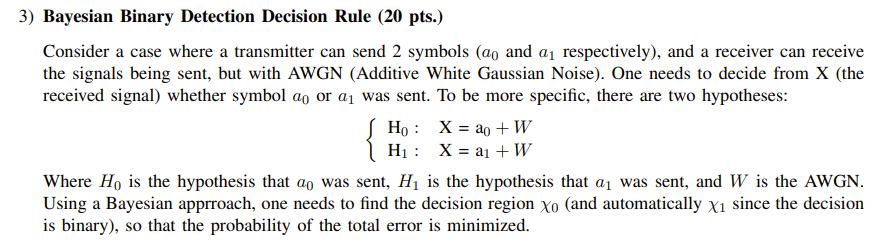
Question: 3) Bayesian Binary Detection Decision Rule (21) pts.) Consider a case where a transmitter can send 2 symbols {an and ti] respectively), and a receiver
![where a transmitter can send 2 symbols {an and ti] respectively), and](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66775a8827c30_99266775a8811f4c.jpg)
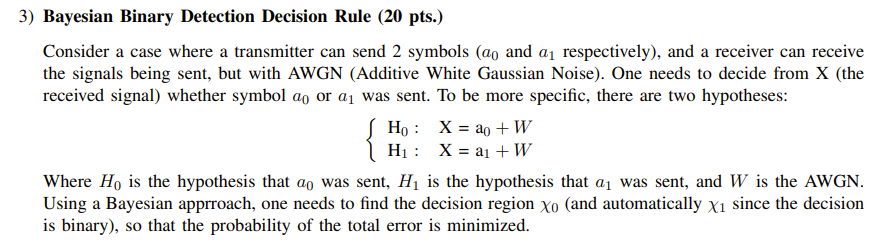

3) Bayesian Binary Detection Decision Rule (21) pts.) Consider a case where a transmitter can send 2 symbols {an and ti] respectively), and a receiver can receive the signals being sent, but with AWGN (Additive White Gaussian Noise}. One needs to decide from X (the received signal) whether symbol ea or o1 was sent. To be more specic, there are two hypotheses: H0: X=ag+W H1: X=a1+W Where Hg is the hypothesis that Go was sent, H1 is the hypothesis that it] was sent, and W is the AWGN. Using a Bayesian apprroach, one needs to nd the decision region X0 (and automatically X1 since the decision is binary), so that the probability of the total error is minimized. b} (5 pts.) To minimize P[E], derive the optimal decision rule to choose H1} over H1. Hint 1: your answer should include likelihoods and priors Hint 2: revisit the idea of Bayesian Detection
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


