Question: (3 points) Consider the following integer array and the alternatives for the partialsum method. public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {1, 4,
![the partialsum method. public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f301c5cd043_73366f301c56f595.jpg)
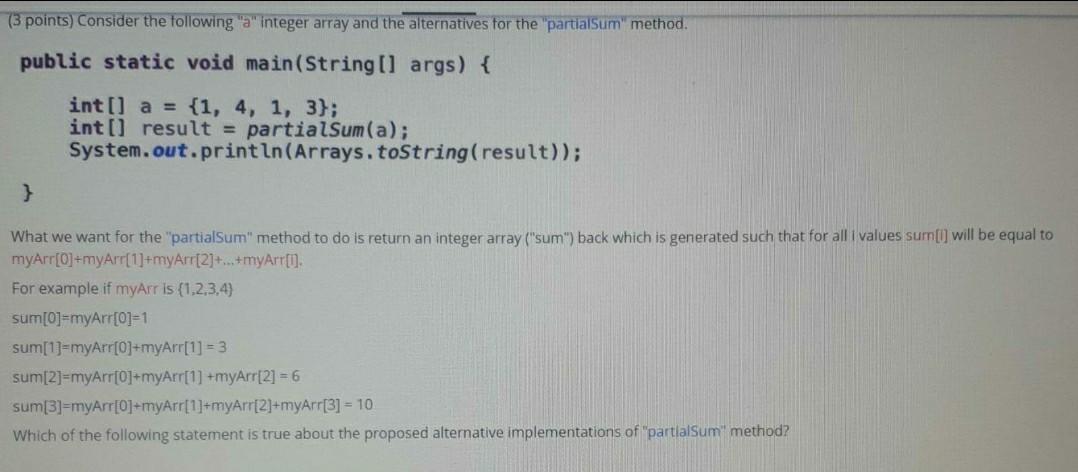
(3 points) Consider the following integer array and the alternatives for the partialsum method. public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {1, 4, 1, 3}; int[] result = partialSum(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result)); } What we want for the "partialSum" method to do is return an integer array("sum) back which is generated such that for all i values sum[] will be equal to myArr[O]+myArr[1]+myArr[2]+...+myArr[1]. For example if myArr is {1,2,3,4) sum[0]=myArr[0]=1 sum[1]=myArr[C]+myArr[1] = 3 sum[2]=myArr[0]+myArr[1] +myArr[2] = 6 sum[3]=myArr[O]+myArr[1]+myArr[2]+myArr[3] = 10 Which of the following statement is true about the proposed alternative implementations of "partialSum" method? Alternative 1 Alternative 2 public static int[l partialSum(int[] myArr) { int(1 sum = new int[myArr. length); for (int j = 0; j return sum; Your answer: Both alternatives will work Both alternatives will not work Alternative 1 will not work, because it will cause an error Alternative 2 will not work, because it will cause an error Clear
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


