Question: 5. Although the ECG does not directly measure mechanical events, scientists and clinicians make assumptions about the heart's mechanical activity based on the ECG.

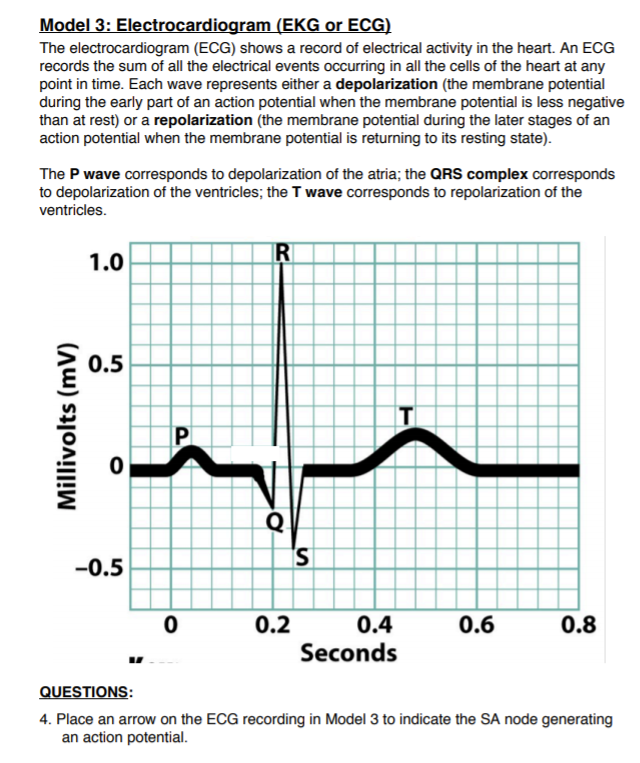
5. Although the ECG does not directly measure mechanical events, scientists and clinicians make assumptions about the heart's mechanical activity based on the ECG. Answer the following questions about this relationship between the ECG and the heart's mechanical activity using information from Models 1, 2 and 3: a) What does the P wave represent? Predict the mechanical event that follows the P wave. b) What does the QRS complex represent? Predict the mechanical event that follows the QRS complex. c) What does the T wave represent? Predict the mechanical event that follows the T wave. Model 3: Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) The electrocardiogram (ECG) shows a record of electrical activity in the heart. An ECG records the sum of all the electrical events occurring in all the cells of the heart at any point in time. Each wave represents either a depolarization (the membrane potential during the early part of an action potential when the membrane potential is less negative than at rest) or a repolarization (the membrane potential during the later stages of an action potential when the membrane potential is returning to its resting state). The P wave corresponds to depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex corresponds to depolarization of the ventricles; the T wave corresponds to repolarization of the ventricles. Millivolts (mV) 1.0 0.5 0 P R Q S -0.5 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 Seconds QUESTIONS: 4. Place an arrow on the ECG recording in Model 3 to indicate the SA node generating an action potential.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Answer The electrical signal that causes the atria to contract and pump blood into the ventricles is ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (2 attachments)
6642f659ce795_971272.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
6642f659ce795_971272.docx
120 KBs Word File


