Question: 4. Prepare an income statement for the year. (Do not prepare a schedule of cost of goods manu factured, all of the information needed for
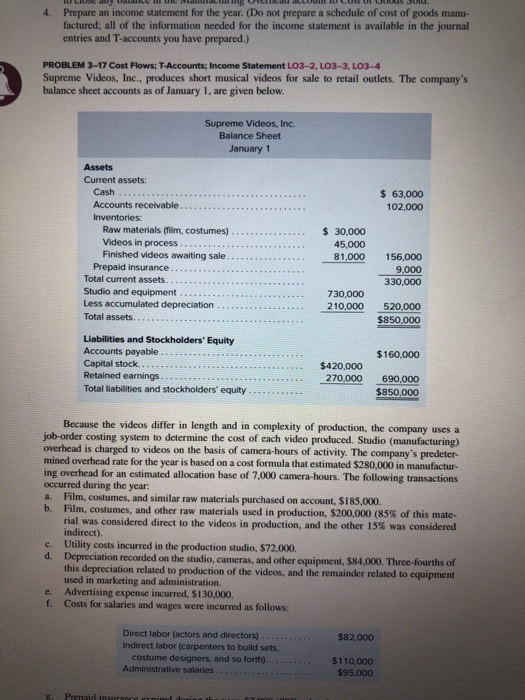
4. Prepare an income statement for the year. (Do not prepare a schedule of cost of goods manu factured, all of the information needed for the income statement is available in the journal entries and T-accounts you have prepared.) PROBLEM 3-17 Cost Flows: T-Accounts; Income Statement L03-2, LO3-3, LO3-4 Supreme Videos, Inc., produces short musical videos for sale to retail outlets. The company's balance sheet accounts as of January 1, are given below. Supreme Videos, Inc. Balance Sheet January 1 Assets Current assets: Cash. $ 63.000 102,000 $ 30,000 45,000 81,000 156,000 Accounts receivable Inventories: Raw materials (film, costumes) Videos in process... Finished videos awaiting sale. Prepaid insurance..... Total current assets...... Studio and equipment Less accumulated depreciation.. Total assets. 9,000 330,000 730,000 210.000 520,000 $850,000 $160,000 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable... Capital stock. Retained earnings.. Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $420,000 270.000 690,000 $850,000 Because the videos differ in length and in complexity of production, the company uses a job-order costing system to determine the cost of each video produced. Studio (manufacturing) overhead is charged to videos on the basis of camera-hours of activity. The company's predeter- mined overhead rate for the year is based on a cost formula that estimated $280,000 in manufactur- ing overhead for an estimated allocation base of 7,000 camera hours. The following transactions occurred during the year. a. Film, costumes, and similar raw materials purchased on account, $185.000 b. Film, costumes, and other raw materials used in production, $200,000 (85% of this mate- rial was considered direct to the videos in production, and the other 15% was considered indirect). c. Utility costs incurred in the production studio, $72,000 Depreciation recorded on the studio, cameras, and other equipment, 584,000. Three-fourths of this depreciation related to production of the videos, and the remainder related to equipment used in marketing and administration. e Advertising expense incurred, S130,000 1. Costs for salaries and wages were incurred as follows: $82,000 Direct labor (actors and directors) .......... Indirect labor (carpenters to build sets, costume designers, and so forth)............. Administrative salaries $110,000 $95.000 4. Prepare an income statement for the year. (Do not prepare a schedule of cost of goods manu factured, all of the information needed for the income statement is available in the journal entries and T-accounts you have prepared.) PROBLEM 3-17 Cost Flows: T-Accounts; Income Statement L03-2, LO3-3, LO3-4 Supreme Videos, Inc., produces short musical videos for sale to retail outlets. The company's balance sheet accounts as of January 1, are given below. Supreme Videos, Inc. Balance Sheet January 1 Assets Current assets: Cash. $ 63.000 102,000 $ 30,000 45,000 81,000 156,000 Accounts receivable Inventories: Raw materials (film, costumes) Videos in process... Finished videos awaiting sale. Prepaid insurance..... Total current assets...... Studio and equipment Less accumulated depreciation.. Total assets. 9,000 330,000 730,000 210.000 520,000 $850,000 $160,000 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable... Capital stock. Retained earnings.. Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $420,000 270.000 690,000 $850,000 Because the videos differ in length and in complexity of production, the company uses a job-order costing system to determine the cost of each video produced. Studio (manufacturing) overhead is charged to videos on the basis of camera-hours of activity. The company's predeter- mined overhead rate for the year is based on a cost formula that estimated $280,000 in manufactur- ing overhead for an estimated allocation base of 7,000 camera hours. The following transactions occurred during the year. a. Film, costumes, and similar raw materials purchased on account, $185.000 b. Film, costumes, and other raw materials used in production, $200,000 (85% of this mate- rial was considered direct to the videos in production, and the other 15% was considered indirect). c. Utility costs incurred in the production studio, $72,000 Depreciation recorded on the studio, cameras, and other equipment, 584,000. Three-fourths of this depreciation related to production of the videos, and the remainder related to equipment used in marketing and administration. e Advertising expense incurred, S130,000 1. Costs for salaries and wages were incurred as follows: $82,000 Direct labor (actors and directors) .......... Indirect labor (carpenters to build sets, costume designers, and so forth)............. Administrative salaries $110,000 $95.000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


