Question: 3rd time posting this one the chegg experts got it wrong both times this is my final attempt the average flow time and days past
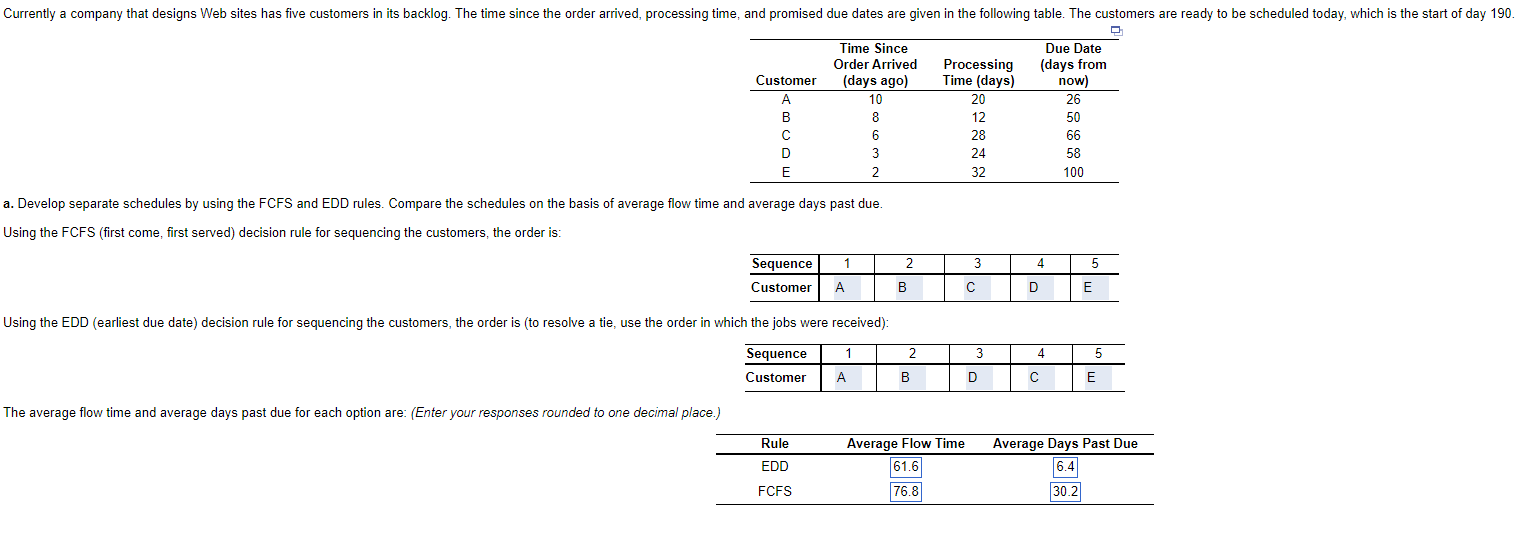 3rd time posting this one the chegg experts got it wrong both times this is my final attempt the average flow time and days past due numbers from the last expert are showing they came back wrong. I also need to know based on your answer I need to know B which is below, below is pearsons example of this problem with different numbers and how they solved it.
3rd time posting this one the chegg experts got it wrong both times this is my final attempt the average flow time and days past due numbers from the last expert are showing they came back wrong. I also need to know based on your answer I need to know B which is below, below is pearsons example of this problem with different numbers and how they solved it.
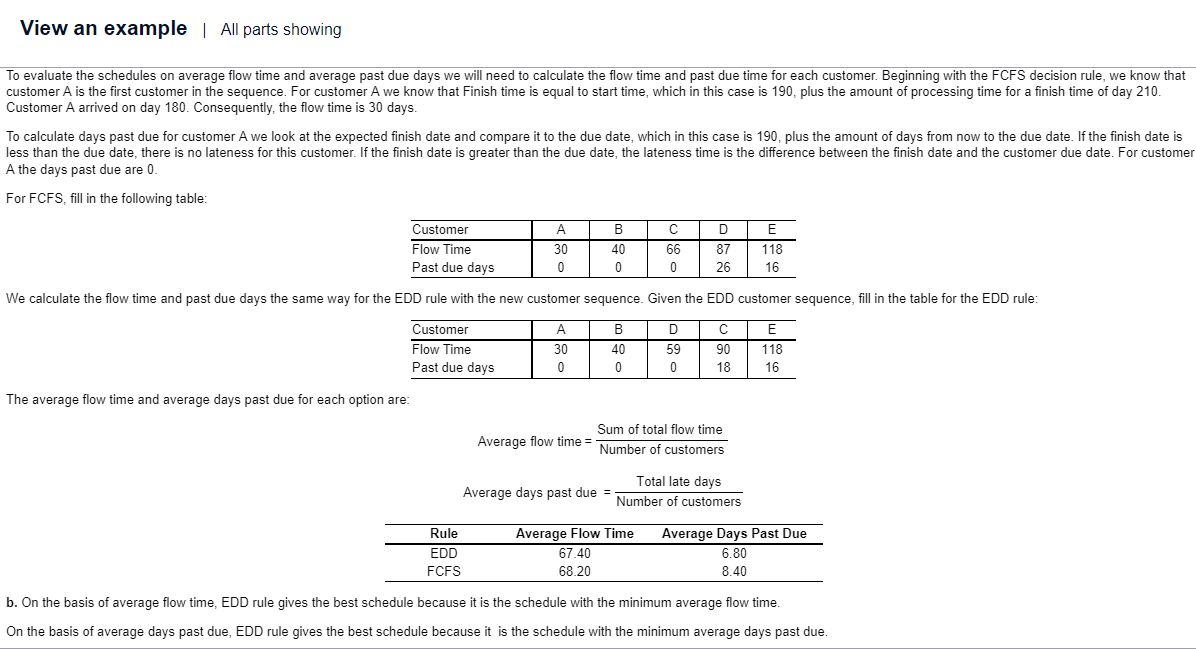
Currently a company that designs Web sites has five customers in its backlog. The time since the order arrived, processing time, and promised due dates are given in the following table. The customers are ready to be scheduled today, which is the start of day 190. Q Customer A B C D E a. Develop separate schedules by using the FCFS and EDD rules. Compare the schedules on the basis of average flow time and average days past due. Using the FCFS (first come, first served) decision rule for sequencing the customers, the order is: The average flow time and average days past due for each option are: (Enter your responses rounded to one decimal place.) Sequence Customer Time Since Order Arrived (days ago) 10 8 6 3 2 Rule EDD FCFS 1 Using the EDD (earliest due date) decision rule for sequencing the customers, the order is (to resolve a tie, use the order in which the jobs were received): Sequence Customer A 1 A 2 B 2 B Processing Time (days) 20 12 Average Flow Time 61.6 76.8 28 24 32 3 3 D 4 D Due Date (days from 4 now) 26 50 66 58 100 5 E 5 E Average Days Past Due 6.4 30.2 View an example | All parts showing To evaluate the schedules on average flow time and average past due days we will need to calculate the flow time and past due time for each customer. Beginning with the FCFS decision rule, we know that customer A is the first customer in the sequence. For customer A we know that Finish time is equal to start time, which in this case is 190, plus the amount of processing time for a finish time of day 210. Customer A arrived on day 180. Consequently, the flow time is 30 days. To calculate days past due for customer A we look at the expected finish date and compare it to the due date, which in this case is 190, plus the amount of days from now to the due date. If the finish date is less than the due date, there is no lateness for this customer. If the finish date is greater than the due date, the lateness time is the difference between the finish date and the customer due date. For customer A the days past due are 0. For FCFS, fill in the following table: Customer Flow Time Past due days The average flow time and average days past due for each option are: A 30 0 Rule EDD FCFS We calculate the flow time and past due days the same way for the EDD rule with the new customer sequence. Given the EDD customer sequence, fill in the table for the EDD rule: A B D E Customer Flow Time Past due days 30 40 59 90 118 0 0 0 18 16 Average flow time= B 40 0 Average days past due = C 66 0 D E 87 118 26 16 Sum of total flow time Number of customers Average Flow Time 67.40 68.20 Total late days Number of customers Average Days Past Due 6.80 8.40 b. On the basis of average flow time, EDD rule gives the best schedule because it is the schedule with the minimum average flow time. On the basis of average days past due, EDD rule gives the best schedule because it is the schedule with the minimum average days past due
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


