Question: 5 MC questions about programming (java language) Consider the following piece of code: Consider the following two classes class A { void printMe() { System.out.println(me());
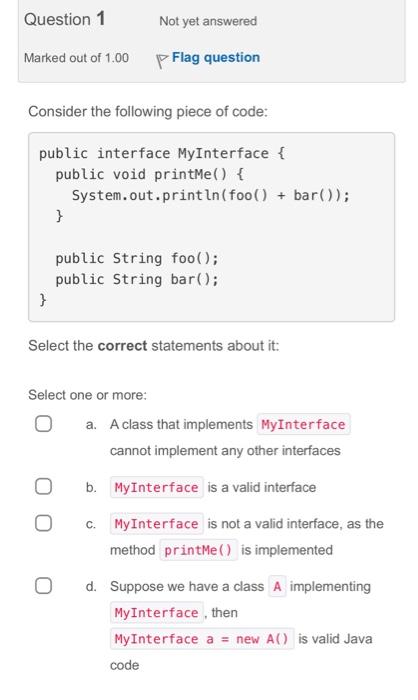

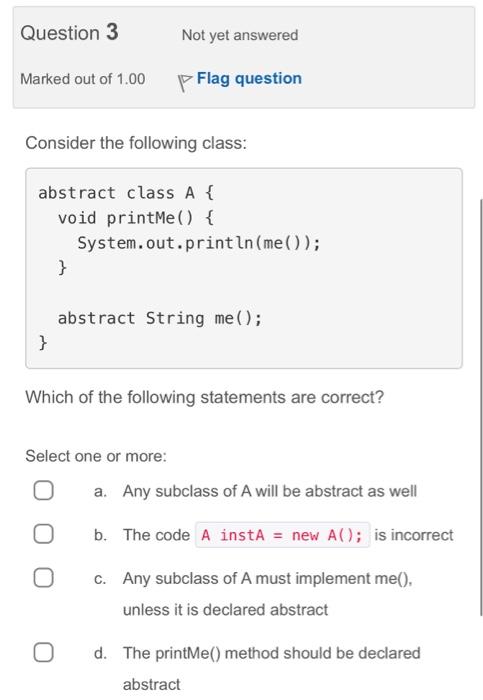

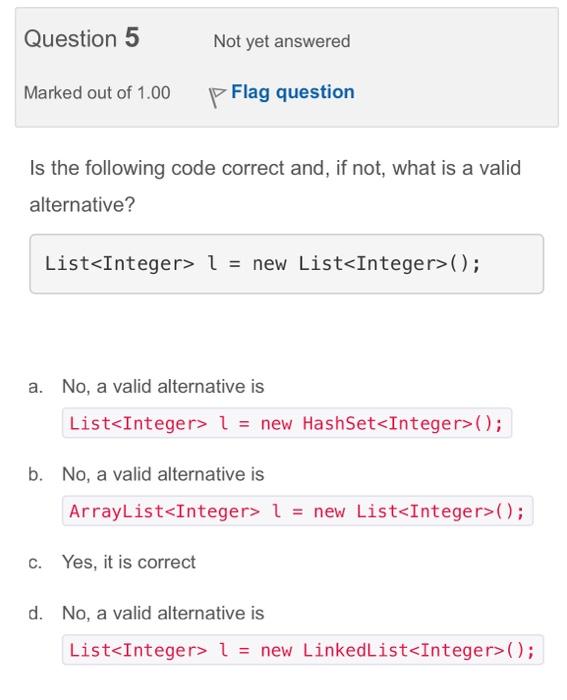
Consider the following piece of code: Consider the following two classes class A \{ void printMe() \{ System.out.println(me()); String me() \{ return "A"; \} class B extends A \{ (a0verride String me() \{ String result = super.me() return result; B; \} What is the sequence of methods called when printMe() is called on an instance of B ? Select one: a. A.printMe B.me A.me b. B.me A.printMe A.me c. A.printMe A.me d. None, because B does not have a printMe method Consider the following class: abstract class A{ void printMe() System.out. print ln(me()) \} abstract String me (); Which of the following statements are correct? Select one or more: a. Any subclass of A will be abstract as well b. The code is incorrect c. Any subclass of A must implement me(), unless it is declared abstract d. The printMe() method should be declared abstract Consider the following classes class A \{ // Code of A \} class B extends A \{ // Code of B \} class C extends A \{ // Code of C \} Which of the following statements about them are correct? Select one or more: a. All these classes are subclasses of Object b. Class C is a subclass of B c. Class B is a subclass of A d. Only A is a subclass of Object Question 5 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 Flag question Is the following code correct and, if not, what is a valid alternative? a. No, a valid alternative is b. No, a valid alternative is c. Yes, it is correct d. No, a valid alternative is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


