Question: 5) Given a byte-addressable memory with 256 bytes, suppose a memory dump yields the results shown below. The address of each memory cell is determined

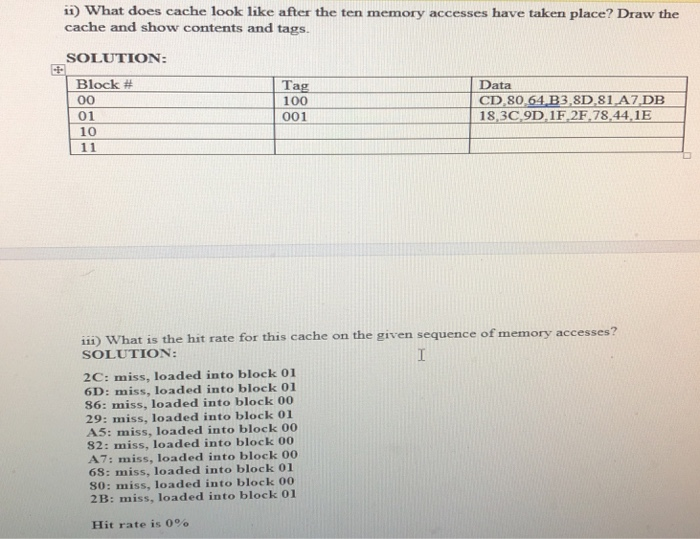
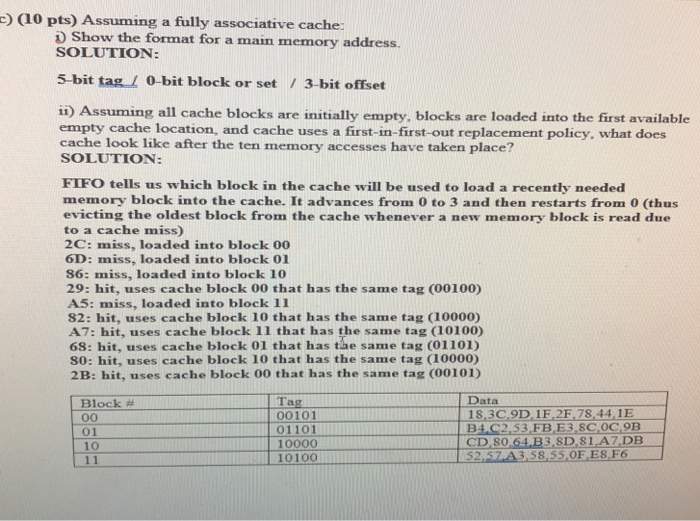

5) Given a byte-addressable memory with 256 bytes, suppose a memory dump yields the results shown below. The address of each memory cell is determined by its row and column. For example, memory address 0x97 is in the 9th row, 7th column, and contains the hexadecimal value 43. Memory location 0xA3 contains the hexadecimal value 58. DC D5 9C 77 C1 99 90AC 33 D1 37 74 B5 82 38 EO FD DO A6 98 BB DE 9A 9E EB 04 AA 86 ES 2 3A 14 F3 59 5C 41 B2 6D 18 3C 9D 1F 2F 78 44 1E 49 E2 23 4 | 6B 69 | 02 | 56 | 7E | DA | 2A | 76 | 89 | 20 | 85 | 88 | 72 | 92 | E9 | 5B S B9 16 A8 FA AE 68 21 25 34 24 B6 48 17 83 75 OA 18 4B 70 84 GE F7 63 3F CA 45 6573 79 C9 FC AS system from which this memory dump was produced contains 4 blocks of cache, where each The block consists of eight bytes. Assume the following sequence of memory addresses take place 0x2C, 0x6D. 0x86, 0x29, 0xA5, 0x82, OxA7, 0x68, 0x80, and 0x2B (5 pts) How many blocks of main memory are ther SOLUTION: We know that we have 256 bytes of main memory and each (memory and cache) block is S bytes, 256/8 32 blocks of main memory b) (1o pts) Assuming a direct mapped cache for a main memory address assuming direct mapped cache SOLUTION: 3-bit tag 1 2-bit block/ 3-bit offset ii) What does cache look like after the ten memory accesses have taken place? Draw the cache and show contents and tags. SOLUTION Block # Tag 100 001 Data CD.80,64 B3 8D 81 A7 DB 18,3C9D1F.2F.78,44,1E 01 10 ii) What is the hit rate for this cache on the given sequence of memory accesses? SOLUTION 2C: miss, loaded into block 01 6D: miss, loaded into block 01 86: miss, loaded into block 00 29: miss, loaded into block 01 A5: miss, loaded into block 00 82: miss, loaded into block 00 A7: miss, loaded into block 00 68: miss, loaded into block 01 S0: miss, loaded into block 00 2B: miss, loaded into block 01 Hit rate is 0 (10 pts) Assuming a fully associative cache: ) Show the format for a main memory address. SOLUTION: 5-bit tag 1 0-bit block or set / 3-bit offset ii) Assuming all cache blocks are initially empty, blocks are loaded into the first available empty cache location, and cache uses a first-in-first-out replacement policy, what does cache look like after the ten memory accesses have taken place? SOLUTION: FIFO tells us which block in the cache will be used to load a recently needed memory block into the cache. It advances from 0 to 3 and then restarts from 0 (thus evicting the oldest block from the cache whenever a new memory block is read due to a cache miss) 2C: miss, loaded into block 00 6D: miss, loaded into block O1 86: miss, loaded into block 10 29: hit, uses cache block 00 that has the same tag (00100) A5: miss, loaded into block 11 82: hit, uses cache block 10 that has the same tag (10000) A7: hit, uses cache block 11 that has the same tag (10100) 68: hit, uses cache block 01 that has the same tag (01101) 80: hit, uses cache block 10 that has the same tag (10000) 2B: hit, uses cache block 00 that has the same tag (00101) Data 18,3C9D 1F.2F.78,44, 11E Tag 00101 01101 10000 10100 Block # 01 10 52.57 A3,58,55,OF ES F6 iii) What is the hit rate for this cache on the given sequences of memory accesses? SOLUTION: Hit rate is 6/10 60% 5. Redo the question for the case that each cache block consists of four bytes
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


