Question: 5. Let G(AUB, E) be a bipartite graph (this means that the set of vertices is AUB, AnB, and every edge of E connects a
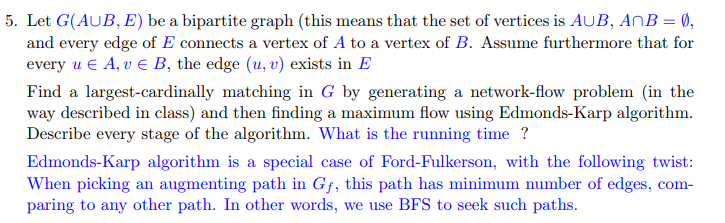
5. Let G(AUB, E) be a bipartite graph (this means that the set of vertices is AUB, AnB, and every edge of E connects a vertex of A to a vertex of B. Assume furthermore that for every u E A,E B, the edge (u, v) exists in E Find a largest-cardinally matching in G by generating a network-flow problem (in the way described in class) and then finding a maximum flow using Edmonds-Karp algorithm. Describe every stage of the algorithm. What is the running time? Edmonds-Karp algorithm is a special case of Ford-Fulkerson, with the following twist: When picking an augmenting path in Gf, this path has minimum number of edges, com- paring to any other path. In other words, we use BFS to seek such paths. 5. Let G(AUB, E) be a bipartite graph (this means that the set of vertices is AUB, AnB, and every edge of E connects a vertex of A to a vertex of B. Assume furthermore that for every u E A,E B, the edge (u, v) exists in E Find a largest-cardinally matching in G by generating a network-flow problem (in the way described in class) and then finding a maximum flow using Edmonds-Karp algorithm. Describe every stage of the algorithm. What is the running time? Edmonds-Karp algorithm is a special case of Ford-Fulkerson, with the following twist: When picking an augmenting path in Gf, this path has minimum number of edges, com- paring to any other path. In other words, we use BFS to seek such paths
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


