Question: 3. Consider the majorized hinge loss optimization problem 2 N 1 (, , {;}) = (1 11 (23*2+b) + ed] = = min Emaj(w, b,
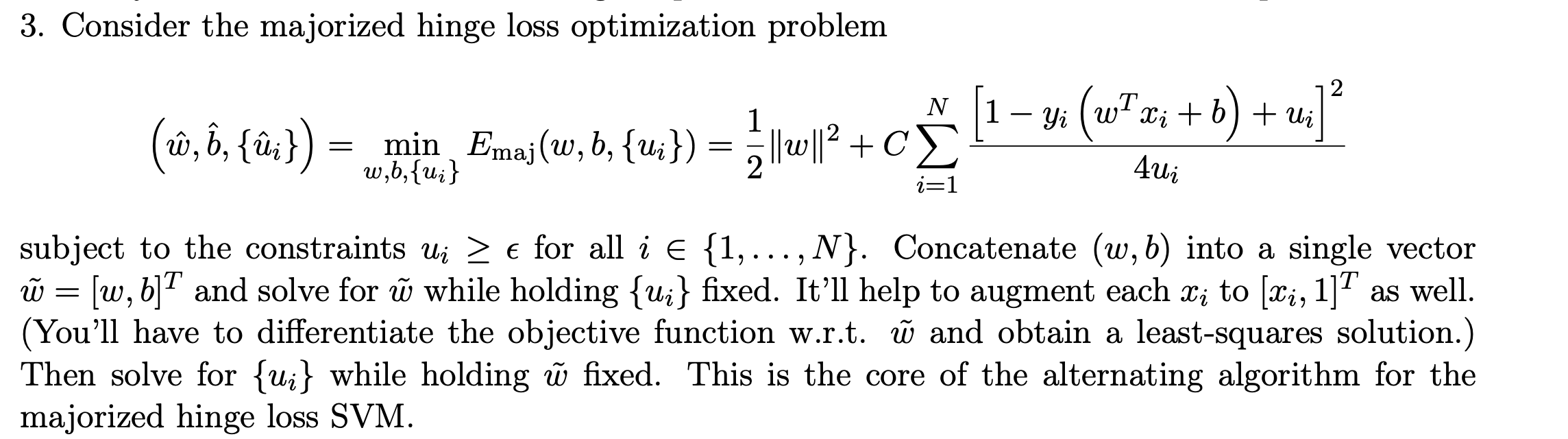
3. Consider the majorized hinge loss optimization problem 2 N 1 (, , {;}) = (1 11 (23*2+b) + ed] = = min Emaj(w, b, {U;}) w,b,{u} [ ||w||2 + 2 4u; i=1 subject to the constraints ui > for all i E {1, ...,N}. Concatenate (w,b) into a single vector W = [w, b]T and solve for while holding {Wi} fixed. It'll help to augment each xi to [Li, 1]T as well. (You'll have to differentiate the objective function w.r.t. and obtain a least-squares solution.) Then solve for {ui} while holding fixed. This is the core of the alternating algorithm for the majorized hinge loss SVM. 3. Consider the majorized hinge loss optimization problem 2 N 1 (, , {;}) = (1 11 (23*2+b) + ed] = = min Emaj(w, b, {U;}) w,b,{u} [ ||w||2 + 2 4u; i=1 subject to the constraints ui > for all i E {1, ...,N}. Concatenate (w,b) into a single vector W = [w, b]T and solve for while holding {Wi} fixed. It'll help to augment each xi to [Li, 1]T as well. (You'll have to differentiate the objective function w.r.t. and obtain a least-squares solution.) Then solve for {ui} while holding fixed. This is the core of the alternating algorithm for the majorized hinge loss SVM
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


