Question: 4. (e) Show/write the basis, Bravais lattice and the primitive unit cell of the 2-0 crsytal structure given below. At room temperature metals are usually
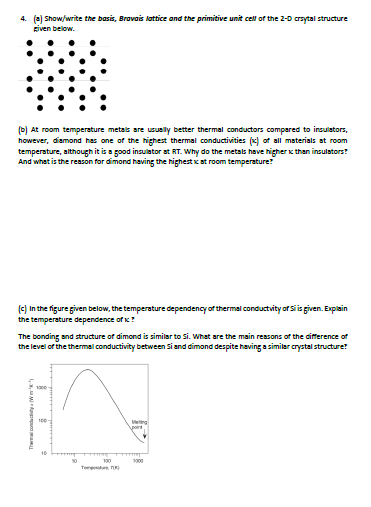
4. (e) Show/write the basis, Bravais lattice and the primitive unit cell of the 2-0 crsytal structure given below. At room temperature metals are usually better thermal conductors compared to inculators, however, diamond has one of the highest thermal conductivities (g) of all materials at room temperature, although it is a good insulator st RT. Why do the metals have higher than insulators: And what is the reason for dimond having the highest stroom temperature! (c) In the figure given below, the temperature dependency of thermal conductvity of Si is given. Explain the temperature dependence of ! The bonding and structure of dimond is similar to si. What are the main reasons of the cifference of the level or the thermal conductivity between si and dimond despite having a similar crystal structure! TO point 10 10 , 4. (e) Show/write the basis, Bravais lattice and the primitive unit cell of the 2-0 crsytal structure given below. At room temperature metals are usually better thermal conductors compared to inculators, however, diamond has one of the highest thermal conductivities (g) of all materials at room temperature, although it is a good insulator st RT. Why do the metals have higher than insulators: And what is the reason for dimond having the highest stroom temperature! (c) In the figure given below, the temperature dependency of thermal conductvity of Si is given. Explain the temperature dependence of ! The bonding and structure of dimond is similar to si. What are the main reasons of the cifference of the level or the thermal conductivity between si and dimond despite having a similar crystal structure! TO point 10 10
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


