Question: 3 Background At Springfield State U there are two classes of students: on-campus students and online students. On-campus students are categorized as residents (R) or
3 Background
At Springfield State U there are two classes of students: on-campus students and online students. On-campus students are
categorized as residents (R) or nonresidents (N) depending on whether they reside within the state in which Springfield
exists or they reside in a different state. The base tuition for on-campus students is $5500 for residents and $12,200 for
non-residents. Some on-campus students, enrolled in certain pre-professional programs, are charged an additional program
fee which varies depending on the program. An on-campus students may enroll for up to 18 credit hours at the base rate
but for each credit hour exceeding 18, they pay an additional fee of $350 for each credit hour over 18.
Online students are neither residents nor non-residents. Rather, their tuition is computed as the number of credit hours
for which they are enrolled multiplied by the online credit hour rate which is $875 per credit hours. Furthermore, some
online students enrolled in certain degree programs pay an online technology fee of $125 per semester.
4 Software Requirements
Your program shall meet these requirements.
1. Student information for Springfield State University is stored in a text file named p02-students.txt. There is one
student record per line, where the format of a student record for an on-campus student is:
C id last-name first-name residency program-fee credits
where:
'C' Identifies the student as an on-campus student.
id The student identifier number. A string of 13 digits.
last-name The student's last name. A contiguous string of characters.
first-name The student's first name. A contiguous string of characters.
residency 'R' if the student is a resident, 'N' if the student is a non-resident.
program-fee A program fee, which may be zero.
credits The number of credit hours for which the student is enrolled.
The format of a student record for an online student is:
O id last-name first-name tech-fee credits
where 'O' identifies the student as an online student, and id, last-name, first-name, and credits are the same as
for an on-campus student. The tech-fee field is 'T' if the student is to be assessed the technology fee or '-' if the
student is not assessed the technology fee.
link
in course schedule info.
Here is an example p02-students.txt file:
Sample p02-students.txt
C 8230123345450 Flintstone Fred R 0 12
C 3873472785863 Simpson Lisa N 750 18
C 4834324308675 Jetson George R 0 20
O 1384349045225 Szyslak Moe - 6
O 5627238253456 Flanders Ned T 3
2. The program shall read the contents of p02-students.txt and calculate the tuition for each student.
3. The program shall write the tuition results to an output file named p02-tuition.txt formatted thusly:
id last-name first-name tuition
id last-name first-name tuition
...
where tuition is the computed tuition for the student. The tuition shall be displayed with two digits after the
decimal point. For example:
Sample p02-tuition.txt
1384349045225 Szyslak Moe 5250.00
3873472785863 Simpson Lisa 12950.00
4834324308675 Jetson George 6200.00
5627238253456 Flanders Ned 2750.00
8230123345450 Flintstone Fred 5500.00
4. The records in the output file shall be sorted in ascending order by id.
5. If the input file p02-students.txt cannot be opened for reading (because it does not exist) then display an error
message on the output window and immediately terminate the program, e.g.,
run program
Sorry, could not open 'p02-students.txt' for reading. Stopping.
5 Software Design
Refer to the UML class diagram in Section 5.7. Your program shall implement this design.
5.1 Main Class
A template for Main is included in the zip archive. The Main class shall contain the main() method which shall
instantiate an object of the Main class and call run() on that object. Complete the code by reading the comments and
implementing the pseudocode.
5.2 TuitionConstants Class
The complete TuitionConstants class is included in the zip archive. This class simply declares some public static constants
that are used in other classes.
5.3 Sorter Class
We shall discuss sorting later in the course, so this code may not make perfect sense at this time. However, I have
provided all of it for you.
The Sorter class contains a public method insertionSort() that can be called to sort a list of ArrayList. When
sorting Students we need to be able to compare one Student A to another Student B to determine if A is less than or
greater than B. Since we are sorting by student id, we have the abstract Student class implement the Comparable
interface and we define Student A to be less than Student B if the mId field of A is less than the mId field of
B. This is how we sort the ArrayList list by student id.
java.lang.Comparable is a generic interface (it requires a type parameter T to be specified when the interface is
implemented) in the Java Class Library that declares one method:
int compareTo(T obj)
where T represents a class type and obj is an object of the class T. The method returns a negative integer if this T (the
object on which the method is invoked) is less than obj, zero if this T and obj are equal, or a positive integer if this T is
greater than obj. To make Student implement the Comparable interface, we write:
public abstract class Student implements Comparable { ... }
Since Student implements Comparable, whenever compareTo() is called in Sorter.keepMoving() to compare two
objects, either OnCampusStudent.compareTo() or OnlineStudent.compareTo() will be called.
5.4 Student Class
The Student class is an abstract class that implements the java.lang.Comparable interface (see 5.3 Sorter Class):
public abstract class Student implements Comparable {
...
}
A Student object contains five instance variables:
mCredits Number of credit hours the student is enrolled for.
mFname The student's first name.
mId The student's id number.
mLname The student's last name.
mTuititon The student's computed tuition.
Most of the Student instance methods should be straightforward to implement so we will only mention the two that are
not so obvious:
+calcTuition(): void
An abstract method that is implemented by subclasses of Student. Abstract methods do not have to be implements, and
this one is not.
+compareTo(pStudent: Student): int
Implements the compareTo() method of the Comparable interface. Returns -1 if the mId instance variable of
this Student is less than the mId instance variable of pStudent. Returns 0 if they are equal (should not happen because id
numbers are unique). Returns 1 if the mId instance variable of this Student is greater than the mId instance variable of
pStudent. The code is for compareTo() is:
return getId().compareTo(pStudent.getId());
5.5 OnCampusStudent Class
The OnCampusStudent class is a direct subclass of Student. It adds new instance variables that are specific to on-campus
students:
mResident True if the OnCampusStudent is a resident, false for non-resident.
mProgramFee Certain OnCampusStudent's pay an additional program fee. This value may be 0.
The OnCampusStudent instance methods are mostly straightforward to implement so we shall only discuss two of them.
+OnCampusStudent(pId: String, pFname: String, pLname: String):
Must call the superclass constructor passing pId, pFname, and pLname as parameters.
Arizona State University Page 3
CSE205 Object Oriented Programming and Data Structures Programming Project 2 :: 25 pts
+calcTuition(): void
Must implement the rules described in Section 3 Background. Note that we cannot directly access the mTuition instance
variable of an OnCampus Student because it is declared as private in Student. So how do we write to mTuition? By calling
the protected setTuition() method that is inherited from Student. The pseudocode for calcTuition() is:
Override Method calcTuititon() Returns Nothing
Declare double variable t
If getResidency() returns true Then
t = TuitionConstants.ONCAMP_RES_BASE
Else
t = TuitionConstants.ONCAMP_NONRES_BASE
End if
t = t + getProgramFee();
If getCredits() > TuitionConstants.MAX_CREDITS Then
t = t + (getCredits() - TuitionConstants.MAX_CREDITS) ~ TuitionConstants.ONCAMP_ADD_CREDITS
End if
Call setTuition(t)
End Method calcTuition()
5.6 OnlineStudent Class
The OnlineStudent class is a direct subclass of Student. It adds a new instance variable that is specific to online students:
mTechFee Certain OnlineStudent's pay an additional technology fee. This instance variable will be true if the
technology fee applies and false if it does not.
The OnlineStudent instance methods are mostly straightforward to implement so we shall only discuss two of them.
+OnlineStudent(pId: String, pFname: String, pLname: String):
Must call the superclass constructor passing pId, pFname, and pLname as parameters.
+calcTuition(): void
Must implement the rules described in Section 3 Background. Note that we cannot directly access the mTuition instance
variable of an OnlineStudent because it is declared as private in Student. So how do we write to mTuition? By calling the
protected setTuition() method that is inherited from Student. The pseudocode for calcTuition() is:
Override Method calcTuititon() Returns Nothing
Declare double variable t = getCredits() ~ TuitionConstants.ONLINE_CREDIT_RATE
If getTechFee() returns true Then
t = t + TuitionConstants.ONLINE_TECH_FEE
End if
Call setTuition(t)
End Method calcTuition()
5.7 UML Class Diagram
The UML class diagram shown below was created using UMLet. See the zip archive for the UMLet file. We have these
relationships:
6 Additional Project Requirements
1. Format your code neatly. Use proper indentation and spacing. Study the examples in the book and the examples the
instructor presents in the lectures and posts on the course website.
2. Put a comment header block at the top of each method formatted thusly:
/**
* A brief description of what the method does.
*/
3. Put a comment header block at the top of each source code file formatted thusly:
//********************************************************************************************************
// CLASS: classname (classname.java)
//
// DESCRIPTION
// A description of the contents of this file.
//
// COURSE AND PROJECT INFO
// Object Oriented Programming and Data Structures, semester and year
// Project Number: project-number
//
// AUTHOR
// your-name (your-email-addr)
//********************************************************************************************************
)(Tuition Constants)
//************************************************************************************************************** // CLASS: TuitionConstants // // DESCRIPTION // Constants that are used in calculating the tuition for on-campus and online students. Use these constants // in the OnCampusStudent and OnlineStudent classes. // // AUTHOR // Kevin R. Burger (burgerk@asu.edu) // Computer Science & Engineering // School of Computing, Informatics, and Decision Systems Engineering // Fulton Schools of Engineering // Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287-8809 // Web: http://www.devlang.com //************************************************************************************************************** package tuition;
public class TuitionConstants {
public static final int ONCAMP_ADD_CREDITS = 350; public static final int MAX_CREDITS = 18; public static final int ONCAMP_NONRES_BASE = 12200; public static final int ONCAMP_RES_BASE = 5500; public static final int ONLINE_CREDIT_RATE = 875; public static final int ONLINE_TECH_FEE = 125;
}
(Main)
//************************************************************************************************************** // CLASS: Main // // DESCRIPTION // The Main class for Project 2. // // AUTHOR // Kevin R. Burger (burgerk@asu.edu) // Computer Science & Engineering // School of Computing, Informatics, and Decision Systems Engineering // Fulton Schools of Engineering // Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287-8809 // Web: http://www.devlang.com //************************************************************************************************************** import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
/** * Instantiate a Main object and call run() on the object. */ public static void main(String[] args) { ??? }
/** * Calculates the tuition for each student. Write an enhanced for loop that iterates over each Student in * pStudentList. For each Student, call calcTuition() on that Student. Note: this is a polymorphic method * call. * * PSEUDOCODE * EnhancedFor each student in pStudentList Do * student.calcTuition() * End EnhancedFor */ private void calcTuition(ArrayList
/** * Reads the student information from "p02-students.txt" and returns the list of students as an ArrayList *
/** * Reads the information for an on-campus student. * * PSEUDOCODE * Declare String object id and assign pIn.next() to id * Declare String object named lname and assign pIn.next() to lname * Declare String object named fname and assign pIn.next() to fname * Declare and create an OnCampusStudent object. Pass id, fname, and lname as params to ctor. * Declare String object named res and assign pIn.next() to res * Declare double variable named fee and assign pIn.nextDouble() to fee * Declare int variable named credits and assign pIn.nextInt() to credits * If res.equals("R") Then * Call setResidency(true) on student * Else * Call setResidency(false) on student * End If * Call setProgramFee(fee) on student * Call setCredits(credits) on student * Return student */ private OnCampusStudent readOnCampusStudent(Scanner pIn) { ??? }
/** * Reads the information for an online student. * * PSEUDOCODE * Declare String object id and assign pIn.next() to id * Declare String object named lname and assign pIn.next() to lname * Declare String object named fname and assign pIn.next() to fname * Declare and create an OnlineStudent object. Pass id, fname, lname as params to the ctor., * Declare String object named fee and assign pIn.next() to fee * Declare int variable named credits and assign pIn.nextInt() to credits * If fee.equals("T")) Then * Call setTechFee(true) on student * Else * Call setTechFee(false) on student * End If * Call setCredits(credits) on student * Return student */ private OnlineStudent readOnlineStudent(Scanner pIn) { ??? }
/** * Calls other methods to implement the sw requirements. * * PSEUDOCODE * Declare ArrayList
/** * Writes the output file to "p02-tuition.txt" per the software requirements. * * PSEUDOCODE * Declare and create a PrintWriter object named out. Open "p02-tuition.txt" for writing. * EnhancedFor each student in pStudentList Do * out.print(student id + " " + student last name + " " + student first name) * out.printf("%.2f%n" student tuition) * End EnhancedFor * Close the output file */ private void writeFile(ArrayList
(Sorter)
//************************************************************************************************************** // CLASS: Sorter // // DESCRIPTION // Implements the insertion sort algorithm to sort an ArrayList of Students. // // AUTHOR // Kevin R. Burger (burgerk@asu.edu) // Computer Science & Engineering Program // Fulton Schools of Engineering // Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287-8809 // http:www.devlang.com //************************************************************************************************************** package tuition;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Sorter {
public static final int SORT_ASCENDING = 0; public static final int SORT_DESCENDING = 1;
/** * Sorts pList into ascending (pOrder = SORT_ASCENDING) or descending (pOrder = SORT_DESCENDING) order * using the insertion sort algorithm. */ public static void insertionSort(ArrayList /** * Returns true if we need to continue moving the element at pIndex until it reaches its proper location. */ private static boolean keepMoving(ArrayList /** * Swaps the elements in pList at pIndex1 and pIndex2. */ private static void swap(ArrayList } (Output p02 tuition) 1384349045225 Szyslak Moe 5250.00 3873472785863 Simpson Lisa 12950.00 4834324308675 Jetson George 6200.00 5627238253456 Flanders Ned 2750.00 8230123345450 Flintstone Fred 5500.00 UML 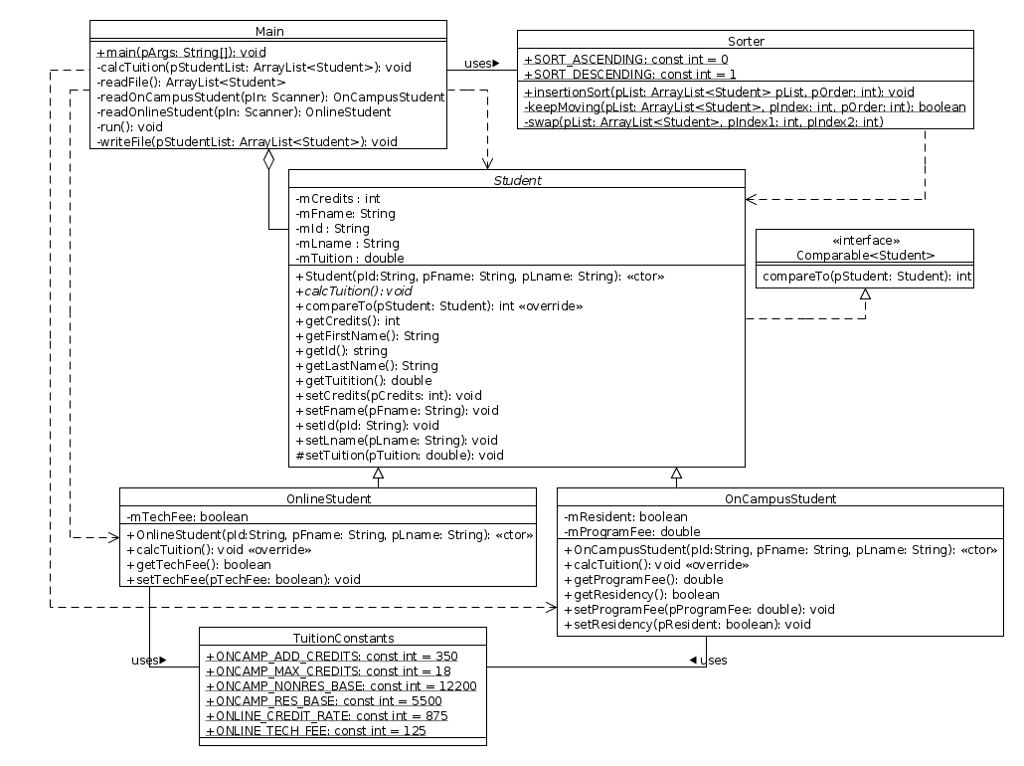
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


