Question: 6 5 4 2 A mm 3 D 2 For full credit, please provide support your solutions with detailed reasoning. P1 - Music Video You
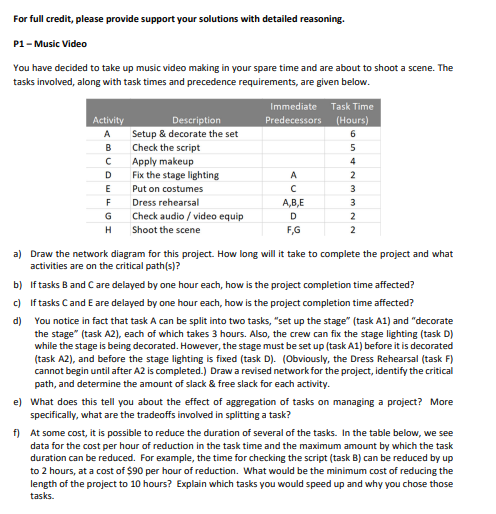
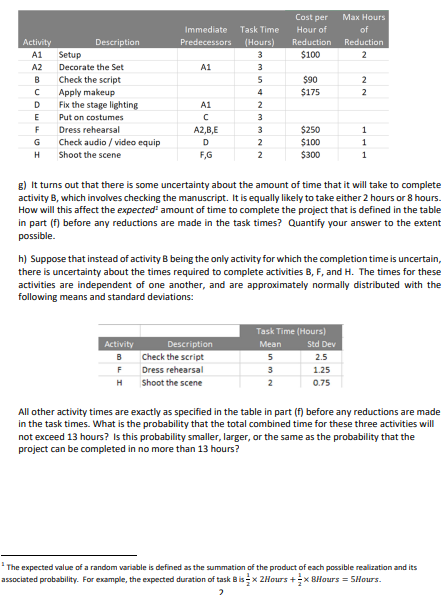
6 5 4 2 A mm 3 D 2 For full credit, please provide support your solutions with detailed reasoning. P1 - Music Video You have decided to take up music video making in your spare time and are about to shoot a scene. The tasks involved, along with task times and precedence requirements, are given below. Immediate Task Time Activity Description Predecessors (Hours) A Setup & decorate the set B Check the script Apply makeup D Fix the stage lighting E Put on costumes 3 F Dress rehearsal A,B,E Check audio/video equip 2 H Shoot the scene F,G a) Draw the network diagram for this project. How long will it take to complete the project and what activities are on the critical path(s)? b) If tasks B and Care delayed by one hour each, how is the project completion time affected? c) Iftasks Cand E are delayed by one hour each, how is the project completion time affected? d) You notice in fact that task A can be split into two tasks, "set up the stage" (task A1) and "decorate the stage" (task A2), each of which takes 3 hours. Also, the crew can fix the stage lighting (task D) while the stage is being decorated. However, the stage must be set up (task A1) before it is decorated (task A2), and before the stage lighting is fixed (task D). (Obviously, the Dress Rehearsal (task F) cannot begin until after A2 is completed.) Draw a revised network for the project, identify the critical path, and determine the amount of slack & free slack for each activity. e) What does this tell you about the effect of aggregation of tasks on managing a project? More specifically, what are the tradeoffs involved in splitting a task? f) At some cost, it is possible to reduce the duration of several of the tasks. In the table below, we see data for the cost per hour of reduction in the task time and the maximum amount by which the task duration can be reduced. For example, the time for checking the script (task B) can be reduced by up to 2 hours, at a cost of $90 per hour of reduction. What would be the minimum cost of reducing the length of the project to 10 hours? Explain which tasks you would speed up and why you chose those tasks. Immediate Predecessors Cost per Hour of Reduction $100 Max Hours of Reduction 2. A1 $90 $175 Task Time (Hours) 3 3 5 4 2 3 2 2 NN Activity A1 A2 B D E F G H Description Setup Decorate the Set Check the script Apply makeup Fix the stage lighting Put on costumes Dress rehearsal Check audio/video equip Shoot the scene A1 A2,BE D F,G 3 2 2 $250 $100 $300 1 1 1 g) it turns out that there is some uncertainty about the amount of time that it will take to complete activity B, which involves checking the manuscript. It is equally likely to take either 2 hours or 8 hours. How will this affect the expected amount of time to complete the project that is defined in the table in part (f) before any reductions are made in the task times? Quantify your answer to the extent possible. h) Suppose that instead of activity B being the only activity for which the completion time is uncertain, there is uncertainty about the times required to complete activities B, F, and H. The times for these activities are independent of one another, and are approximately normally distributed with the following means and standard deviations: Activity Description B Check the script F Dress rehearsal H Shoot the scene Task Time (Hours) Mean Std Dev 5 2.5 3 1.25 0.75 All other activity times are exactly as specified in the table in part (f) before any reductions are made in the task times. What is the probability that the total combined time for these three activities will not exceed 13 hours? Is this probability smaller, larger, or the same as the probability that the project can be completed in no more than 13 hours? The expected value of a random variable is defined as the summation of the product of each possible realization and its associated probability. For example, the expected duration of task Bis x 2Hours +1x BHours = SHours






