Question: 5 . 1 . Two - Dimensional Convolution as a Matrix - Vector Multiplication ( 1 0 points ) . Consider a convolutional neural network
TwoDimensional Convolution as a MatrixVector Multiplication points
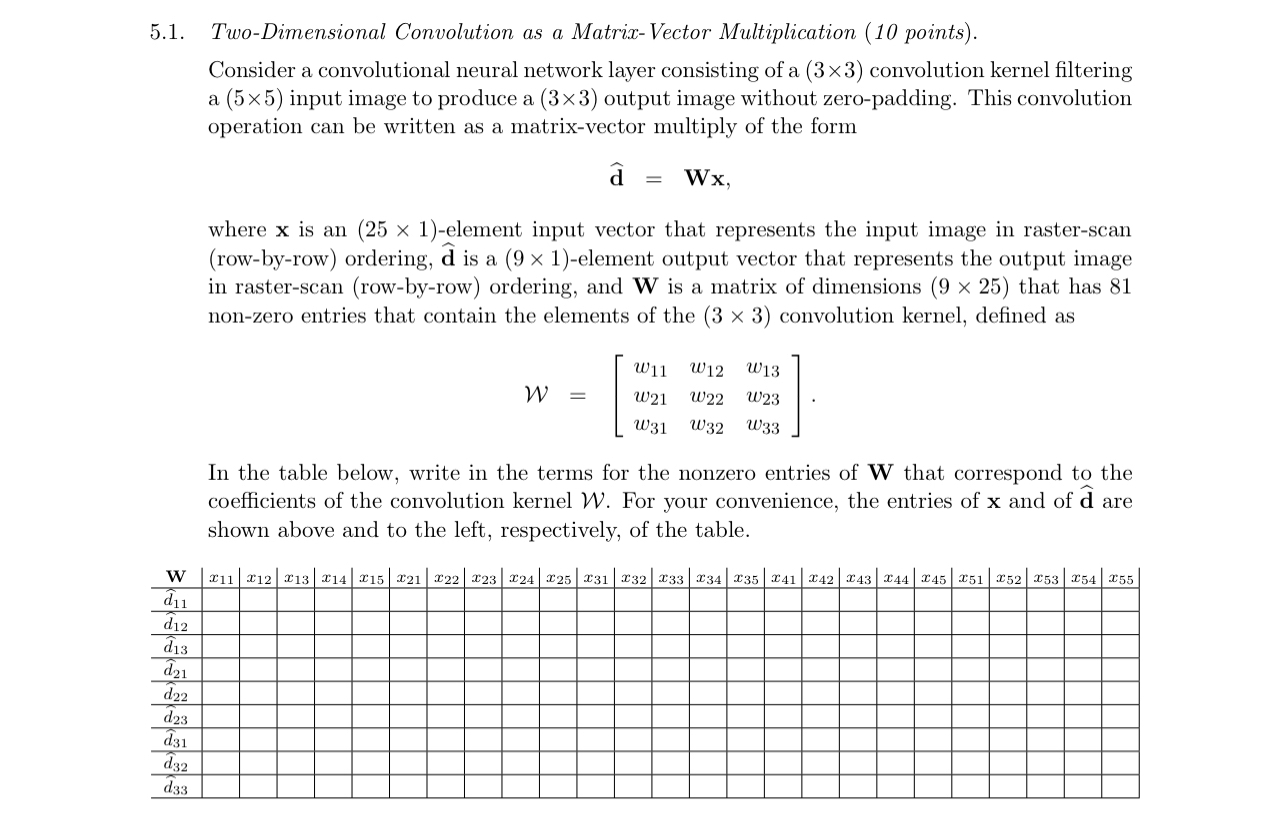
Consider a convolutional neural network layer consisting of a convolution kernel filtering a input image to produce a output image without zeropadding. This convolution operation can be written as a matrixvector multiply of the form
widehat
where is an element input vector that represents the input image in rasterscan rowbyrow ordering, widehat is a element output vector that represents the output image in rasterscan rowbyrow ordering, and is a matrix of dimensions that has nonzero entries that contain the elements of the convolution kernel, defined as
In the table below, write in the terms for the nonzero entries of that correspond to the coefficients of the convolution kernel For your convenience, the entries of and of widehat are shown above and to the left, respectively, of the table.
tableW
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


