Question: _._3 4. The diagram is a rectangular prism. Let E = E, 13 2 AD and W 2 3?. Express each vector as a linear
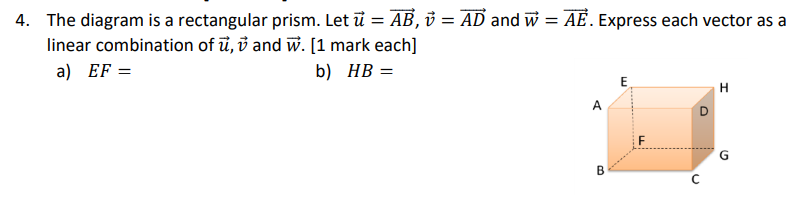
![a linear combination of E. :3 and W. [1 mark each] a]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6661382438437_39566613823f30cf.jpg)
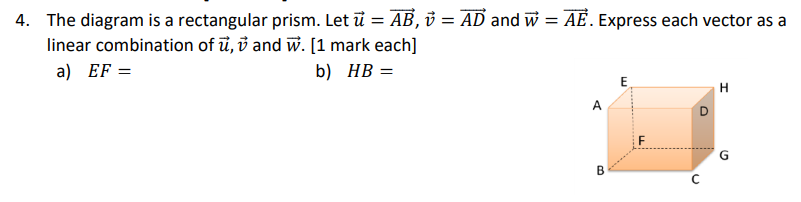
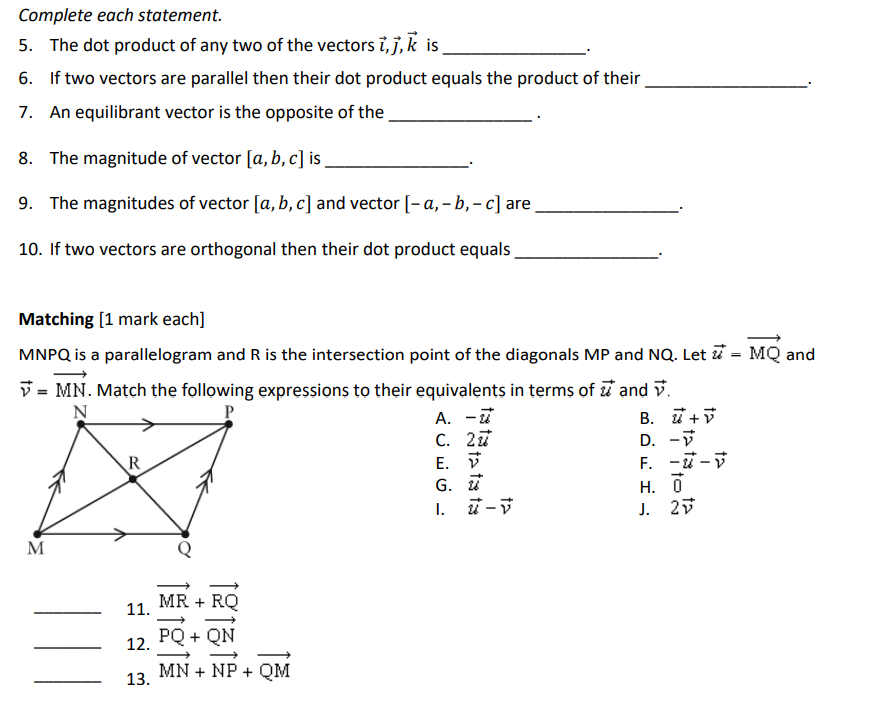
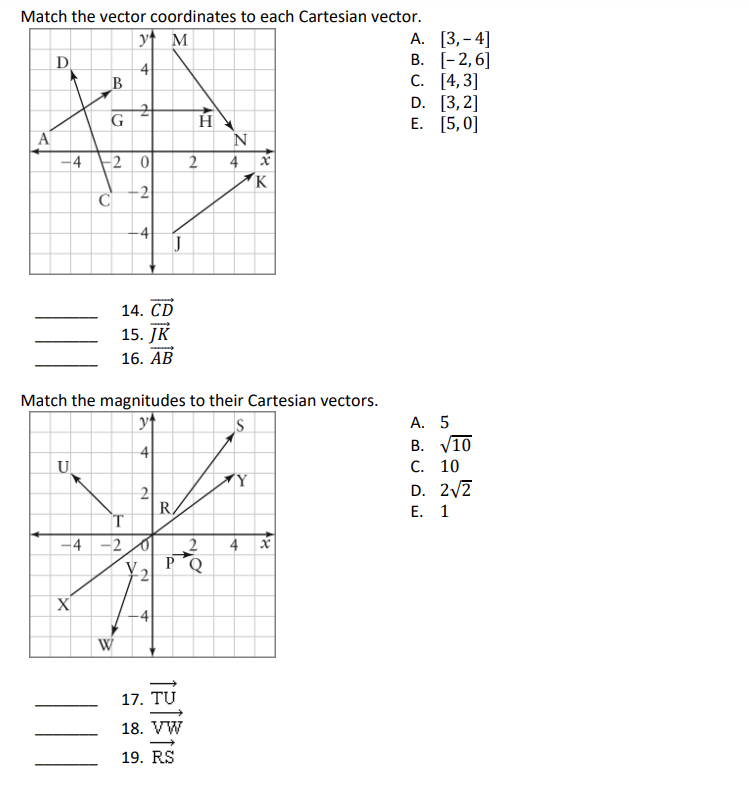
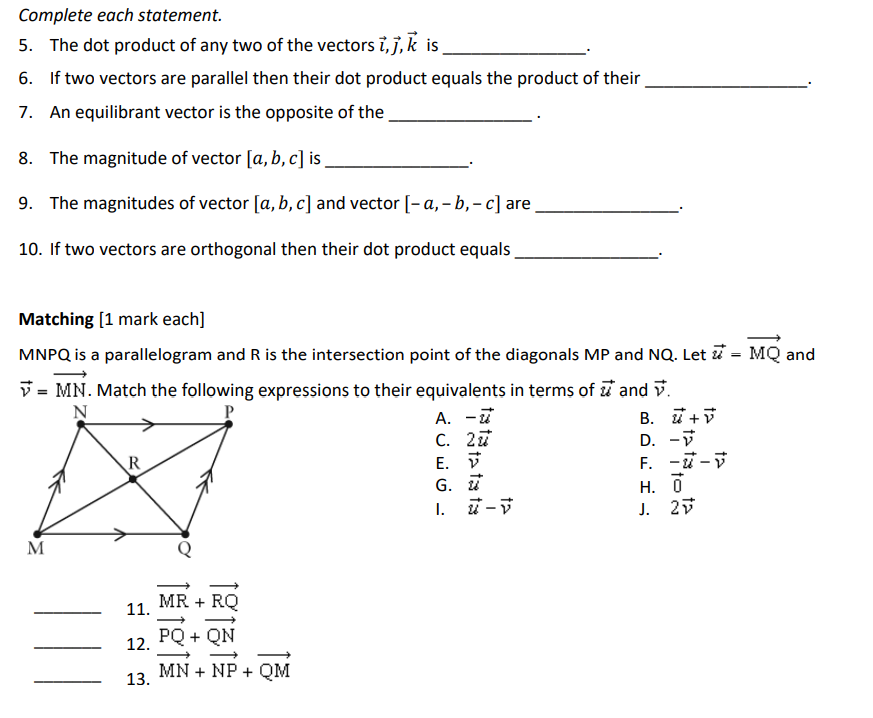
_._3 4. The diagram is a rectangular prism. Let E = E, 13 2 AD and W 2 3?. Express each vector as a linear combination of E. :3 and W. [1 mark each] a] BF: b} H3: Complete each statement. 5. The dot product of any two of the vectors i, j, k is 6. If two vectors are parallel then their dot product equals the product of their 7. An equilibrant vector is the opposite of the 8. The magnitude of vector [a, b, c] is 9. The magnitudes of vector [a, b, c] and vector [- a, - b, - c] are 10. If two vectors are orthogonal then their dot product equals Matching [1 mark each] MNPQ is a parallelogram and R is the intersection point of the diagonals MP and NQ. Let & = MQ and V = MN. Match the following expressions to their equivalents in terms of a and v. N A. - u B. u+ V 2 u D. -V E. F. - u - V G . H. 0 1. u - V J. 2V 11. MR + RO 12. PQ + ON 13, MN + NP + QMMatch the vector coordinates to each Cartesian vector. M A. [3, -4] D -4 B. [-2,6] B C. [4, 3] 2 D. [3,2] G H E. [5, 0] N 4 -2 0 2 4 X K -2 -4 14. CD 15. JK 16. AB Match the magnitudes to their Cartesian vectors. A. 5 B. V10 U C. 10 2 D. 2V2 R E. 1 -2 4 x PO X -4 W 17. TU, 18. VW 19. RS
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


