Question: 5. (5) pts) Using Cramer's Rule set up the determinants, but DO NOT SOLVE, for the x component of the solution of the system below
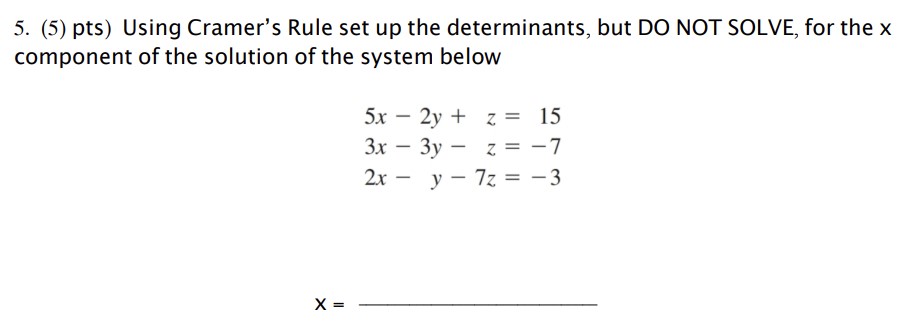

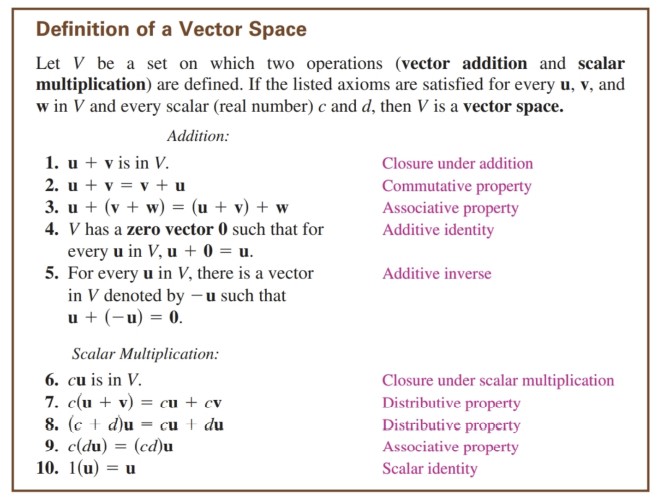
5. (5) pts) Using Cramer's Rule set up the determinants, but DO NOT SOLVE, for the x component of the solution of the system below 5x - 2y + z = 15 3x - 3y - z=-7 2x - y - 7z = -3 X =6. (10 pts) Find a nontrivial linear com binatien of the vectors (1, 0, 1), (1, 1, 2) and (0, 1, 4) so that the sum is the zero vector (0, 0, 0). Show all work for full credit. Definition of a Vector Space Let V be a set on which two operations (vector addition and scalar multiplication) are defined. If the listed axioms are satisfied for every u, v, and w in V and every scalar (real number) c and d, then V is a vector space. Addition: 1. u + v is in V. Closure under addition 2. utv= v+u Commutative property 3. ut ( v + w) = (utv) +w Associative property 4. V has a zero vector 0 such that for Additive identity every u in V, u + 0 = u. 5. For every u in V, there is a vector Additive inverse in V denoted by - u such that u+ (-u) = 0. Scalar Multiplication: 6. cu is in V. Closure under scalar multiplication 7. clu + v) = cu+ cv Distributive property 8. (c + d)u = cu + du Distributive property 9. c(du) = (cd)u Associative property 10. 1(u) = u Scalar identity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


