Question: 3. The relationship between marginal and average costs The following scenario examines the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Parker is a high school
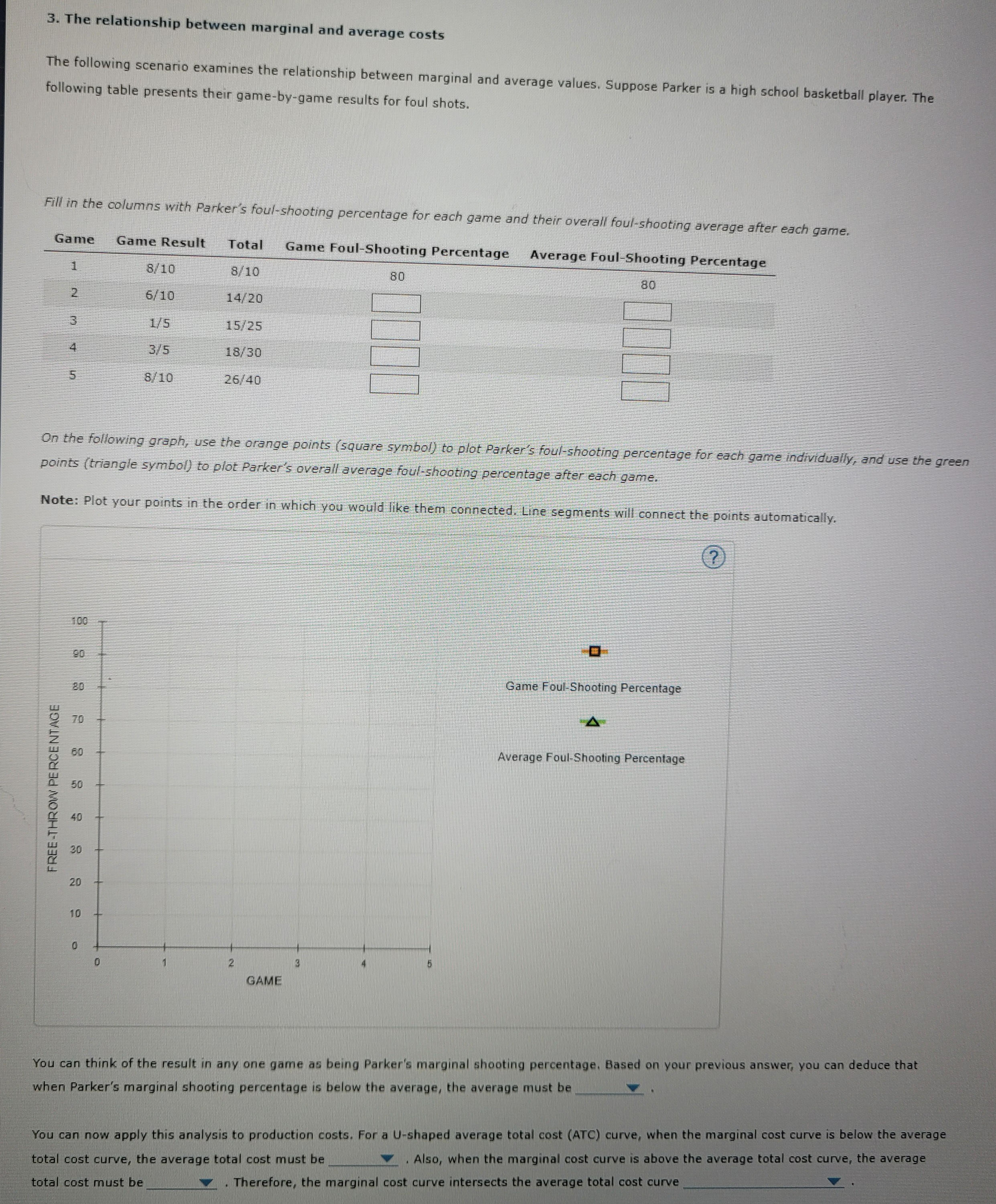
3. The relationship between marginal and average costs The following scenario examines the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Parker is a high school basketball player. The following table presents their game-by-game results for foul shots. Fill in the columns with Parker's foul-shooting percentage for each game and their overall foul-shooting average after each game. Game Game Result Total Game Foul-Shooting Percentage Average Foul-Shooting Percentage 8/10 8/10 80 80 2 610 14/20 1/5 15/25 3/5 18/30 8/ 10 26/40 On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot Parker's foul-shooting percentage for each game individually, and use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot Parker's overall average foul-shooting percentage after each game. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically. (? 100 90 Game Foul-Shooting Percentage 80 70 Average Foul-Shooting Percentage FREE-THROW PERCENTAGE 20 GAME You can think of the result in any one game as being Parker's marginal shooting percentage, Based on your previous answer, you can deduce that when Parker's marginal shooting percentage is below the average, the average must be You can now apply this analysis to production costs. For a U-shaped average total cost (ATC) curve, when the marginal cost curve is below the average . Also, when the marginal cost curve is above the average total cost curve, the average total cost curve, the average total cost must be total cost must be_ . Therefore, the marginal cost curve intersects the average total cost curve
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


