Question: ? 5202v 1.1. Adding continuous dividends to the Black-Scholes (BS) model. Suppose that the stock pays continuous dividends with dividend rate q. The remaining assumptions
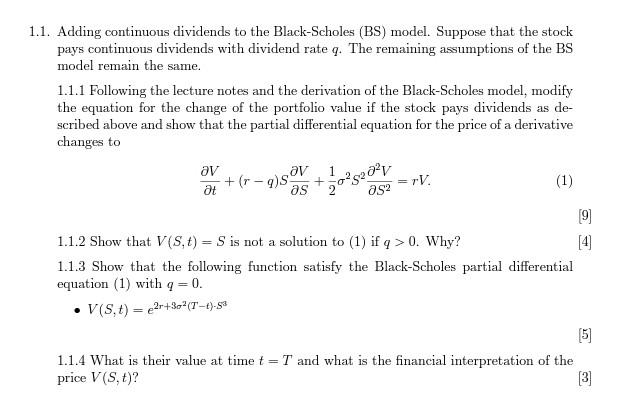
? 5202v 1.1. Adding continuous dividends to the Black-Scholes (BS) model. Suppose that the stock pays continuous dividends with dividend rate q. The remaining assumptions of the BS model remain the same. 1.1.1 Following the lecture notes and the derivation of the Black-Scholes model, modify the equation for the change of the portfolio value if the stock pays dividends as de- scribed above and show that the partial differential equation for the price of a derivative changes to av 1 + + (-9) SOV at TV. as 20 as2 9 1.1.2 Show that V(S, t) = S is not a solution to (1) if q> 0. Why? 1.1.3 Show that the following function satisfy the Black-Scholes partial differential equation (1) with q=0. V(S,t) = 2r+32(T-1)-98 (5) 1.1.4 What is their value at time t = T and what is the financial interpretation of the price V(S, t)? (3 ? 5202v 1.1. Adding continuous dividends to the Black-Scholes (BS) model. Suppose that the stock pays continuous dividends with dividend rate q. The remaining assumptions of the BS model remain the same. 1.1.1 Following the lecture notes and the derivation of the Black-Scholes model, modify the equation for the change of the portfolio value if the stock pays dividends as de- scribed above and show that the partial differential equation for the price of a derivative changes to av 1 + + (-9) SOV at TV. as 20 as2 9 1.1.2 Show that V(S, t) = S is not a solution to (1) if q> 0. Why? 1.1.3 Show that the following function satisfy the Black-Scholes partial differential equation (1) with q=0. V(S,t) = 2r+32(T-1)-98 (5) 1.1.4 What is their value at time t = T and what is the financial interpretation of the price V(S, t)? (3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


