Question: 6. Hypothesis tests and confidence interval estimators Consumers with at least one credit card have a mean of 4.34 credit cards. [Source-.- Sumit .tganyalr John
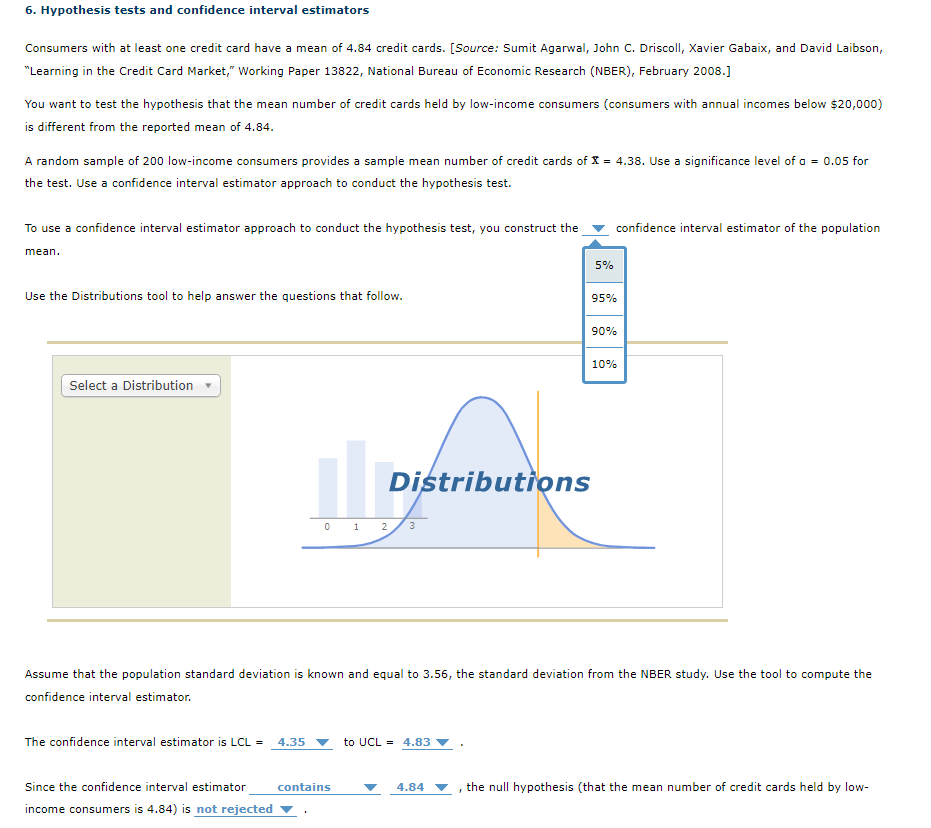
6. Hypothesis tests and confidence interval estimators Consumers with at least one credit card have a mean of 4.34 credit cards. [Source-.- Sumit .tganyalr John C. Driscollr Xavier GabaixJ and David Laibsonf \"Learning in the Credit Card Market," Working Paper 13322. National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER], February 2008.] You want to test the hypothesis that the mean number of credit cards held by low-income consumers [consumers with annual incomes below 520,000} is different from the reported mean of 4.84. A random sample of 200 low-income consumers provides a sample mean number of credit cards of I = 4.33. Use a significance level of o = 0.05 for the test. Use a confidence interval estimator approach to conduct the hypothesis test. To use a condence interval estimator approach to conduct the hypothesis test, you construct the V confidence interval estimator of the population mean. Use the Distributions tool to help answer the questions that follow. Select a Distribution - Assume that the population standard deviation is known and equal to 3.56, the standard deviation from the NBER study. Use the tool to compute the confidence interval estimator. The condence interval estimator is LCL = 4.35 V to UCL = 4.83 V . Since the confidence interval estimator contains 7 4.34 Y . the null hypothesis [that the mean number of credit cards held by low- income consumers is 4.84} is not rejected 7
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


