Question: 3. Please read the lecture slide of Chapter 5, Range Queries Over M-Tree, and prove the pruning strategy for the range query below (Hint: use
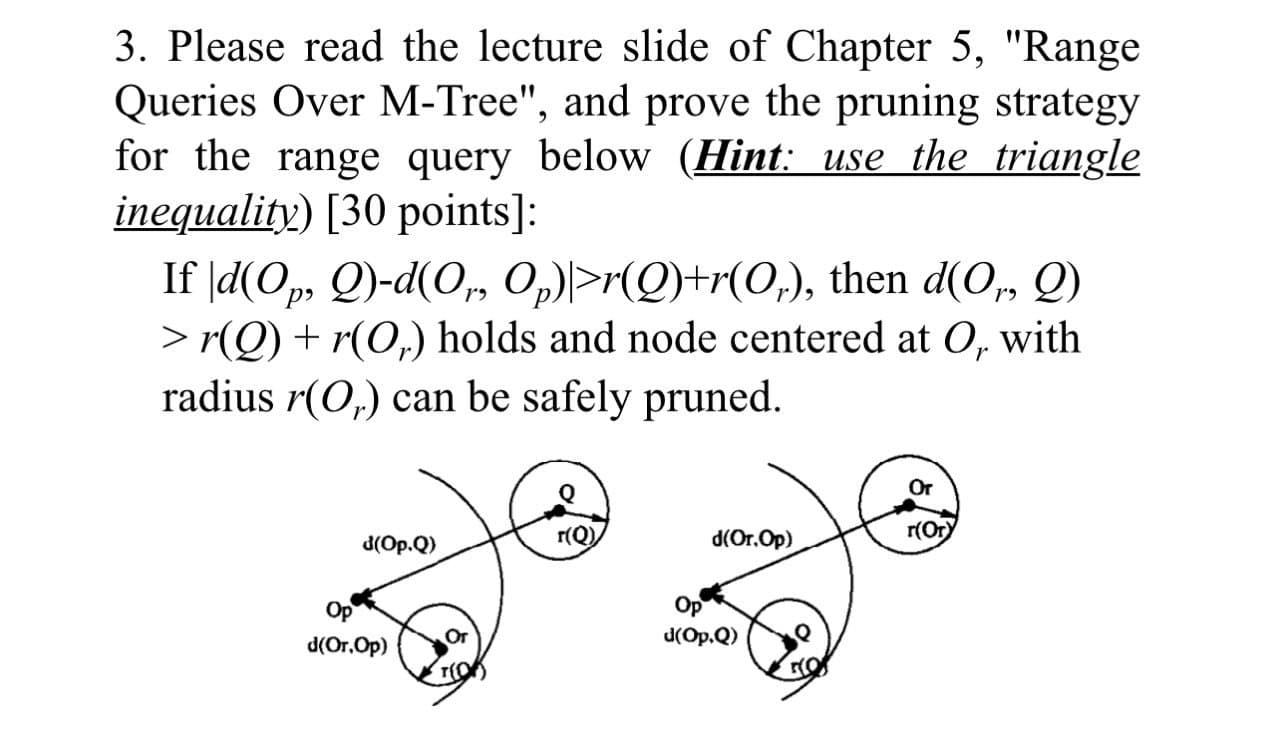
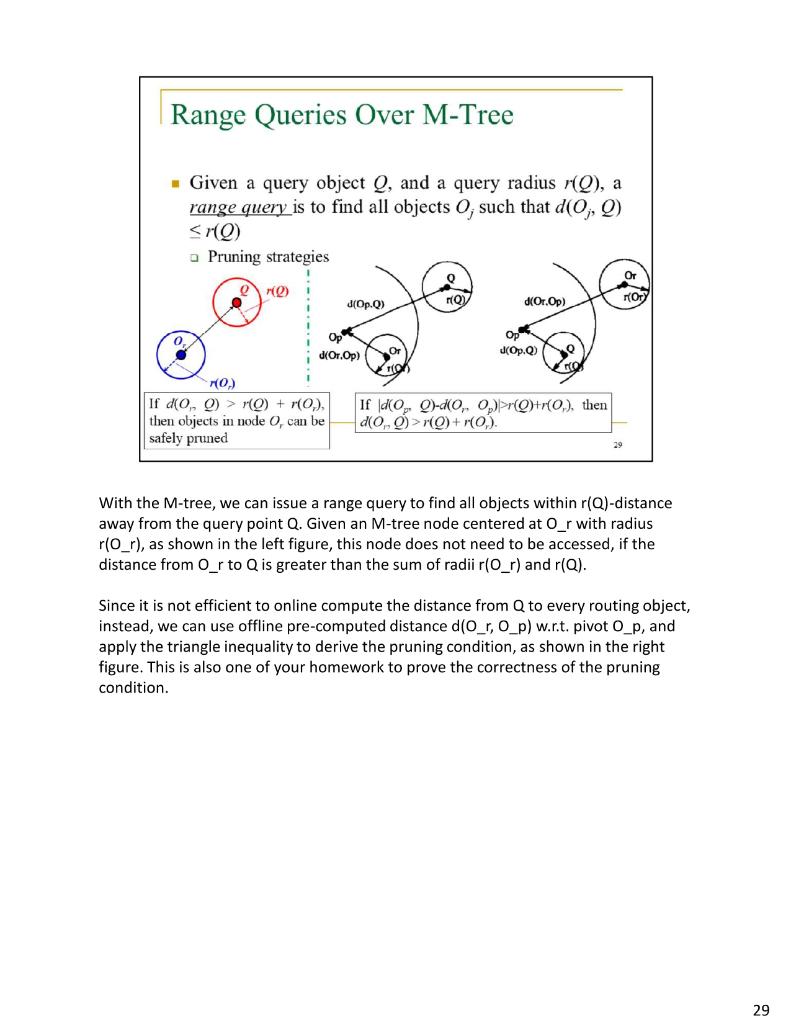
3. Please read the lecture slide of Chapter 5, "Range Queries Over M-Tree", and prove the pruning strategy for the range query below (Hint: use the triangle inequality) [30 points]: If |d(Op, Q)-d(0, Op)>r(Q)+r(0,), then d(0, Q) >r(Q)+r(0,) holds and node centered at 0, with radius r(Or) can be safely pruned. Or r(Q). d(Op.) r(Ory d(Or.Op) Op Op d(Or.Op) J(Op.Q) TO Range Queries Over M-Tree Given a query object Q, and a query radius rQ), a range query is to find all objects 0, such that d(0, 2) MQ) + (0), then objects in node , can be safely pruned If do, Q-do, p)>rQ+r(0,), then d(0,0) >r(Q)+ro). With the M-tree, we can issue a range query to find all objects within r(Q)-distance away from the query point Q. Given an M-tree node centered at O_r with radius ro_r), as shown in the left figure, this node does not need to be accessed, if the distance from O_r to Q is greater than the sum of radii r(O_r) and r(Q). Since it is not efficient to online compute the distance from Q to every routing object, instead, we can use offline pre-computed distance do_r, O_p) w.rit. pivot O_p, and apply the triangle inequality to derive the pruning condition, as shown in the right figure. This is also one of your homework to prove the correctness of the pruning condition. 29 3. Please read the lecture slide of Chapter 5, "Range Queries Over M-Tree", and prove the pruning strategy for the range query below (Hint: use the triangle inequality) [30 points]: If |d(Op, Q)-d(0, Op)>r(Q)+r(0,), then d(0, Q) >r(Q)+r(0,) holds and node centered at 0, with radius r(Or) can be safely pruned. Or r(Q). d(Op.) r(Ory d(Or.Op) Op Op d(Or.Op) J(Op.Q) TO Range Queries Over M-Tree Given a query object Q, and a query radius rQ), a range query is to find all objects 0, such that d(0, 2) MQ) + (0), then objects in node , can be safely pruned If do, Q-do, p)>rQ+r(0,), then d(0,0) >r(Q)+ro). With the M-tree, we can issue a range query to find all objects within r(Q)-distance away from the query point Q. Given an M-tree node centered at O_r with radius ro_r), as shown in the left figure, this node does not need to be accessed, if the distance from O_r to Q is greater than the sum of radii r(O_r) and r(Q). Since it is not efficient to online compute the distance from Q to every routing object, instead, we can use offline pre-computed distance do_r, O_p) w.rit. pivot O_p, and apply the triangle inequality to derive the pruning condition, as shown in the right figure. This is also one of your homework to prove the correctness of the pruning condition. 29





