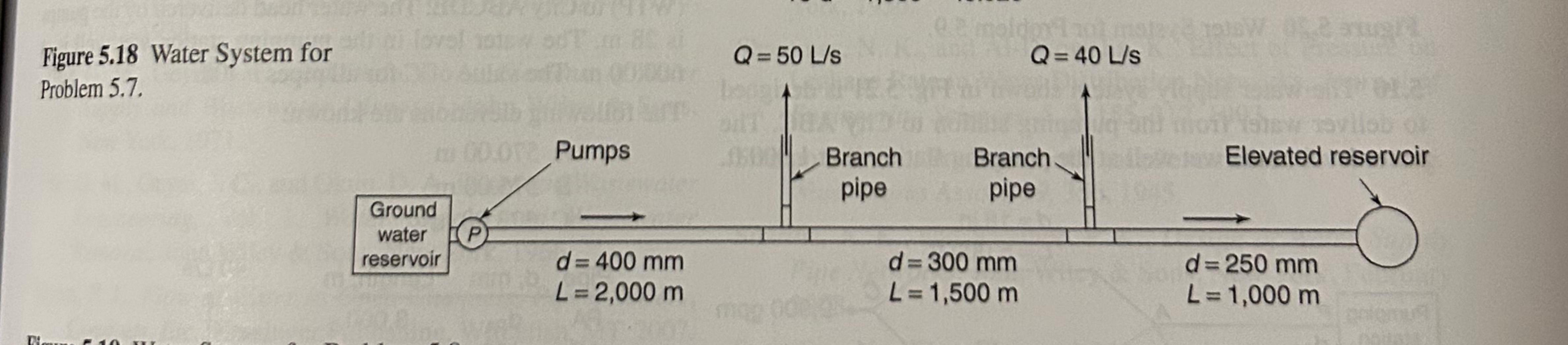
Question: 5 . 7 , p . 1 7 3 The ground water reservoir in Fig. 5 . 3 1 is the same thing as the
p
The "ground water reservoir" in Fig. is the same thing as the "underground tank." The
water surface is open to atmospheric pressure.
"against a total dynamic head of m means that
Draw the EGL and HGL along the pipeline, showing minor losses as well as frictional head loss. Q LsFigure Water System for
Problem
Use to find the velocity in each pipe.
Given use the HazenWilliams equation to calculate frictional head losses.
Neglecting minor losses, use the energy equation to calculate the water surface elevation in the
elevated reservoir; use this to calculate the depth of water in the reservoir.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


