Question: 3. The structural features found within H2 receptor antagonists include a basic functional group that is protonated at physiological pH (A), an aromatic ring (B)
3. The structural features found within H2 receptor antagonists include a basic functional group that is protonated at physiological pH (A), an aromatic ring (B) and a terminal non-basic polar functional group (C) that is separated from the aromatic ring by the equivalent of a four-carbon chain. The terminal non-basic polar functional group participates in a key ion-dipole interaction with an ionized carboxylic acid found in the binding region within the H2 receptor. - C B A A. Identify all of the functional groups that are present in the structure of famotidine. Famotidine (Pepcid) B. Guanidines and amidines that are substituted with electron withdrawing groups have signifi cantly decreased basicity compared to unsubstituted guanidines (pKa ~ 12.5) and amidines (pKa ~ 9) and are unprotonated (unionized) at physiological pH. Name the two electron withdrawing functional groups found within famotidine. C. The boxed functional group (show below) participates in a key ion-dipole interaction with an ionized carboxylic acid group found in the H2 receptor binding region. Provide a brief rationale why this functional group is not protonated (ionized) at physiological pH. Famotidine (Pepcid)
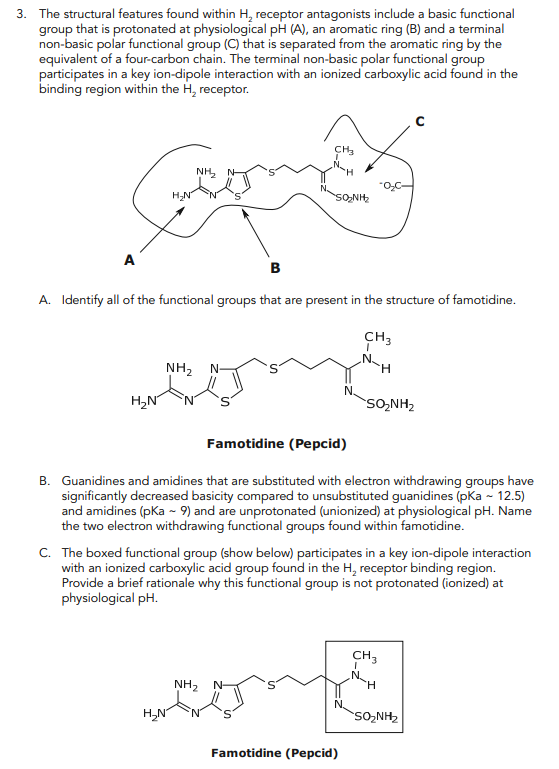
3. The structural features found within H2 receptor antagonists include a basic functional group that is protonated at physiological pH(A), an aromatic ring (B) and a terminal non-basic polar functional group (C) that is separated from the aromatic ring by the equivalent of a four-carbon chain. The terminal non-basic polar functional group participates in a key ion-dipole interaction with an ionized carboxylic acid found in the binding region within the H2 receptor. A. Identify all of the functional groups that are present in the structure of famotidine. Famotidine (Pepcid) B. Guanidines and amidines that are substituted with electron withdrawing groups have significantly decreased basicity compared to unsubstituted guanidines (pKa 12.5) and amidines (pKa9) and are unprotonated (unionized) at physiological pH. Name the two electron withdrawing functional groups found within famotidine. C. The boxed functional group (show below) participates in a key ion-dipole interaction with an ionized carboxylic acid group found in the H2 receptor binding region. Provide a brief rationale why this functional group is not protonated (ionized) at physiological pH. 3. The structural features found within H2 receptor antagonists include a basic functional group that is protonated at physiological pH(A), an aromatic ring (B) and a terminal non-basic polar functional group (C) that is separated from the aromatic ring by the equivalent of a four-carbon chain. The terminal non-basic polar functional group participates in a key ion-dipole interaction with an ionized carboxylic acid found in the binding region within the H2 receptor. A. Identify all of the functional groups that are present in the structure of famotidine. Famotidine (Pepcid) B. Guanidines and amidines that are substituted with electron withdrawing groups have significantly decreased basicity compared to unsubstituted guanidines (pKa 12.5) and amidines (pKa9) and are unprotonated (unionized) at physiological pH. Name the two electron withdrawing functional groups found within famotidine. C. The boxed functional group (show below) participates in a key ion-dipole interaction with an ionized carboxylic acid group found in the H2 receptor binding region. Provide a brief rationale why this functional group is not protonated (ionized) at physiological pH
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


