Question: # 3 encrypt the plaintext message CSULA Small Problems 1. A hash algorithm creates a digest of N bits. How many different digests can be
# 3 encrypt the plaintext message "CSULA"
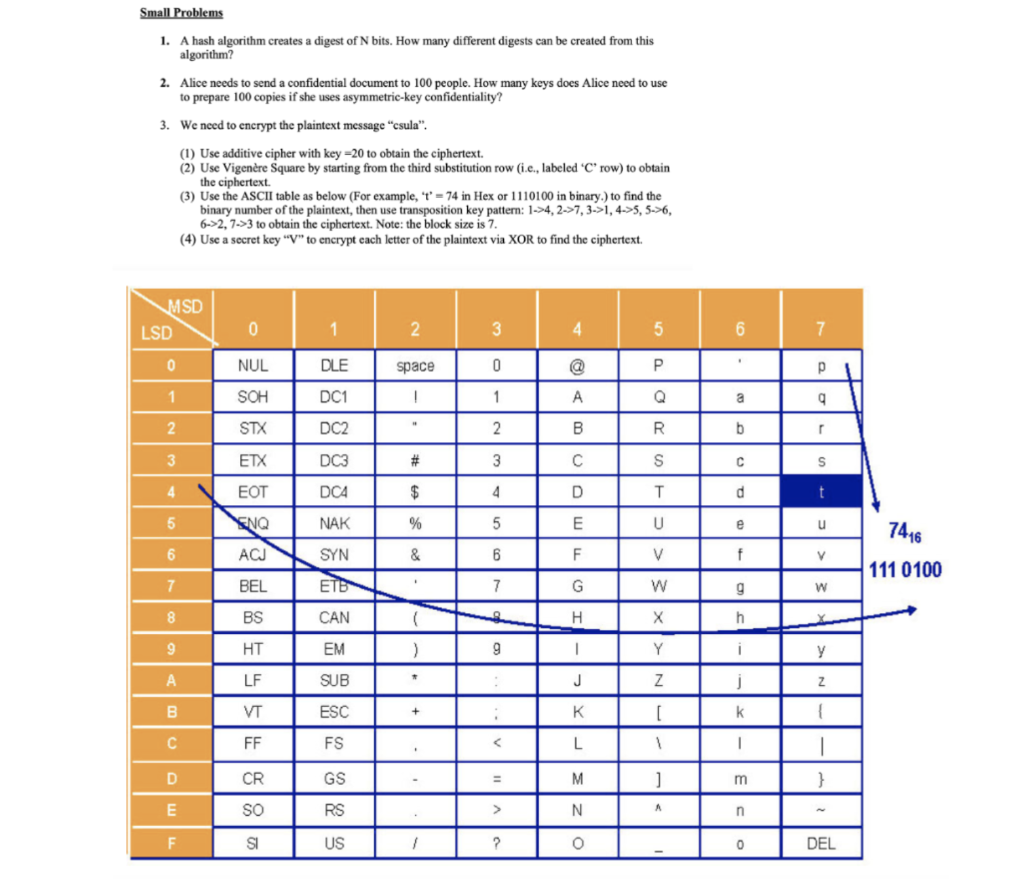
Small Problems 1. A hash algorithm creates a digest of N bits. How many different digests can be created from this algorithm? 2. Alice needs to send a confidential document to 100 people. How many keys does Alice need to use to prepare 100 copies if she uses asymmetric-key confidentiality? 3. We need to encrypt the plaintext message "csula". (1) Use additive cipher with key =20 to obtain the ciphertext. (2) Use Vigenre Square by starting from the third substitution row (1.c., labeled "Crow) to obtain the ciphertext. (3) Use the ASCII table as below (For example, "t' = 74 in Hex or 1110100 in binary.) to find the binary number of the plaintext, then use transposition key pattern: 1->4, 2->7, 3->1, 4->5,5-6, 6->2, 7->3 to obtain the ciphertext. Note: the block size is 7. (4) Use a secret key "V" to encrypt cach letter of the plaintext via XOR to find the ciphertext. MSD LSD 0 1 2. 4 5 6 o w 0 NUL DLE space ! 1 SOH DC1 1 A Q a g 2 STX DC2 2 B R b 3 ETX DC3 # 3 S S 4 EOT DCA $ 4 D T d t 5 ENQ NAK % 5 E U e u 7416 6 ACJ SYN & 6 F V f V 111 0100 7 BEL ETB 7 G w g w 8 BS CAN ( H h 9 HT EM 2 9 1 Y i LF SUB J Z j Z B VT ESC + K [ k FF FS
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


