Question: 4. Contingent Claim Analysis Basic (optional) D. You just bought a share of WideCo for $48. You realize that this asset will either have a

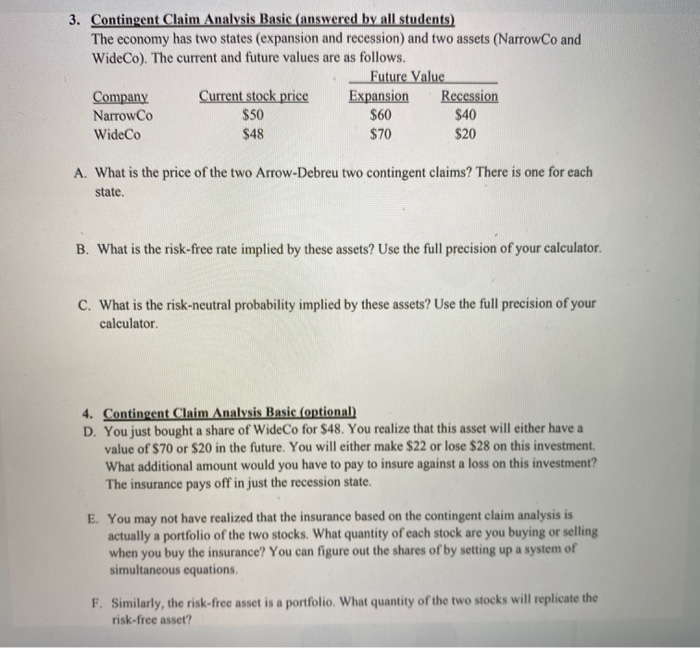
4. Contingent Claim Analysis Basic (optional) D. You just bought a share of WideCo for $48. You realize that this asset will either have a value of $70 or $20 in the future. You will either make $22 or lose $28 on this investment. What additional amount would you have to pay to insure against a loss on this investment? The insurance pays off in just the recession state. E. You may not have realized that the insurance based on the contingent claim analysis is actually a portfolio of the two stocks. What quantity of each stock are you buying or selling when you buy the insurance? You can figure out the shares of by setting up a system of simultaneous equations. F. Similarly, the risk-free asset is a portfolio. What quantity of the two stocks will replicate the risk-free asset? 3. Contingent Claim Analysis Basic (answered by all students) The economy has two states (expansion and recession) and two assets (NarrowCo and WideCo). The current and future values are as follows. Future Value Company Current stock price Expansion Recession NarrowCo $50 $60 $40 WideCo $48 $70 $20 A. What is the price of the two Arrow-Debreu two contingent claims? There is one for each state. B. What is the risk-free rate implied by these assets? Use the full precision of your calculator C. What is the risk-neutral probability implied by these assets? Use the full precision of your calculator 4. Contingent Claim Analysis Basic (optional) D. You just bought a share of WideCo for $48. You realize that this asset will either have a value of $70 or $20 in the future. You will either make $22 or lose $28 on this investment. What additional amount would you have to pay to insure against a loss on this investment? The insurance pays off in just the recession state. E. You may not have realized that the insurance based on the contingent claim analysis is actually a portfolio of the two stocks. What quantity of each stock are you buying or selling when you buy the insurance? You can figure out the shares of by setting up a system of simultaneous equations, F. Similarly, the risk-free asset is a portfolio. What quantity of the two stocks will replicate the risk-free asset? 4. Contingent Claim Analysis Basic (optional) D. You just bought a share of WideCo for $48. You realize that this asset will either have a value of $70 or $20 in the future. You will either make $22 or lose $28 on this investment. What additional amount would you have to pay to insure against a loss on this investment? The insurance pays off in just the recession state. E. You may not have realized that the insurance based on the contingent claim analysis is actually a portfolio of the two stocks. What quantity of each stock are you buying or selling when you buy the insurance? You can figure out the shares of by setting up a system of simultaneous equations. F. Similarly, the risk-free asset is a portfolio. What quantity of the two stocks will replicate the risk-free asset? 3. Contingent Claim Analysis Basic (answered by all students) The economy has two states (expansion and recession) and two assets (NarrowCo and WideCo). The current and future values are as follows. Future Value Company Current stock price Expansion Recession NarrowCo $50 $60 $40 WideCo $48 $70 $20 A. What is the price of the two Arrow-Debreu two contingent claims? There is one for each state. B. What is the risk-free rate implied by these assets? Use the full precision of your calculator C. What is the risk-neutral probability implied by these assets? Use the full precision of your calculator 4. Contingent Claim Analysis Basic (optional) D. You just bought a share of WideCo for $48. You realize that this asset will either have a value of $70 or $20 in the future. You will either make $22 or lose $28 on this investment. What additional amount would you have to pay to insure against a loss on this investment? The insurance pays off in just the recession state. E. You may not have realized that the insurance based on the contingent claim analysis is actually a portfolio of the two stocks. What quantity of each stock are you buying or selling when you buy the insurance? You can figure out the shares of by setting up a system of simultaneous equations, F. Similarly, the risk-free asset is a portfolio. What quantity of the two stocks will replicate the risk-free asset
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


