Question: 4. (18 marks) Gingko biloba, commonly known as gingko, is an ancient tree species native to China. It is marketed as having the ability to
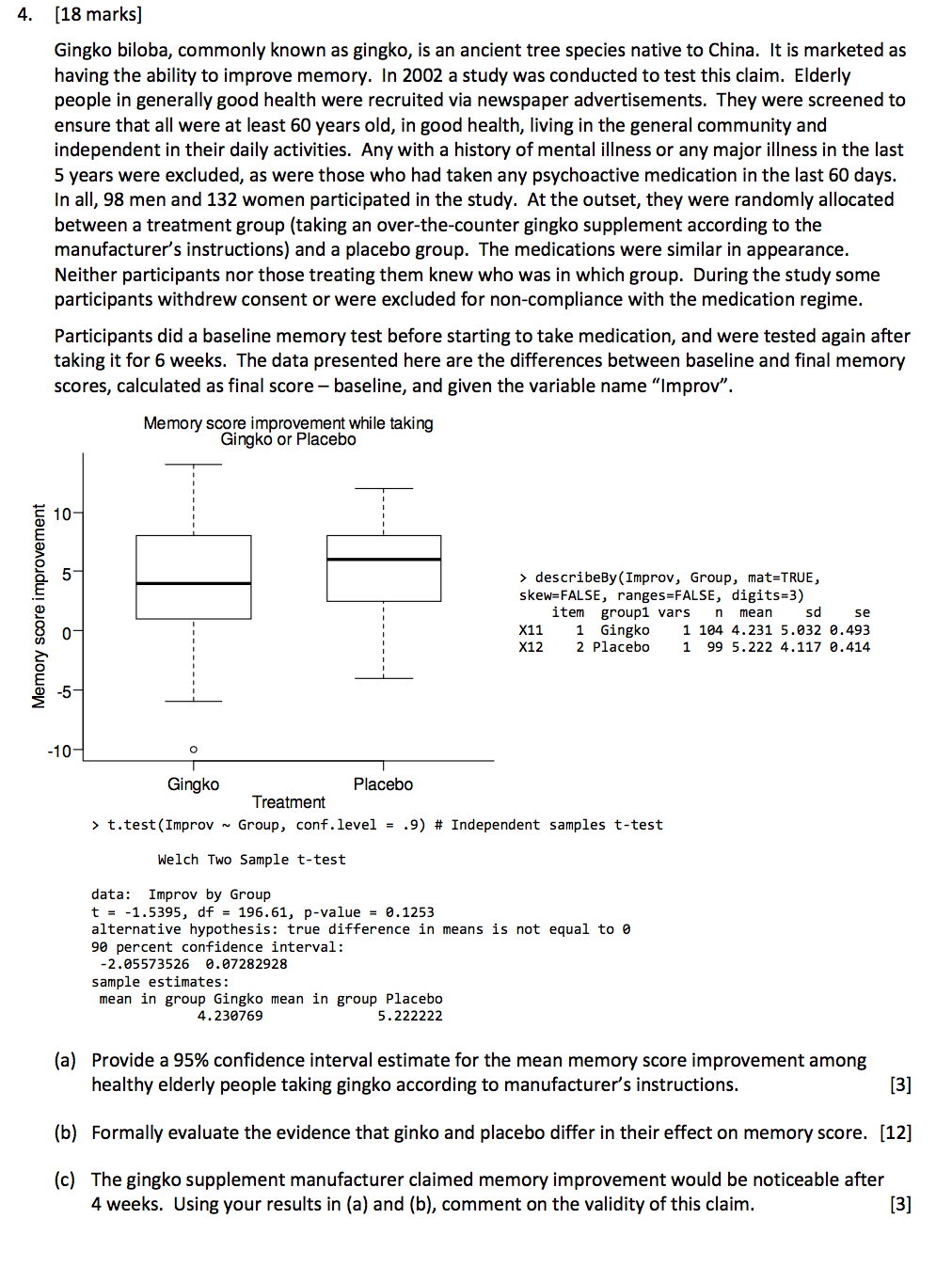
4. (18 marks) Gingko biloba, commonly known as gingko, is an ancient tree species native to China. It is marketed as having the ability to improve memory. In 2002 a study was conducted to test this claim. Elderly people in generally good health were recruited via newspaper advertisements. They were screened to ensure that all were at least 60 years old, in good health, living in the general community and independent in their daily activities. Any with a history of mental illness or any major illness in the last 5 years were excluded, as were those who had taken any psychoactive medication in the last 60 days. In all, 98 men and 132 women participated in the study. At the outset, they were randomly allocated between a treatment group (taking an over-the-counter gingko supplement according to the manufacturer's instructions) and a placebo group. The medications were similar in appearance. Neither participants nor those treating them knew who was in which group. During the study some participants withdrew consent or were excluded for non-compliance with the medication regime. Participants did a baseline memory test before starting to take medication, and were tested again after taking it for 6 weeks. The data presented here are the differences between baseline and final memory scores, calculated as final score - baseline, and given the variable name "Improv". Memory score improvement while taking Gingko or Placebo 10 Memory score improvement > describeBy (Improv, Group, mat=TRUE, skew=FALSE, ranges=FALSE, digits=3) item group1 vars n mean sd se X11 1 Gingko 1 104 4.231 5.032 0.493 X12 2 Placebo 99 5.222 4.117 0.414 -10- Gingko Placebo Treatment > t.test(Improv ~ Group, conf.level = .9) # Independent samples t-test Welch Two Sample t-test data: Improv by Group t = -1.5395, df = 196.61, p-value = 0.1253 alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to o 90 percent confidence interval: -2.05573526 0.07282928 sample estimates: mean in group Gingko mean in group Placebo 4.230769 5.222222 (a) Provide a 95% confidence interval estimate for the mean memory score improvement among healthy elderly people taking gingko according to manufacturer's instructions. [3] (b) Formally evaluate the evidence that ginko and placebo differ in their effect on memory score. [12] (c) The gingko supplement manufacturer claimed memory improvement would be noticeable after 4 weeks. Using your results in (a) and (b), comment on the validity of this claim. [3] 4. (18 marks) Gingko biloba, commonly known as gingko, is an ancient tree species native to China. It is marketed as having the ability to improve memory. In 2002 a study was conducted to test this claim. Elderly people in generally good health were recruited via newspaper advertisements. They were screened to ensure that all were at least 60 years old, in good health, living in the general community and independent in their daily activities. Any with a history of mental illness or any major illness in the last 5 years were excluded, as were those who had taken any psychoactive medication in the last 60 days. In all, 98 men and 132 women participated in the study. At the outset, they were randomly allocated between a treatment group (taking an over-the-counter gingko supplement according to the manufacturer's instructions) and a placebo group. The medications were similar in appearance. Neither participants nor those treating them knew who was in which group. During the study some participants withdrew consent or were excluded for non-compliance with the medication regime. Participants did a baseline memory test before starting to take medication, and were tested again after taking it for 6 weeks. The data presented here are the differences between baseline and final memory scores, calculated as final score - baseline, and given the variable name "Improv". Memory score improvement while taking Gingko or Placebo 10 Memory score improvement > describeBy (Improv, Group, mat=TRUE, skew=FALSE, ranges=FALSE, digits=3) item group1 vars n mean sd se X11 1 Gingko 1 104 4.231 5.032 0.493 X12 2 Placebo 99 5.222 4.117 0.414 -10- Gingko Placebo Treatment > t.test(Improv ~ Group, conf.level = .9) # Independent samples t-test Welch Two Sample t-test data: Improv by Group t = -1.5395, df = 196.61, p-value = 0.1253 alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to o 90 percent confidence interval: -2.05573526 0.07282928 sample estimates: mean in group Gingko mean in group Placebo 4.230769 5.222222 (a) Provide a 95% confidence interval estimate for the mean memory score improvement among healthy elderly people taking gingko according to manufacturer's instructions. [3] (b) Formally evaluate the evidence that ginko and placebo differ in their effect on memory score. [12] (c) The gingko supplement manufacturer claimed memory improvement would be noticeable after 4 weeks. Using your results in (a) and (b), comment on the validity of this claim. [3]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


