Question: 3.6-3. The following data are provided for a linear programming problem where the objective is to minimize the cost of conducting two non-negative activities in
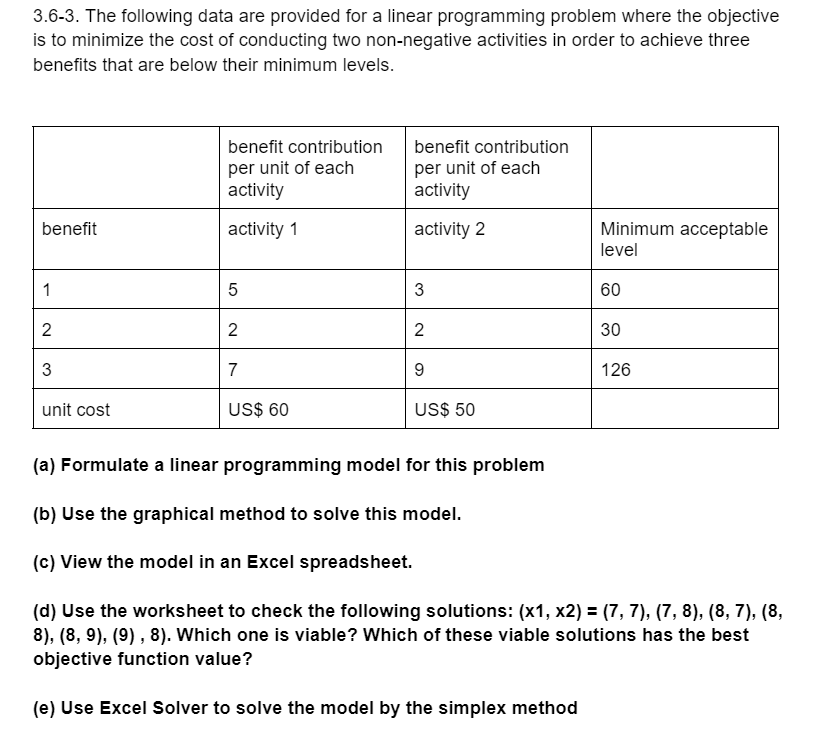
3.6-3. The following data are provided for a linear programming problem where the objective is to minimize the cost of conducting two non-negative activities in order to achieve three benefits that are below their minimum levels. benefit contribution per unit of each activity benefit contribution per unit of each activity benefit activity 1 activity 2 Minimum acceptable level 1 5 3 3 60 2 N 30 N 3 7 9 126 unit cost US$ 60 US$ 50 (a) Formulate a linear programming model for this problem (b) Use the graphical method to solve this model. (C) View the model in an Excel spreadsheet. (d) Use the worksheet to check the following solutions: (x1, x2) = (7, 7), (7, 8), (8, 7), (8, 8), (8,9), (9), 8). Which one is viable? Which of these viable solutions has the best objective function value? (e) Use Excel Solver to solve the model by the simplex method 3.6-3. The following data are provided for a linear programming problem where the objective is to minimize the cost of conducting two non-negative activities in order to achieve three benefits that are below their minimum levels. benefit contribution per unit of each activity benefit contribution per unit of each activity benefit activity 1 activity 2 Minimum acceptable level 1 5 3 3 60 2 N 30 N 3 7 9 126 unit cost US$ 60 US$ 50 (a) Formulate a linear programming model for this problem (b) Use the graphical method to solve this model. (C) View the model in an Excel spreadsheet. (d) Use the worksheet to check the following solutions: (x1, x2) = (7, 7), (7, 8), (8, 7), (8, 8), (8,9), (9), 8). Which one is viable? Which of these viable solutions has the best objective function value? (e) Use Excel Solver to solve the model by the simplex method
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


