Question: 3. (5 pts.) Drawing Trees on a grid. When drawing trees on a grid, each node must be assigned an and y coordinate. Edges are
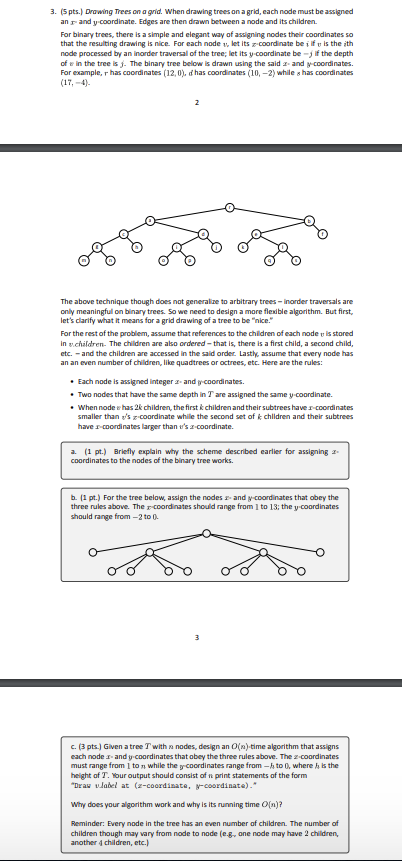
3. (5 pts.) Drawing Trees on a grid. When drawing trees on a grid, each node must be assigned an and y coordinate. Edges are then drawn between a node and its children. For binary trees, there is a simple and elegant way of assigning nodes their coordinates so that the resulting drawing is nice. For each node, let its coordinate be if u is the ith node processed by an inorder traversal of the tree; let its y coordinate bej if the depth of in the tree is f. The binary tree below is drawn using the said 2- and y-coordinates. For example, has coordinates (12,0). d has coordinates (10,-2) while shas coordinates (17.-4) 2 The above technique though does not generalize to arbitrary trees - inorder traversals are only meaningfull on binary trees. So we need to design a more flexible algorithm. But first, let's clarify what it means for a grid drawing of a tree to be "nice." For the rest of the problem, assume that references to the children of each node vis stored in .children. The children are also ordered that is, there is a first child, a second child etc. - and the children are accessed in the said order. Lastly, assume that every node has an an even number of children, like quadtrees or octrees, etc. Here are the rules: Each node is assigned integer sandy coordinates. Two nodes that have the same depth in T are assigned the same y coordinate. . When node has 2k children, the first k children and their subtrees haver-coordinates smaller than y's z.Coordinate while the second set of children and their subtrees have a I coordinates larger than t's a coordinate. 2. (1 pt.) Briefly explain why the scheme described earlier for assigning 2- coordinates to the nodes of the binary tree works. b. (1 pt.) For the tree below, assign the nodes - and y-coordinates that obey the three rules above. The coordinates should range from 1 to 13; the y coordinates should range from 2 to 0. C. (3 pts. Given a tree T with nodes, design an O(n).time algorithm that assigns each node 1 and y-coordinates that obey the three rules above. The 2-coordinates must range from 1 to while the y Coordinates range from 1 to 0, where he is the height of T. Your output should consist of print statements of the form *Draw label at (2-coordinate, y-coordinate)." Why does your algorithm work and why is its running time O(n)? Reminder: Every node in the tree has an even number of children. The number of children though may vary from node to node (c.8. one node may have 2 children, another children, etc.) 3. (5 pts.) Drawing Trees on a grid. When drawing trees on a grid, each node must be assigned an and y coordinate. Edges are then drawn between a node and its children. For binary trees, there is a simple and elegant way of assigning nodes their coordinates so that the resulting drawing is nice. For each node, let its coordinate be if u is the ith node processed by an inorder traversal of the tree; let its y coordinate bej if the depth of in the tree is f. The binary tree below is drawn using the said 2- and y-coordinates. For example, has coordinates (12,0). d has coordinates (10,-2) while shas coordinates (17.-4) 2 The above technique though does not generalize to arbitrary trees - inorder traversals are only meaningfull on binary trees. So we need to design a more flexible algorithm. But first, let's clarify what it means for a grid drawing of a tree to be "nice." For the rest of the problem, assume that references to the children of each node vis stored in .children. The children are also ordered that is, there is a first child, a second child etc. - and the children are accessed in the said order. Lastly, assume that every node has an an even number of children, like quadtrees or octrees, etc. Here are the rules: Each node is assigned integer sandy coordinates. Two nodes that have the same depth in T are assigned the same y coordinate. . When node has 2k children, the first k children and their subtrees haver-coordinates smaller than y's z.Coordinate while the second set of children and their subtrees have a I coordinates larger than t's a coordinate. 2. (1 pt.) Briefly explain why the scheme described earlier for assigning 2- coordinates to the nodes of the binary tree works. b. (1 pt.) For the tree below, assign the nodes - and y-coordinates that obey the three rules above. The coordinates should range from 1 to 13; the y coordinates should range from 2 to 0. C. (3 pts. Given a tree T with nodes, design an O(n).time algorithm that assigns each node 1 and y-coordinates that obey the three rules above. The 2-coordinates must range from 1 to while the y Coordinates range from 1 to 0, where he is the height of T. Your output should consist of print statements of the form *Draw label at (2-coordinate, y-coordinate)." Why does your algorithm work and why is its running time O(n)? Reminder: Every node in the tree has an even number of children. The number of children though may vary from node to node (c.8. one node may have 2 children, another children, etc.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


