Question: 4. [25 points] In this problem you will design an adsorption system to remove compound A from water with granular activated carbon (GAC). The
![4. [25 points] In this problem you will design an adsorption system](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/questions/2024/03/6601c4c03e9e6_1711391814879.jpg)
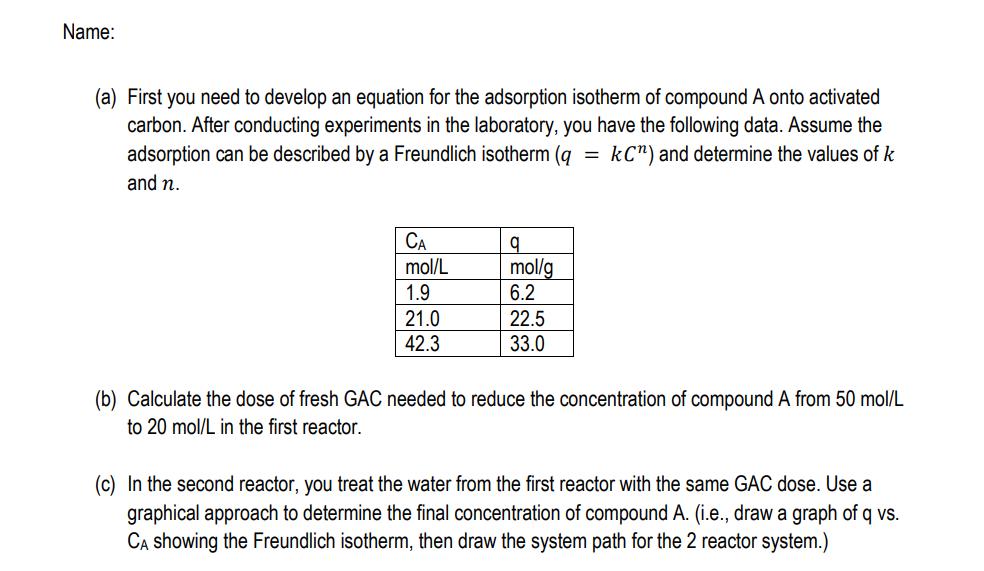

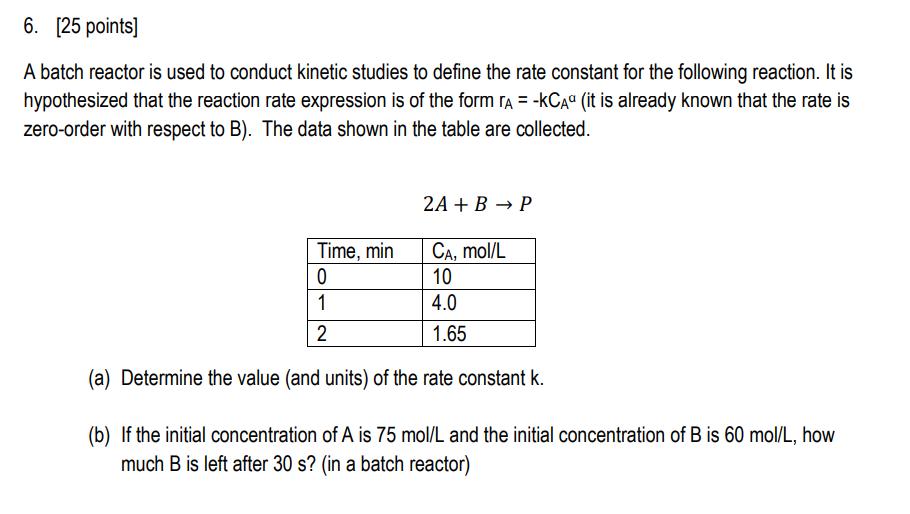
4. [25 points] In this problem you will design an adsorption system to remove compound A from water with granular activated carbon (GAC). The system consists of two batch reactors that contain the same dose of GAC, and treat water sequentially (i.e., first a batch of water is treated in reactor 1 and then in reactor 2). Name: (a) First you need to develop an equation for the adsorption isotherm of compound A onto activated carbon. After conducting experiments in the laboratory, you have the following data. Assume the adsorption can be described by a Freundlich isotherm (q = kC") and determine the values of k and n. CA q mol/L mol/g 1.9 6.2 21.0 22.5 42.3 33.0 (b) Calculate the dose of fresh GAC needed to reduce the concentration of compound A from 50 mol/L to 20 mol/L in the first reactor. (c) In the second reactor, you treat the water from the first reactor with the same GAC dose. Use a graphical approach to determine the final concentration of compound A. (i.e., draw a graph of q vs. CA showing the Freundlich isotherm, then draw the system path for the 2 reactor system.) 5. [25 points] A stripping column is designed to remove chloroform (a chlorine disinfection by-product) from treated drinking water. The treatment goal is to reduce chloroform from 120 to 30 g/L. (a) Calculate the effluent concentration of chloroform (CG,out) given the following: CG,in = 0 g/L QL = 0.1 m/s Qc = 0.9 m3 /s H = 0.16 LL/LG K = 0.08 s1 (b) Draw a graph of CG VS. CL (both in g/L) showing the line for Henry's Law and the operating line for the stripping column. (c) What is the rate of gas transfer at the top of the stripping column? (in g/L-s) 6. [25 points] A batch reactor is used to conduct kinetic studies to define the rate constant for the following reaction. It is hypothesized that the reaction rate expression is of the form A = -KCA (it is already known that the rate is zero-order with respect to B). The data shown in the table are collected. 2A + B P Time, min CA, mol/L 0 10 4.0 1.65 1 2 (a) Determine the value (and units) of the rate constant k. (b) If the initial concentration of A is 75 mol/L and the initial concentration of B is 60 mol/L, how much B is left after 30 s? (in a batch reactor)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


