Question: 4. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES - 1 Radius R > >S NX -X +0 Potential difference in a capacitor A capacitor consists of two
![4. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES - 1 Radius R >](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6676e8de345c9_8946676e8de0d2a2.jpg)

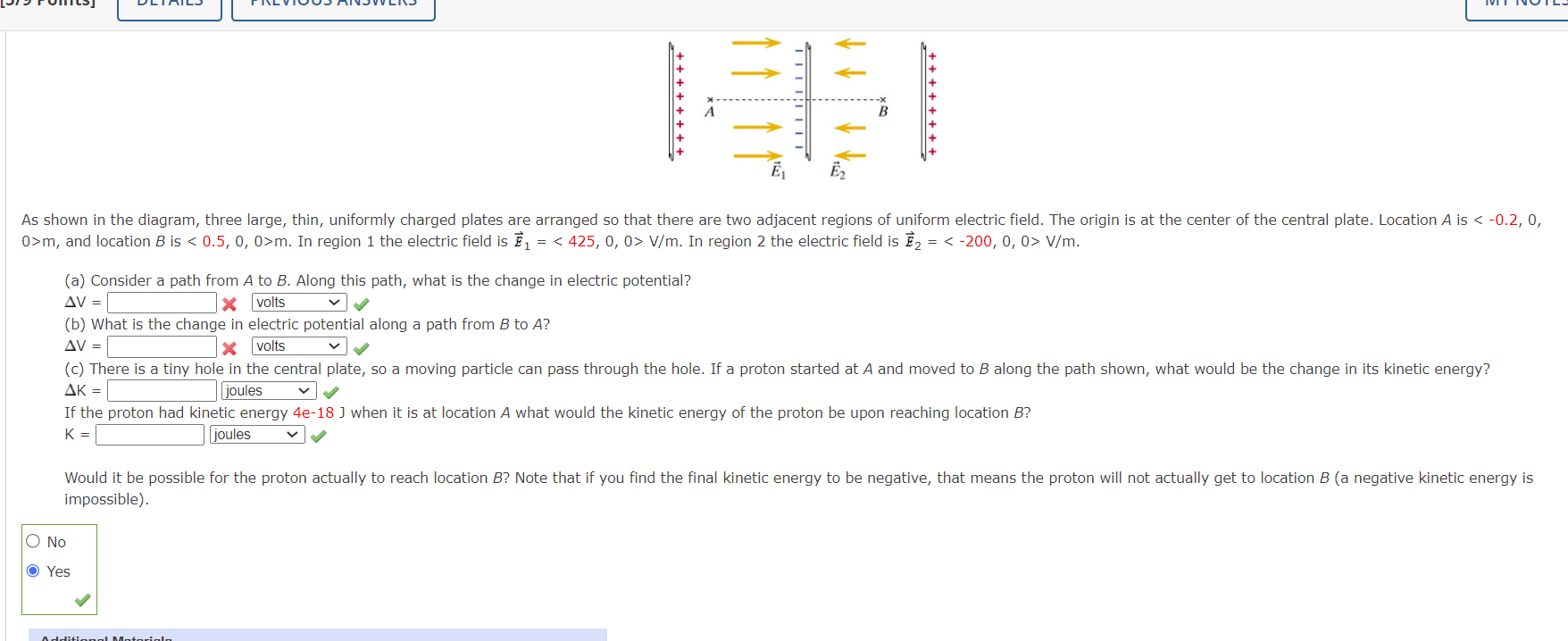
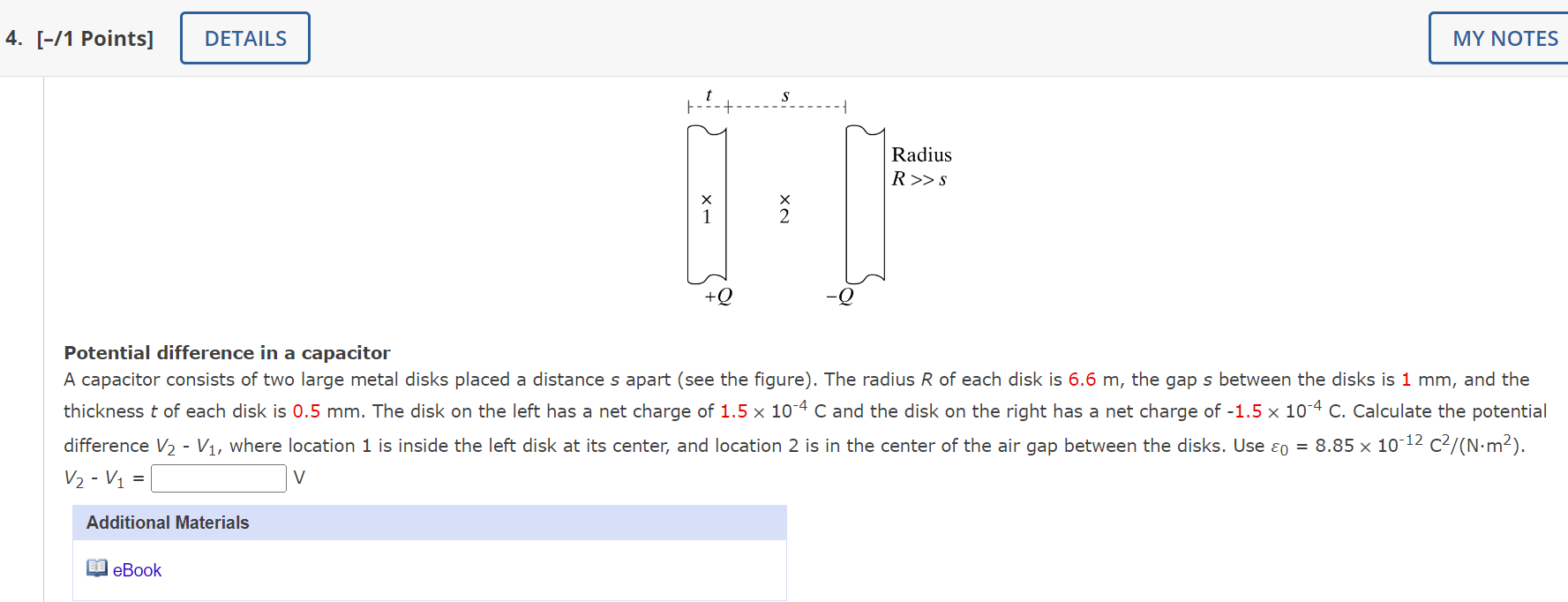

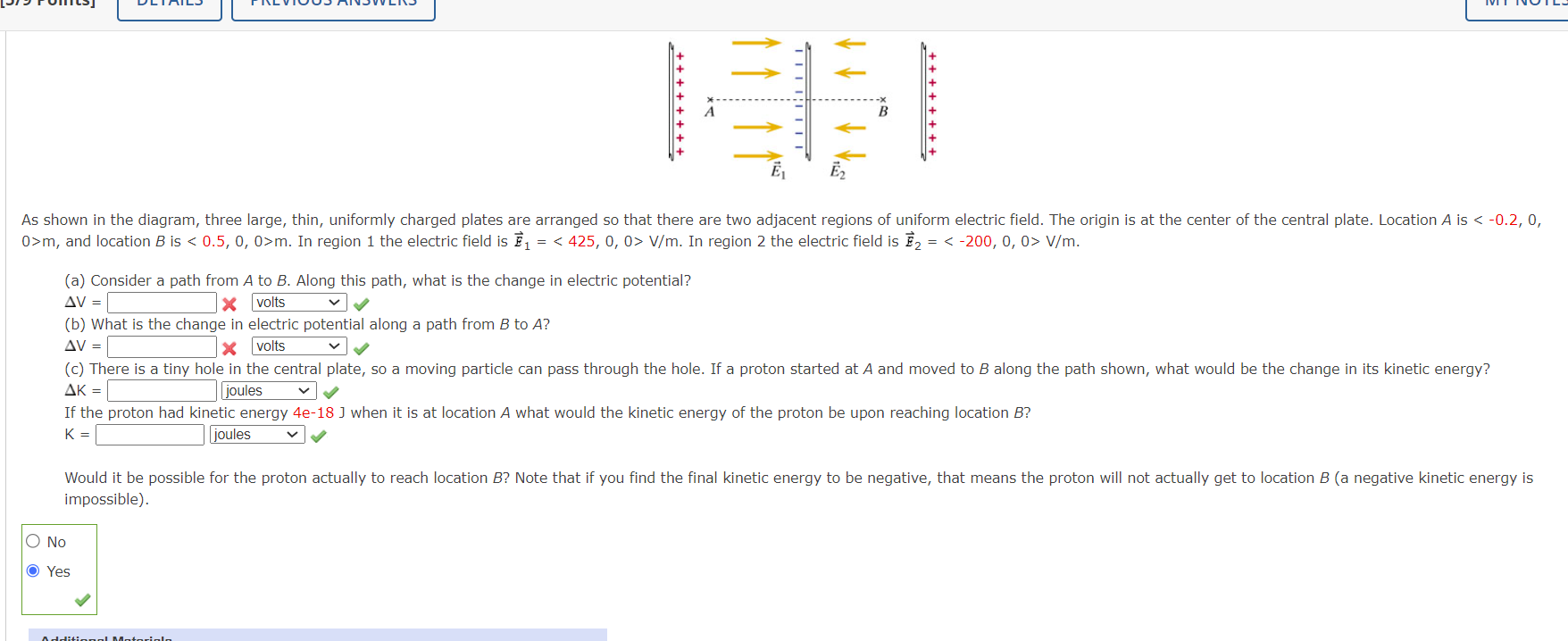
4. [-/1 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES - 1 Radius R > >S NX -X +0 Potential difference in a capacitor A capacitor consists of two large metal disks placed a distance s apart (see the figure). The radius R of each disk is 6.6 m, the gap s between the disks is 1 mm, and the thickness t of each disk is 0.5 mm. The disk on the left has a net charge of 1.5 x 10-4 C and the disk on the right has a net charge of -1.5 x 10-4 C. Calculate the potential difference V2 - V1, where location 1 is inside the left disk at its center, and location 2 is in the center of the air gap between the disks. Use co = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/(N.m?). V2 - V1 = Additional Materials eBookA dipole is centered at the origin, with its axis along the y axis, so that at locations on the y axis, the electric field due to the dipole is given by E=l 47150 yd m The charges making up the dipole are q1 = +7 nC and q2 = 7 nC, and the dipole separation is s = 4 mm (see figure below). What is the potential difference along a path starting at location P1 = (0, 0.02, O) rn and ending at location P2 = (0, 0.03, O) rn? :iv fi'u ++++++++ + + + + ++++ E1 Ez As shown in the diagram, three large, thin, uniformly charged plates are arranged so that there are two adjacent regions of uniform electric field. The origin is at the center of the central plate. Location A is m, and location B is m. In region 1 the electric field is F1 = V/m. In region 2 the electric field is E2 = V/m. (a) Consider a path from A to B. Along this path, what is the change in electric potential? AV = x volts v v (b) What is the change in electric potential along a path from B to A? AV = x volts vv (c) There is a tiny hole in the central plate, so a moving particle can pass through the hole. If a proton started at A and moved to B along the path shown, what would be the change in its kinetic energy? AK = joules v V If the proton had kinetic energy 4e-18 J when it is at location A what would the kinetic energy of the proton be upon reaching location B? K = joules Would it be possible for the proton actually to reach location B? Note that if you find the final kinetic energy to be negative, that means the proton will not actually get to location B (a negative kinetic energy is impossible). O No O Yes
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


