Question: 6. Consider the Barings case discussed in class. Suppose the volatilities of the JGB and the Nikkei are 0.3% and 1.2% per month and correlation
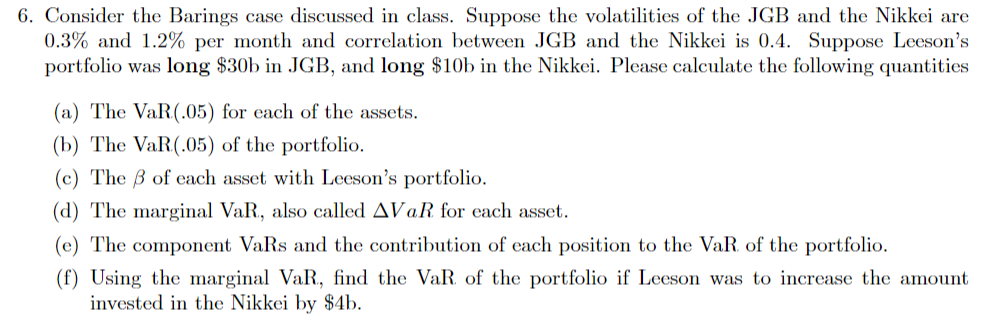
6. Consider the Barings case discussed in class. Suppose the volatilities of the JGB and the Nikkei are 0.3% and 1.2% per month and correlation between JGB and the Nikkei is 0.4. Suppose Leeson's portfolio was long $30b in JGB, and long $10b in the Nikkei. Please calculate the following quantities (a) The VaR(.05) for each of the assets. (b) The VaR(.05) of the portfolio. (c) The B of each asset with Leeson's portfolio. (d) The marginal VaR, also called AVaR for each asset. (e) The component VaRs and the contribution of each position to the VaR of the portfolio. (f) Using the marginal VaR, find the VaR of the portfolio if Leeson was to increase the amount invested in the Nikkei by $4b. 6. Consider the Barings case discussed in class. Suppose the volatilities of the JGB and the Nikkei are 0.3% and 1.2% per month and correlation between JGB and the Nikkei is 0.4. Suppose Leeson's portfolio was long $30b in JGB, and long $10b in the Nikkei. Please calculate the following quantities (a) The VaR(.05) for each of the assets. (b) The VaR(.05) of the portfolio. (c) The B of each asset with Leeson's portfolio. (d) The marginal VaR, also called AVaR for each asset. (e) The component VaRs and the contribution of each position to the VaR of the portfolio. (f) Using the marginal VaR, find the VaR of the portfolio if Leeson was to increase the amount invested in the Nikkei by $4b
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


