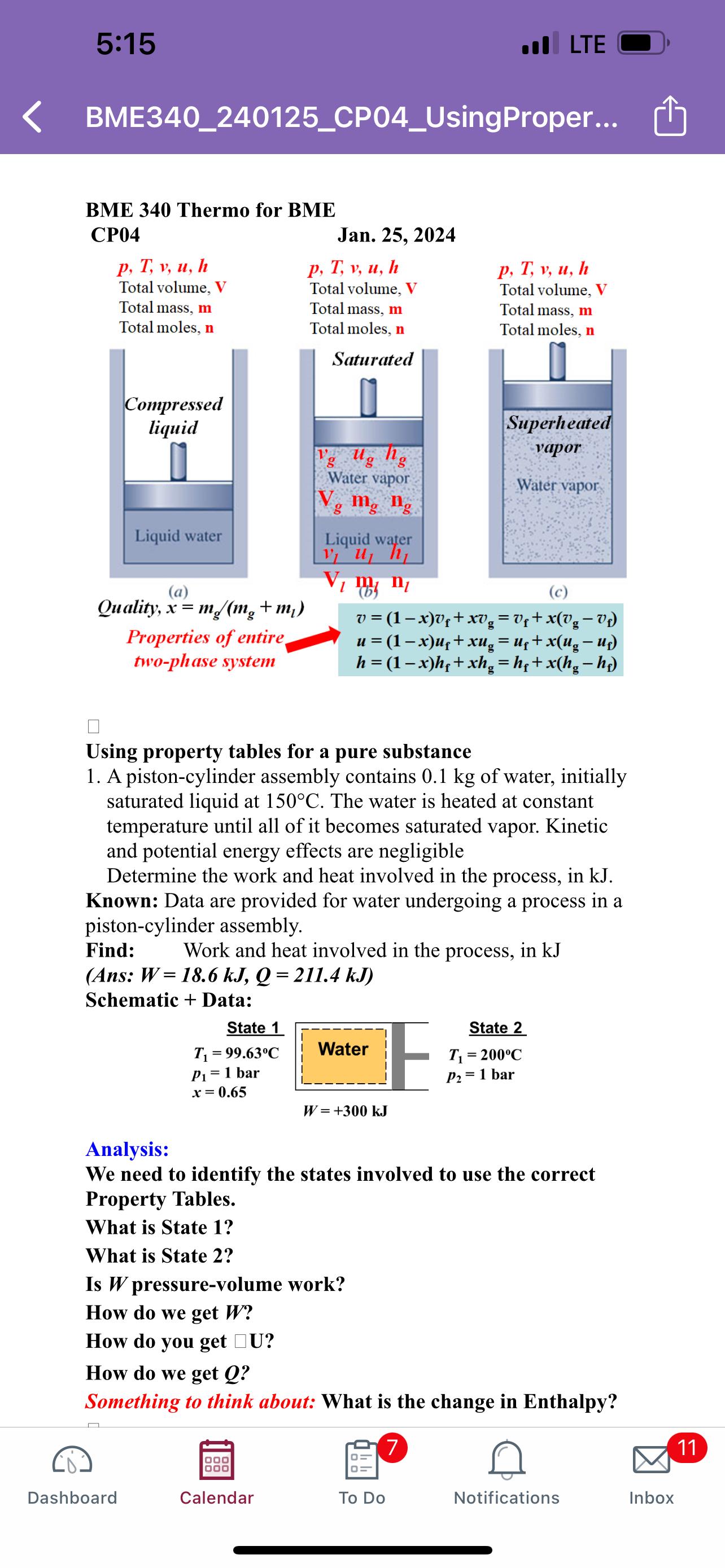
Question: 5:15 .II LTE , BME340_240125_CP04_UsingProper... BME 340 Thermo for BME CP04 Jan. 25, 2024 (c) Quality, x=(m_(g))/(m_(g)+m_(l)) Properties of entire two-phase system v=(1-x)v_(f)+xv_(g)=v_(f)+x(v_(g)-v_(f)) u=(1-x)u_(f)+xu_(g)=u_(f)+x(u_(g)-u_(f))
5:15\ .II LTE
,\ BME340_240125_CP04_UsingProper...\ BME 340 Thermo for BME\ CP04\ Jan. 25, 2024\ (c)\ Quality,
x=(m_(g))/(m_(g)+m_(l))\ Properties of entire two-phase system\
v=(1-x)v_(f)+xv_(g)=v_(f)+x(v_(g)-v_(f))\ u=(1-x)u_(f)+xu_(g)=u_(f)+x(u_(g)-u_(f))\ h=(1-x)h_(f)+xh_(g)=h_(f)+x(h_(g)-h_(f))\ Using property tables for a pure substance\ A piston-cylinder assembly contains
0.1kgof water, initially saturated liquid at
150\\\\deg C. The water is heated at constant temperature until all of it becomes saturated vapor. Kinetic and potential energy effects are negligible\ Determine the work and heat involved in the process, in
kJ.\ Known: Data are provided for water undergoing a process in a piston-cylinder assembly.\ Find: Work and heat involved in the process, in kJ\ (Ans:
W=18.6kJ,Q=211.4kJ)\ Schematio + Data.\ Analysis:\ We need to identify the states involved to use the correct Property Tables.\ What is State 1?\ What is State 2?\ Is
Wpressure-volume work?\ How do we get
W?\ How do you get
U?\ How do we get
Q?\ Something to think about: What is the change in Enthalpy?\ Dashboard\ Calendar\ [\ 11\ To Do\ Notifications\ Inbox
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


