Question: 421 Electrons keep passing from the reducing agent XH; to the oxidizing agent Or. but in this case it is through the membrane-associated electron transport
421 Electrons keep passing from the reducing agent XH; to the oxidizing agent Or. but in this case it is through the membrane-associated electron transport chain. The free energy from these oxidation-reduction reactions is stored as the protonmotive force of the pruton concentration gradient, and is recovered in ADP phosphorylation: Recall from Section 9.11 that the Gibbs free energy change for trans- carrying a polar molecule is
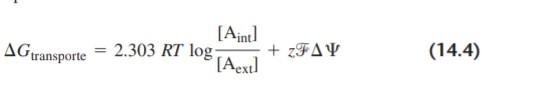
where the first term is the Gibbs free energy due to the concentration gradient, and the second term (zAV) is due to the charge difference across the membrane. For protons, the charge per molecule is 1 z= L0), and the total Gibbs free energy change for the proton gradient is
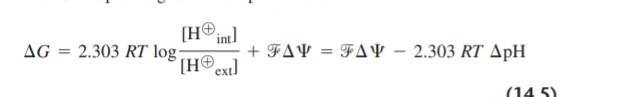
This is a measure of the protonmotive force generated by the proton gradient. In hepatic mitochondria, the potential across the membrane (AY) is -0.17 V (inner negative) and the pH difference is 0.5 (ApH = 0.5). At 37C (7 - 310K). the available Gibbs free energy is

atheized This means that the return transport of a single protein across the membrane is associated with a free energy change of -19.4 kJ mol, The standard Gibbs free energy change for the synthesis of ATP from of ADP is 32 J mol(AG" - 32 J mol) (Section 10.6). Ast, more than one proton must be translocated for each molecule of ATP synthesized. Note that 85% (-16.4/-19.4) - 85%) of the Gibbs free energy change is due to the charge gradient across the membrane, and only 15% (-3.0/-19.4 = 15%) is due to the proton concentration gradient.14.4 Electron Transport We now describe the reactions of the membrane-associated electron transport chain Four oligomeric sets of proteins are found in the inner membrane of mitochondria, or in the plasma membrane of bacteria, Enzyme complexes have been isolated in their active forms by solubilizing them with care using detergents.
Each complex catalyzes a separate part of the energy transduction process. These complexes are assigned numbers I through IV. The complex is ATP synthase. A.
IV Complexes Electron transport complexes can diffuse independently in the membrane, but they tend to form large structures through weak interactions with each other. All four enzyme complexes contain a wide variety of daido-reducing centers. Pucden set cofactors, such as FAD. FMN to ubiquinone (Q).
Other centers have Fe-S clusters, protein coenzymes such as cytochromes, heme-containing, and copper-bearing proteins. The flow of electrons is carried out by reduction and oxidation.
make a summary please let it be on the computer then I don't understand thanks
AG transporte [Aint] 2.303 RT log [Aext] + zFAY (14.4) [Hint) 2.303 RT log AG + FAV = FAY - 2.303 RT ApH [H Pexe] (14 5) AG = [96485 X -0.17] - [2.303 X 8.315 X 310 X 0.5] = - 16402 J mol-! - 2968 J mol-! = -19.4 kJ mol- (14.6) e are decir orto de reaca de un colo protn dalambe
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


