Question: 3. Consider the flow through the converging/diverging nozzle shown below in Figure Q3.1. A manometer, filled with mercury (SG=13.56), is connected between the throat,
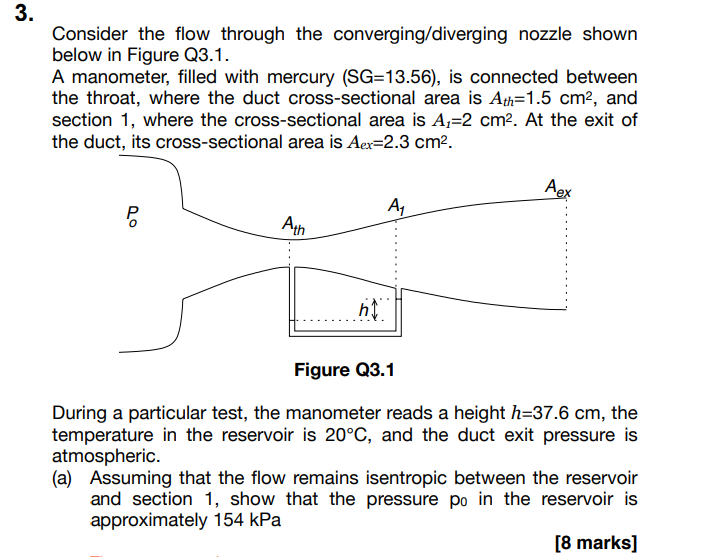


3. Consider the flow through the converging/diverging nozzle shown below in Figure Q3.1. A manometer, filled with mercury (SG=13.56), is connected between the throat, where the duct cross-sectional area is Ath=1.5 cm, and section 1, where the cross-sectional area is A=2 cm. At the exit of the duct, its cross-sectional area is Aex=2.3 cm. Do P A Ath hy Aex Figure Q3.1 During a particular test, the manometer reads a height h=37.6 cm, the temperature in the reservoir is 20C, and the duct exit pressure is atmospheric. (a) Assuming that the flow remains isentropic between the reservoir and section 1, show that the pressure po in the reservoir is approximately 154 kPa [8 marks] LEICESTER (b) If the flow were to remain isentropic throughout the duct, estimate what the pressure at the exit would be. Hence deduce that a normal shock must stand in the diverging section of the duct. [5 marks] (c) If the exit temperature is 3C, estimate what the duct cross sectional area is at the point where the shock occurs, and what the Mach number immediately upstream of the shock is. [7 marks]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


