Question: 6. (ANOVA Calculation) Suppose a model has two predictors ind Y; 'N(Bo + B1li1 + B2li2,0), i = 1, ..., N. n = 546. The
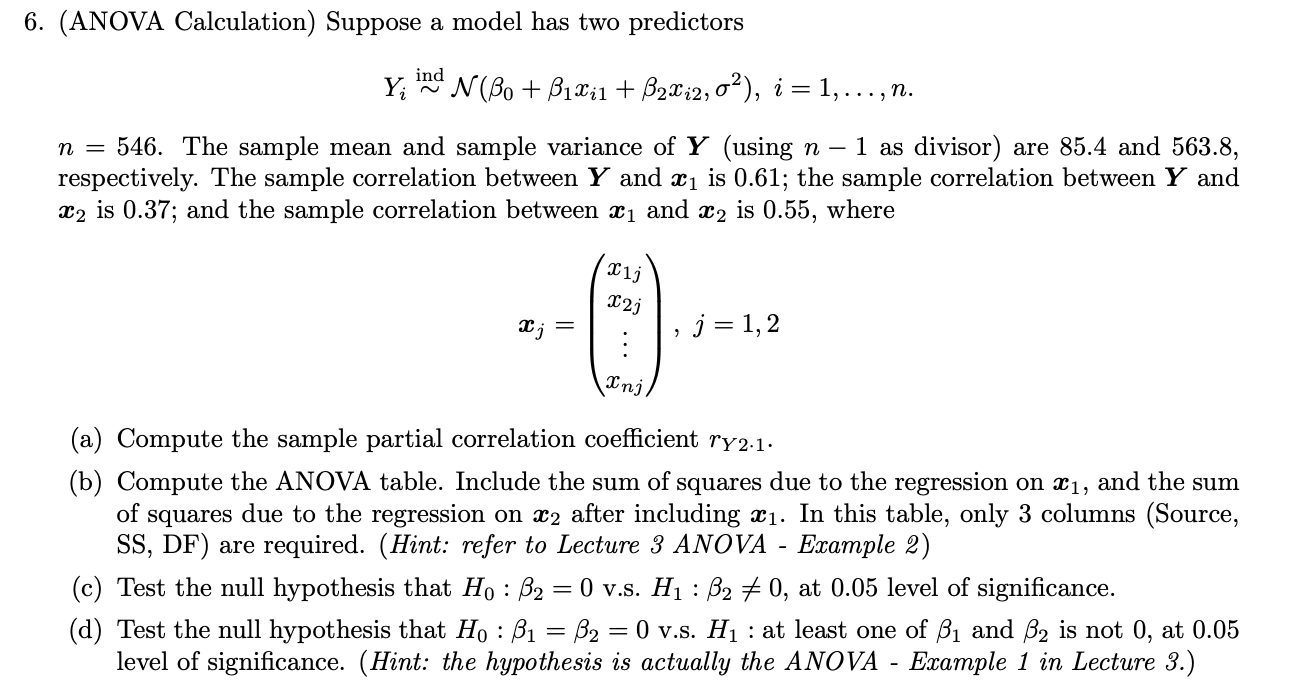
6. (ANOVA Calculation) Suppose a model has two predictors ind Y; 'N(Bo + B1li1 + B2li2,0), i = 1, ..., N. n = 546. The sample mean and sample variance of Y (using n - 1 as divisor) are 85.4 and 563.8, respectively. The sample correlation between Y and X is 0.61; the sample correlation between Y and X2 is 0.37; and the sample correlation between Xi and X2 is 0.55, where Ilj 12 j , j = 1,2 xnj. (a) Compute the sample partial correlation coefficient ry2.1. (b) Compute the ANOVA table. Include the sum of squares due to the regression on 21, and the sum of squares due to the regression on 22 after including X1. In this table, only 3 columns (Source, SS, DF) are required. (Hint: refer to Lecture 3 ANOVA - Example 2) (c) Test the null hypothesis that Ho : 32 = 0 v.s. H1 : B2 + 0, at 0.05 level of significance. (d) Test the null hypothesis that Ho : B1 = B2 = 0 v.s. Hi : at least one of B1 and B2 is not 0, at 0.05 level of significance. (Hint: the hypothesis is actually the ANOVA - Example 1 in Lecture 3.) 6. (ANOVA Calculation) Suppose a model has two predictors ind Y; 'N(Bo + B1li1 + B2li2,0), i = 1, ..., N. n = 546. The sample mean and sample variance of Y (using n - 1 as divisor) are 85.4 and 563.8, respectively. The sample correlation between Y and X is 0.61; the sample correlation between Y and X2 is 0.37; and the sample correlation between Xi and X2 is 0.55, where Ilj 12 j , j = 1,2 xnj. (a) Compute the sample partial correlation coefficient ry2.1. (b) Compute the ANOVA table. Include the sum of squares due to the regression on 21, and the sum of squares due to the regression on 22 after including X1. In this table, only 3 columns (Source, SS, DF) are required. (Hint: refer to Lecture 3 ANOVA - Example 2) (c) Test the null hypothesis that Ho : 32 = 0 v.s. H1 : B2 + 0, at 0.05 level of significance. (d) Test the null hypothesis that Ho : B1 = B2 = 0 v.s. Hi : at least one of B1 and B2 is not 0, at 0.05 level of significance. (Hint: the hypothesis is actually the ANOVA - Example 1 in Lecture 3.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


