Question: 4. A plane-strain machining operation is modeled as a 2-dimensional orthogonal cutting process. Two different cutting conditions are shown in Figure 1 and Figure
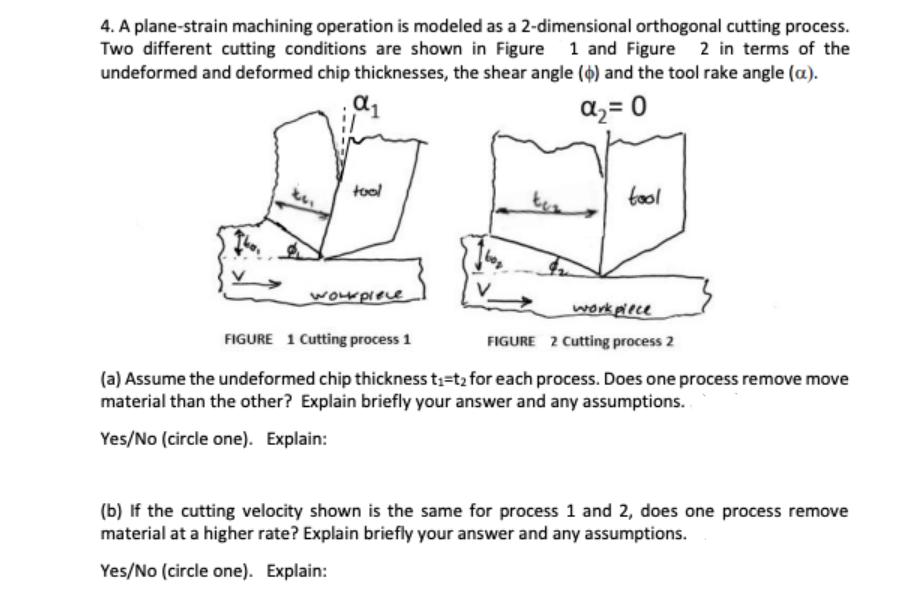

4. A plane-strain machining operation is modeled as a 2-dimensional orthogonal cutting process. Two different cutting conditions are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 in terms of the undeformed and deformed chip thicknesses, the shear angle () and the tool rake angle (a). = 0 in tool workpiece tool workpiece FIGURE 1 Cutting process 1 FIGURE 2 Cutting process 2 (a) Assume the undeformed chip thickness t-t for each process. Does one process remove move material than the other? Explain briefly your answer and any assumptions. Yes/No (circle one). Explain: (b) If the cutting velocity shown is the same for process 1 and 2, does one process remove material at a higher rate? Explain briefly your answer and any assumptions. Yes/No (circle one). Explain: (c) For both cutting conditions (Fig. 1 and 2) show how to derive the cutting ratio, undeformed chip thickness sin o r= deformed chip thickness cos (-a) (d) How can the chip ratio be used to determine the shear strain in metal cutting?
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a YesNo circle one Explain To determine which process removes more material we can compare the volum... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


