Question: 3. Prey-Predator System Eigenvalues and eigenvectors provide the key to understanding the long-term behaviour of a discrete dynamical system, one example being the prey-predator system.


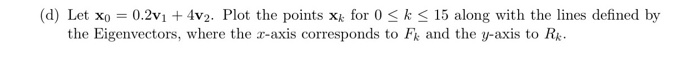
3. Prey-Predator System Eigenvalues and eigenvectors provide the key to understanding the long-term behaviour of a discrete dynamical system, one example being the prey-predator system. Denote the fox and rabbit populations at time k by x of foxes in the region studied, and Rk is the number of rabbits. Suppose Fk , where k is the time in months, Fk is the number where p > 0 is a positive parameter The term 0.4Fe means that if there are no rabbits in the forest, then 40% of the foxes will survive each month . The term 1.2Rk means that if there are no foxes in the forest hunting them, then the rabbit population will grow by 20% per month If there are plenty of rabbits in the forest, the term 0.3Rk will increase the fox population; the term -pFk takes account the deaths of rabbits due to predation by foxes. Fk Rk (a) Rewrite the discrete dynamical system in the matrix form xk+1 = MXp where X,- Setting p 0.325, find the eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenvectors of the matrix M. From now on, we will call the biggest Eigenvalue, 2 the smallest Eigenvalue, and vi, v2 their respective Eigenvectors. Hint. You m.ay use that the Eigenvalues of a 2 2 matric are given by the foTTnula T(M) 1:/ Tr(M)12-4 det(M). where Tr(M) is defined as the sum of the diagonal entries of the matrix M
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


