Question: 4. (15 marks) a) Zinc dissolves much slower in acidic solutions at room temperature than iron even though the reversible potential for reduction of Fe2+
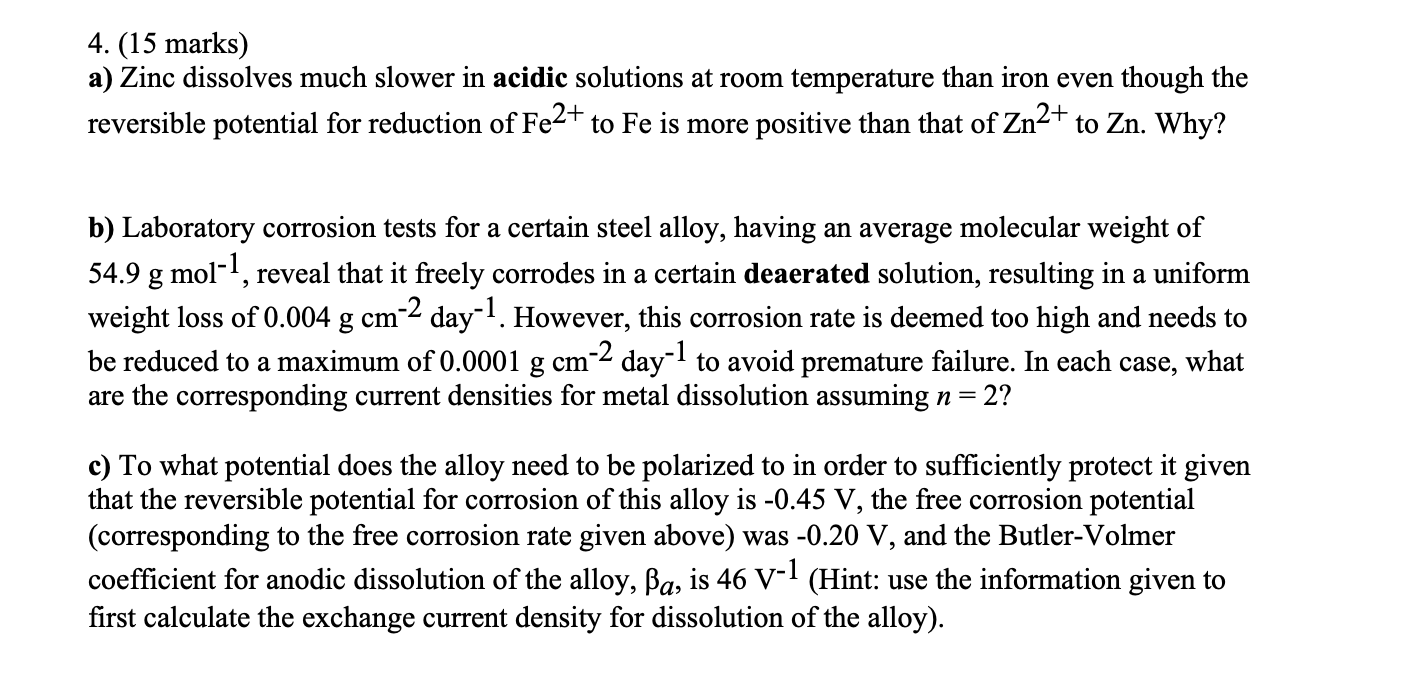
4. (15 marks) a) Zinc dissolves much slower in acidic solutions at room temperature than iron even though the reversible potential for reduction of Fe2+ to Fe is more positive than that of Zn2+ to Zn. Why? b) Laboratory corrosion tests for a certain steel alloy, having an average molecular weight of 54.9 g mol-1, reveal that it freely corrodes in a certain deaerated solution, resulting in a uniform weight loss of 0.004 g cm-2 day-1. However, this corrosion rate is deemed too high and needs to be reduced to a maximum of 0.0001 g cm-2 day-1 to avoid premature failure. In each case, what are the corresponding current densities for metal dissolution assuming n= 2? g c) To what potential does the alloy need to be polarized to in order to sufficiently protect it given that the reversible potential for corrosion of this alloy is -0.45 V, the free corrosion potential (corresponding to the free corrosion rate given above) was -0.20 V, and the Butler-Volmer coefficient for anodic dissolution of the alloy, Ba, is 46 V-1 (Hint: use the information given to first calculate the exchange current density for dissolution of the alloy). 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


