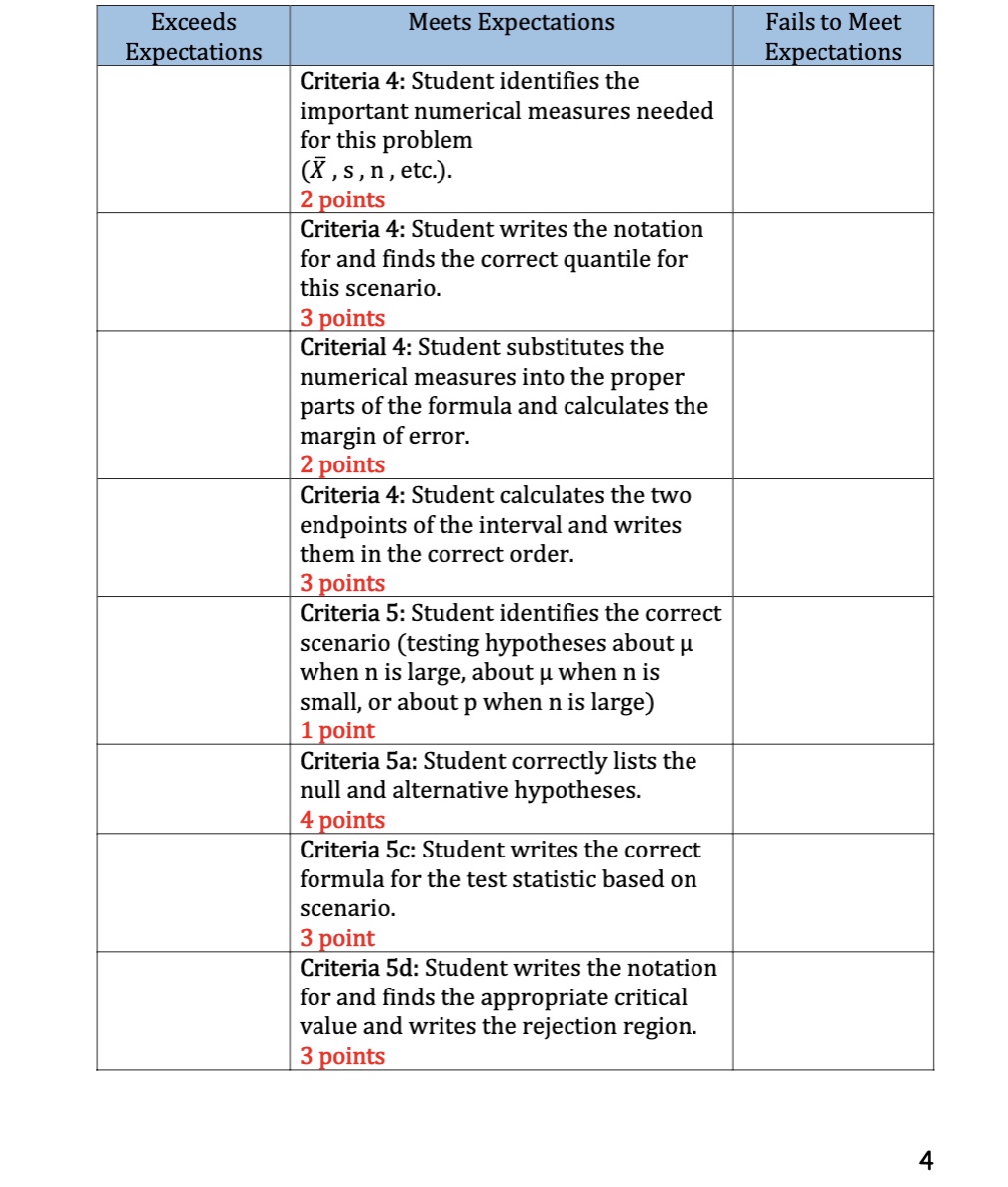
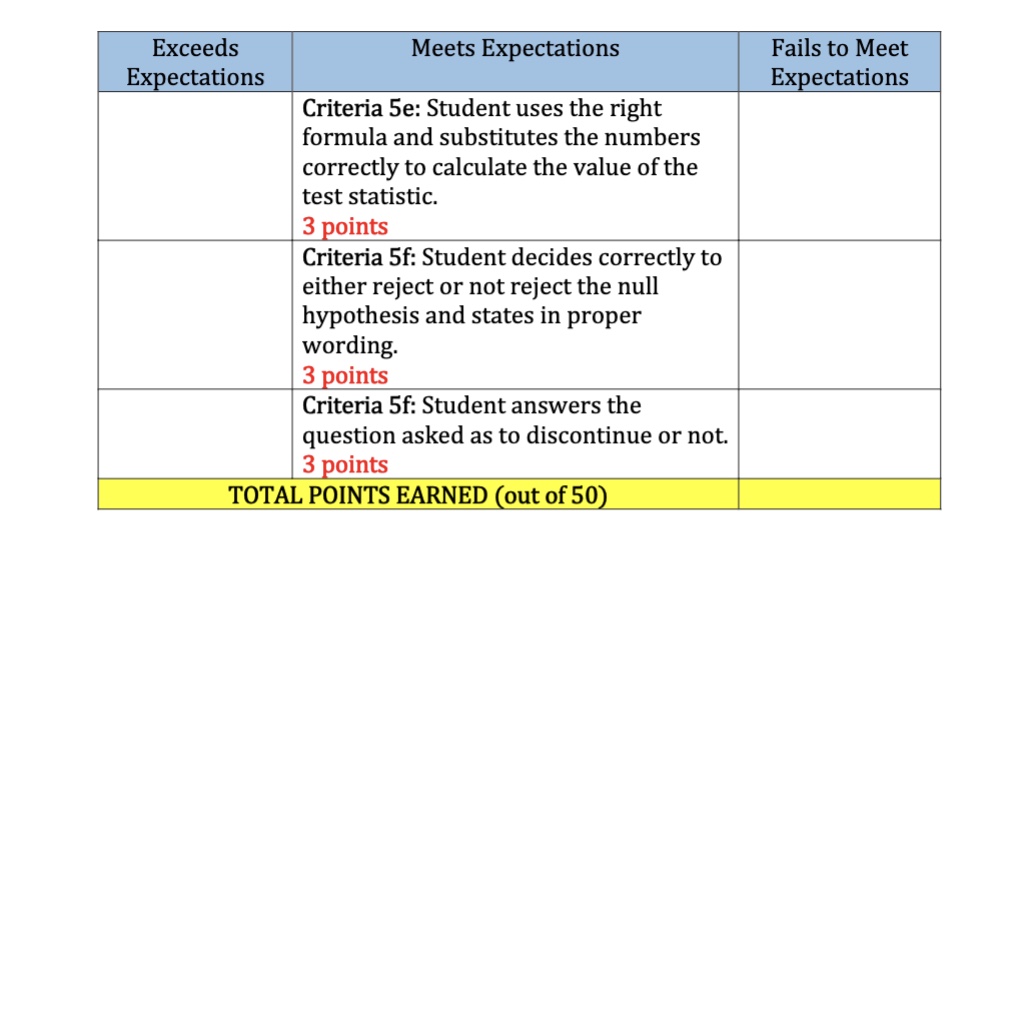
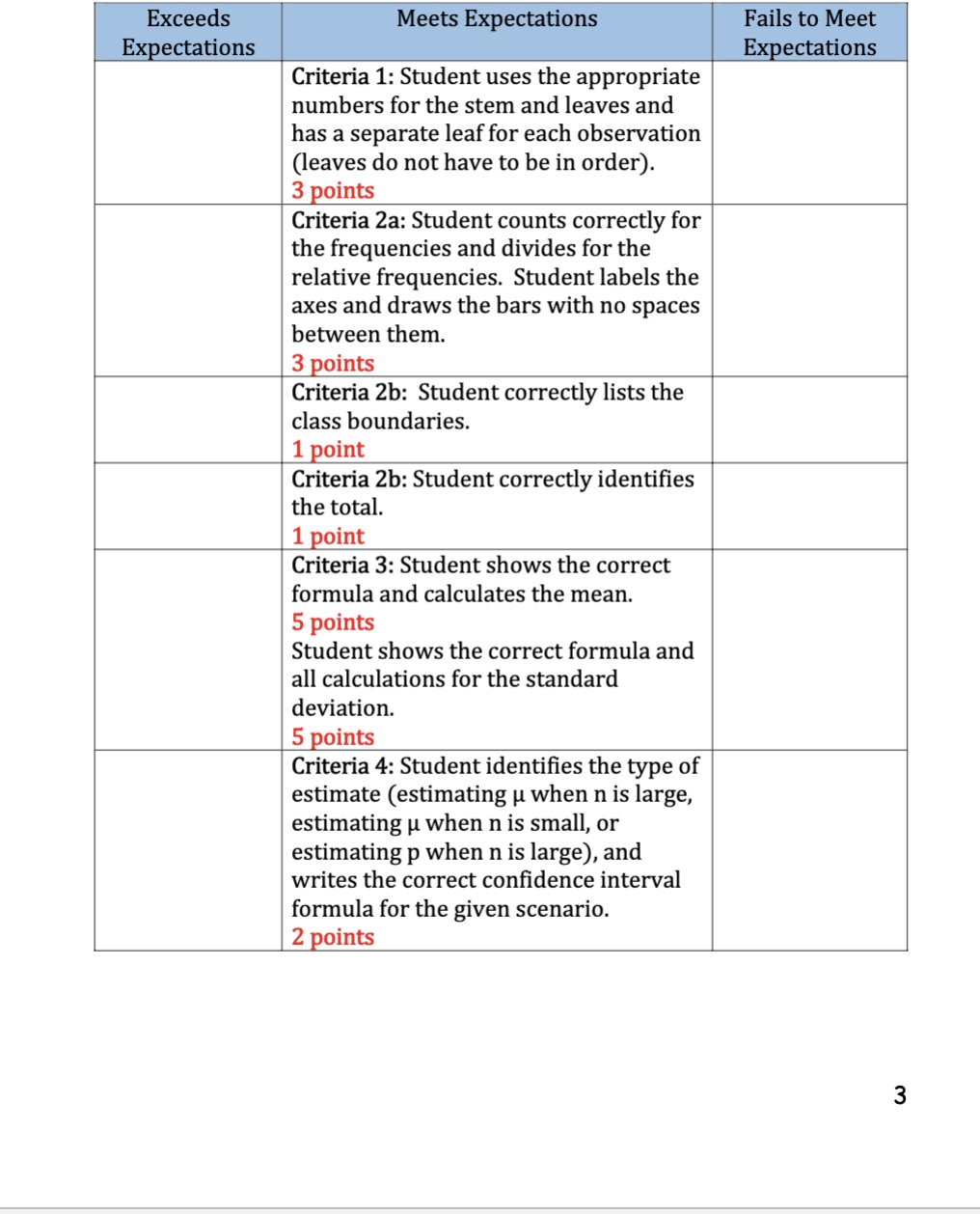
3. 4. Find the mean, X and the standard deviation, s for this data. Ans 3 X = S= Estimate the mean completion time for all students using a 90% CI. Ans 4 5. If this assignment takes more than 43 minutes to complete, it will be discontinued as a graded assignment by the instructor. At the .05 level of significance, is there enough evidence to discontinue the assignment? Complete the following six steps: a. n = Set up Ho: X = S= the appropriate hypotheses for this test. b. HA: = .05 C. List the appropriate test statistic. d. State the appropriate rejection region. e. Calculate the value of your test statistic. f. State your conclusion. Give your practical conclusion (answer the question). 2 The following set of data represents the number of minutes it takes for students to complete a graded assignment designed to gather data on the quantitative reasoning skills of degree graduates. 1. 40 40 52 37 35 49 43 50 44 39 50 45 42 51 41 Construct a stem and leaf plot for this data. STEM LEAVES 2. a. b. Complete the frequency table and draw a frequency histogram for this data. Completion Times Class frequency Class relative frequency 34.5 - 39.5 39.5-44.5 44.5 - 49.5 49.5 - 54.5 Completion times (in minutes) Where do most completion times fall? C. What proportion of the times are longer than 44.5 minutes? Exceeds Expectations Meets Expectations Criteria 4: Student identifies the important numerical measures needed for this problem (X, s, n, etc.). 2 points Criteria 4: Student writes the notation for and finds the correct quantile for this scenario. 3 points Criterial 4: Student substitutes the numerical measures into the proper parts of the formula and calculates the margin of error. 2 points Criteria 4: Student calculates the two endpoints of the interval and writes them in the correct order. 3 points Criteria 5: Student identifies the correct scenario (testing hypotheses about when n is large, about when n is small, or about p when n is large) 1 point Criteria 5a: Student correctly lists the null and alternative hypotheses. 4 points Criteria 5c: Student writes the correct formula for the test statistic based on scenario. 3 point Criteria 5d: Student writes the notation for and finds the appropriate critical value and writes the rejection region. 3 points Fails to Meet Expectations 4 Exceeds Expectations Meets Expectations Criteria 5e: Student uses the right formula and substitutes the numbers correctly to calculate the value of the test statistic. 3 points Criteria 5f: Student decides correctly to either reject or not reject the null hypothesis and states in proper Fails to Meet Expectations wording. 3 points Criteria 5f: Student answers the question asked as to discontinue or not. 3 points TOTAL POINTS EARNED (out of 50) Exceeds Expectations Meets Expectations Criteria 1: Student uses the appropriate numbers for the stem and leaves and has a separate leaf for each observation (leaves do not have to be in order). 3 points Criteria 2a: Student counts correctly for the frequencies and divides for the relative frequencies. Student labels the axes and draws the bars with no spaces between them. 3 points Criteria 2b: Student correctly lists the class boundaries. 1 point Criteria 2b: Student correctly identifies the total. 1 point Criteria 3: Student shows the correct formula and calculates the mean. 5 points Student shows the correct formula and all calculations for the standard deviation. 5 points Criteria 4: Student identifies the type of estimate (estimating when n is large, estimating when n is small, or estimating p when n is large), and writes the correct confidence interval formula for the given scenario. 2 points Fails to Meet Expectations 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To find the mean and standard deviation we first need to list all the data points 404052373549434550443950425141 Mean X The mean is calculated by summ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


