Question: 5.7 A. Interfacial tension (IFT) o can be estimated using the Weinaug-Katz vari- ation of the Macleod-Sugden correlation: N. o' = chi x PL M,
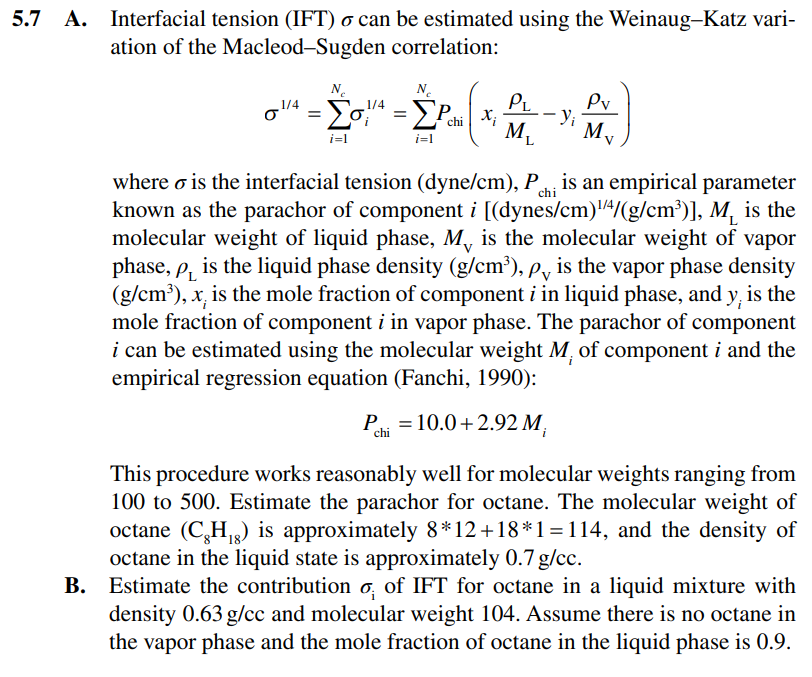
5.7 A. Interfacial tension (IFT) o can be estimated using the Weinaug-Katz vari- ation of the Macleod-Sugden correlation: N. o' = chi x PL M, M Pv yi M i=1 i=1 where o is the interfacial tension (dyne/cm), P chi is an empirical parameter known as the parachor of component i [(dynes/cm)/4/(g/cm)], M, is the molecular weight of liquid phase, M, is the molecular weight of vapor phase, p, is the liquid phase density (g/cm), py is the vapor phase density (g/cm), x, is the mole fraction of component i in liquid phase, and y, is the mole fraction of component i in vapor phase. The parachor of component i can be estimated using the molecular weight M, of component i and the empirical regression equation (Fanchi, 1990): Pchi = 10.0+2.92 M This procedure works reasonably well for molecular weights ranging from 100 to 500. Estimate the parachor for octane. The molecular weight of octane (C2H/3) is approximately 8*12+18*1 =114, and the density of octane in the liquid state is approximately 0.7 g/cc. Estimate the contribution o. of IFT for octane in a liquid mixture with density 0.63 g/cc and molecular weight 104. Assume there is no octane in the vapor phase and the mole fraction of octane in the liquid phase is 0.9. B. 5.7 A. Interfacial tension (IFT) o can be estimated using the Weinaug-Katz vari- ation of the Macleod-Sugden correlation: N. o' = chi x PL M, M Pv yi M i=1 i=1 where o is the interfacial tension (dyne/cm), P chi is an empirical parameter known as the parachor of component i [(dynes/cm)/4/(g/cm)], M, is the molecular weight of liquid phase, M, is the molecular weight of vapor phase, p, is the liquid phase density (g/cm), py is the vapor phase density (g/cm), x, is the mole fraction of component i in liquid phase, and y, is the mole fraction of component i in vapor phase. The parachor of component i can be estimated using the molecular weight M, of component i and the empirical regression equation (Fanchi, 1990): Pchi = 10.0+2.92 M This procedure works reasonably well for molecular weights ranging from 100 to 500. Estimate the parachor for octane. The molecular weight of octane (C2H/3) is approximately 8*12+18*1 =114, and the density of octane in the liquid state is approximately 0.7 g/cc. Estimate the contribution o. of IFT for octane in a liquid mixture with density 0.63 g/cc and molecular weight 104. Assume there is no octane in the vapor phase and the mole fraction of octane in the liquid phase is 0.9. B
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


