Question: 6. (10 points) Write a function void paritize (void *p, unsigned int num_bytes); that accepts a void pointer that points to an array of bytes
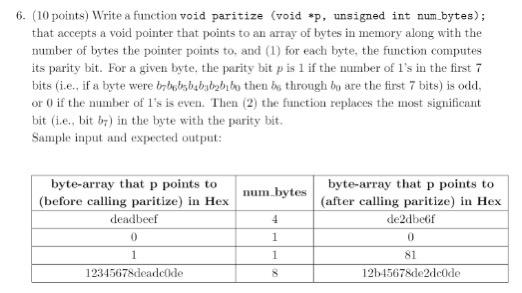
6. (10 points) Write a function void paritize (void *p, unsigned int num_bytes); that accepts a void pointer that points to an array of bytes in memory along with the mumber of bytes the pointer points to, and (1) for each byte, the function computes its parity bit. For a given byte, the party bit pis 1 if the mumber of 1's in the first 7 bits (i.e., if a byte were brbotnsbabybrzblbo then be through by are the first 7 bits) is old, or 0 if the number of l's is even. Then (2) the function replaces the most significant bit (ie, bit by) in the byte with the parity bit. Sample input and expected output: num bytes byte-array that p points to (before calling paritize) in Hex deadbeel 4 byte-array that p points to (after calling paritize) in Hex de2dber 0 81 12b45678de2dcide 0 1 1 1 12345678deado de 6. (10 points) Write a function void paritize (void *p, unsigned int num_bytes); that accepts a void pointer that points to an array of bytes in memory along with the mumber of bytes the pointer points to, and (1) for each byte, the function computes its parity bit. For a given byte, the party bit pis 1 if the mumber of 1's in the first 7 bits (i.e., if a byte were brbotnsbabybrzblbo then be through by are the first 7 bits) is old, or 0 if the number of l's is even. Then (2) the function replaces the most significant bit (ie, bit by) in the byte with the parity bit. Sample input and expected output: num bytes byte-array that p points to (before calling paritize) in Hex deadbeel 4 byte-array that p points to (after calling paritize) in Hex de2dber 0 81 12b45678de2dcide 0 1 1 1 12345678deado de
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


