Question: 5 . Mixed Forecasting. Explain the mixed technique for forecasting exchange rates. 6 . Detecting a Forecast Bias. Explain how to assess performance in forecasting
Mixed Forecasting. Explain the mixed technique for forecasting exchange rates.
Detecting a Forecast Bias. Explain how to assess performance in forecasting exchange rates. Explain how to detect a bias in forecasting exchange rates.
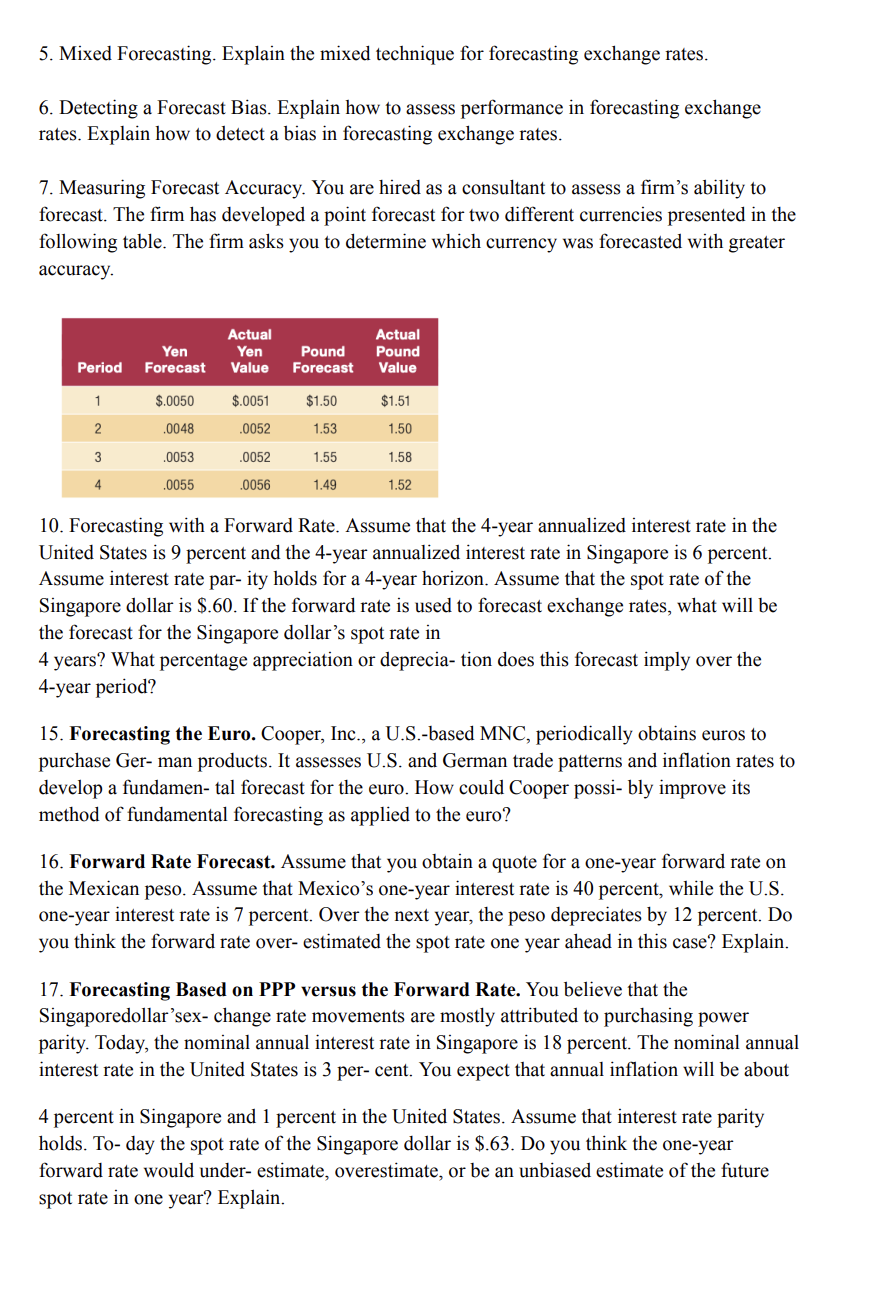
Measuring Forecast Accuracy. You are hired as a consultant to assess a firms ability to forecast. The firm has developed a point forecast for two different currencies presented in the following table. The firm asks you to determine which currency was forecasted with greater accuracy.
Forecasting with a Forward Rate. Assume that the year annualized interest rate in the United States is percent and the year annualized interest rate in Singapore is percent. Assume interest rate par ity holds for a year horizon. Assume that the spot rate of the Singapore dollar is $ If the forward rate is used to forecast exchange rates, what will be the forecast for the Singapore dollars spot rate in
years? What percentage appreciation or deprecia tion does this forecast imply over the year period?
Forecasting the Euro. Cooper, Inc., a USbased MNC periodically obtains euros to purchase Ger man products. It assesses US and German trade patterns and inflation rates to develop a fundamen tal forecast for the euro. How could Cooper possi bly improve its method of fundamental forecasting as applied to the euro?
Forward Rate Forecast. Assume that you obtain a quote for a oneyear forward rate on the Mexican peso. Assume that Mexicos oneyear interest rate is percent, while the US oneyear interest rate is percent. Over the next year, the peso depreciates by percent. Do you think the forward rate over estimated the spot rate one year ahead in this case? Explain.
Forecasting Based on PPP versus the Forward Rate. You believe that the Singaporedollarsex change rate movements are mostly attributed to purchasing power parity. Today, the nominal annual interest rate in Singapore is percent. The nominal annual interest rate in the United States is per cent. You expect that annual inflation will be about percent in Singapore and percent in the United States. Assume that interest rate parity holds. To day the spot rate of the Singapore dollar is $ Do you think the oneyear forward rate would under estimate, overestimate, or be an unbiased estimate of the future spot rate in one year? Explain. Mixed Forecasting. Explain the mixed technique for forecasting exchange rates.
Detecting a Forecast Bias. Explain how to assess performance in forecasting exchange
rates. Explain how to detect a bias in forecasting exchange rates.
Measuring Forecast Accuracy. You are hired as a consultant to assess a firm's ability to
forecast. The firm has developed a point forecast for two different currencies presented in the
following table. The firm asks you to determine which currency was forecasted with greater
accuracy.
Forecasting with a Forward Rate. Assume that the year annualized interest rate in the
United States is percent and the year annualized interest rate in Singapore is percent.
Assume interest rate par ity holds for a year horizon. Assume that the spot rate of the
Singapore dollar is $ If the forward rate is used to forecast exchange rates, what will be
the forecast for the Singapore dollar's spot rate in
years? What percentage appreciation or deprecia tion does this forecast imply over the
year period?
Forecasting the Euro. Cooper, Inc., a USbased MNC periodically obtains euros to
purchase Ger man products. It assesses US and German trade patterns and inflation rates to
develop a fundamen tal forecast for the euro. How could Cooper possi bly improve its
method of fundamental forecasting as applied to the euro?
Forward Rate Forecast. Assume that you obtain a quote for a oneyear forward rate on
the Mexican peso. Assume that Mexico's oneyear interest rate is percent, while the US
oneyear interest rate is percent. Over the next year, the peso depreciates by percent. Do
you think the forward rate over estimated the spot rate one year ahead in this case? Explain.
Forecasting Based on PPP versus the Forward Rate. You believe that the
Singaporedollar'sex change rate movements are mostly attributed to purchasing power
parity. Today, the nominal annual interest rate in Singapore is percent. The nominal annual
interest rate in the United States is per cent. You expect that annual inflation will be about
percent in Singapore and percent in the United States. Assume that interest rate parity
holds. To day the spot rate of the Singapore dollar is $ Do you think the oneyear
forward rate would under estimate, overestimate, or be an unbiased estimate of the future
spot rate in one year? Explain.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


