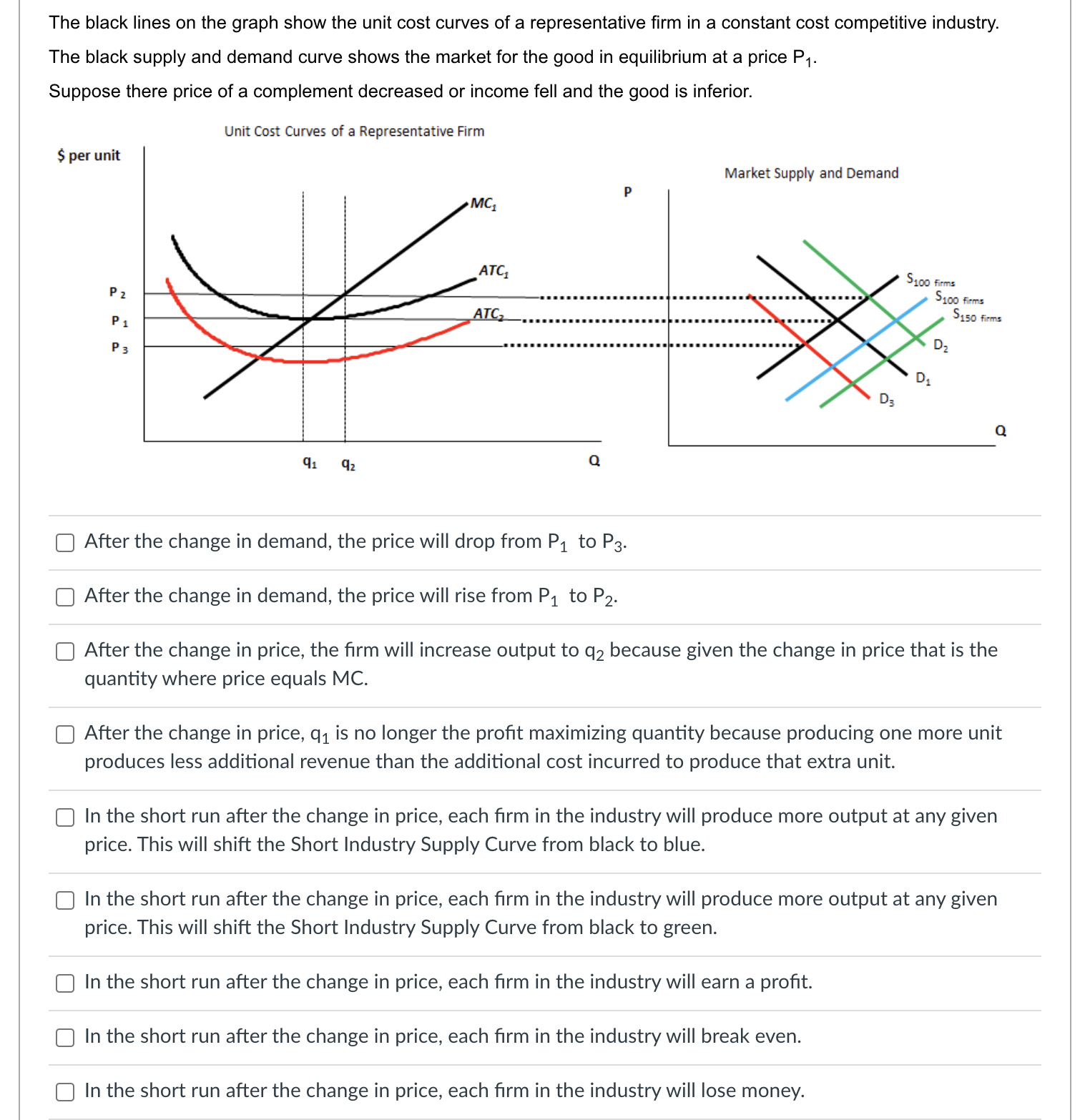
Question: #6 The black lines on the graph show the unit cost curves of a representative rm in a constant cost competitive industry. The black supply


!['11 '11 Q C] After the change in demand, the price will](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66697738aecc9_832666977388ae9c.jpg)
#6
![drop from P1 to P3. C] After the change in demand, the](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6669773921ae2_8336669773901d2e.jpg)
![price will rise from P1 to P2. C] After the change in](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66697739b39f1_833666977395969c.jpg)
![in price that is the quantity where price equals MC. C] After](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6669773a7eb59_8346669773a648c8.jpg)

![cost incurred to produce that extra unit. C] In the short run](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6669773ba6b49_8356669773b8bfaf.jpg)
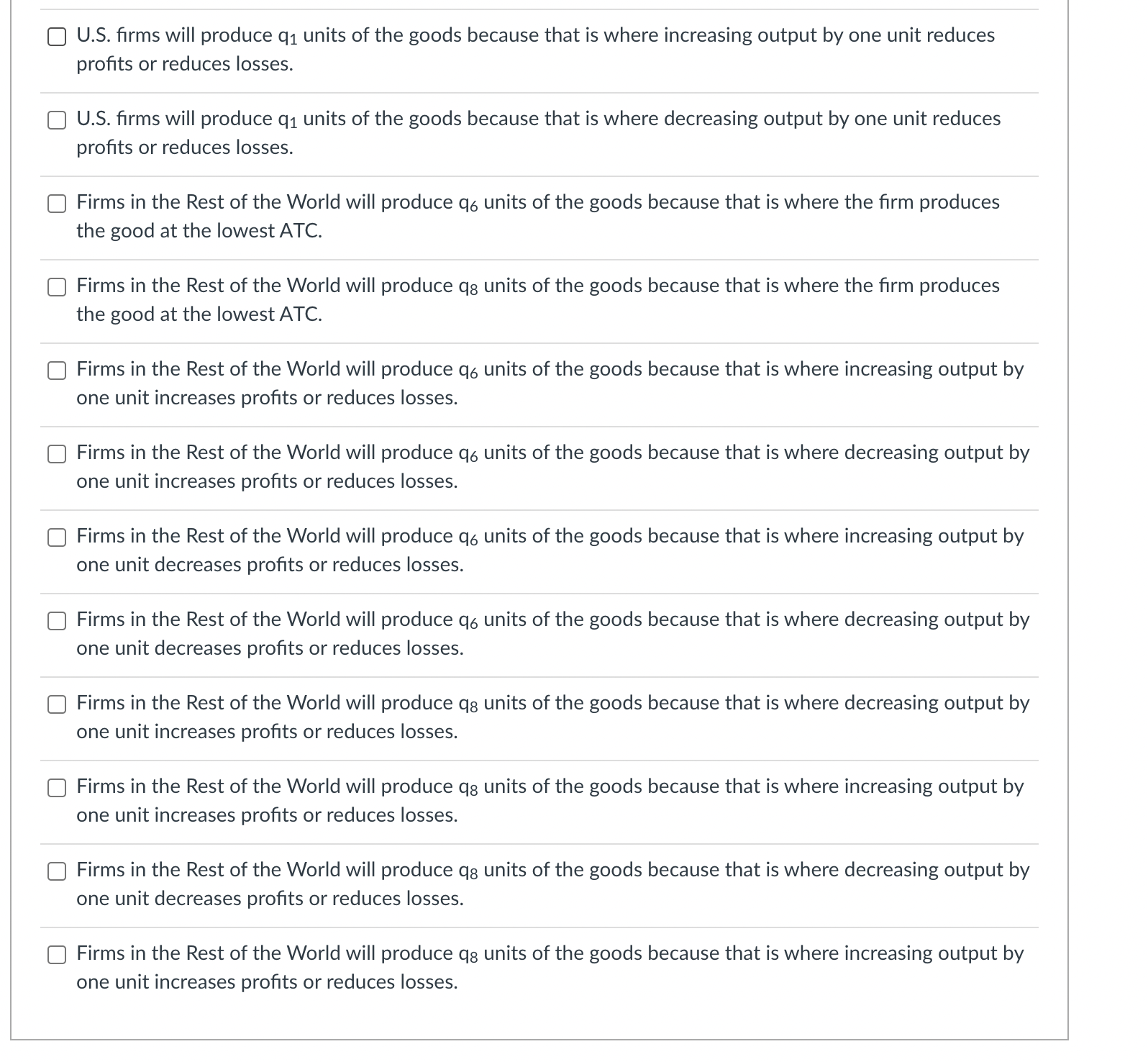
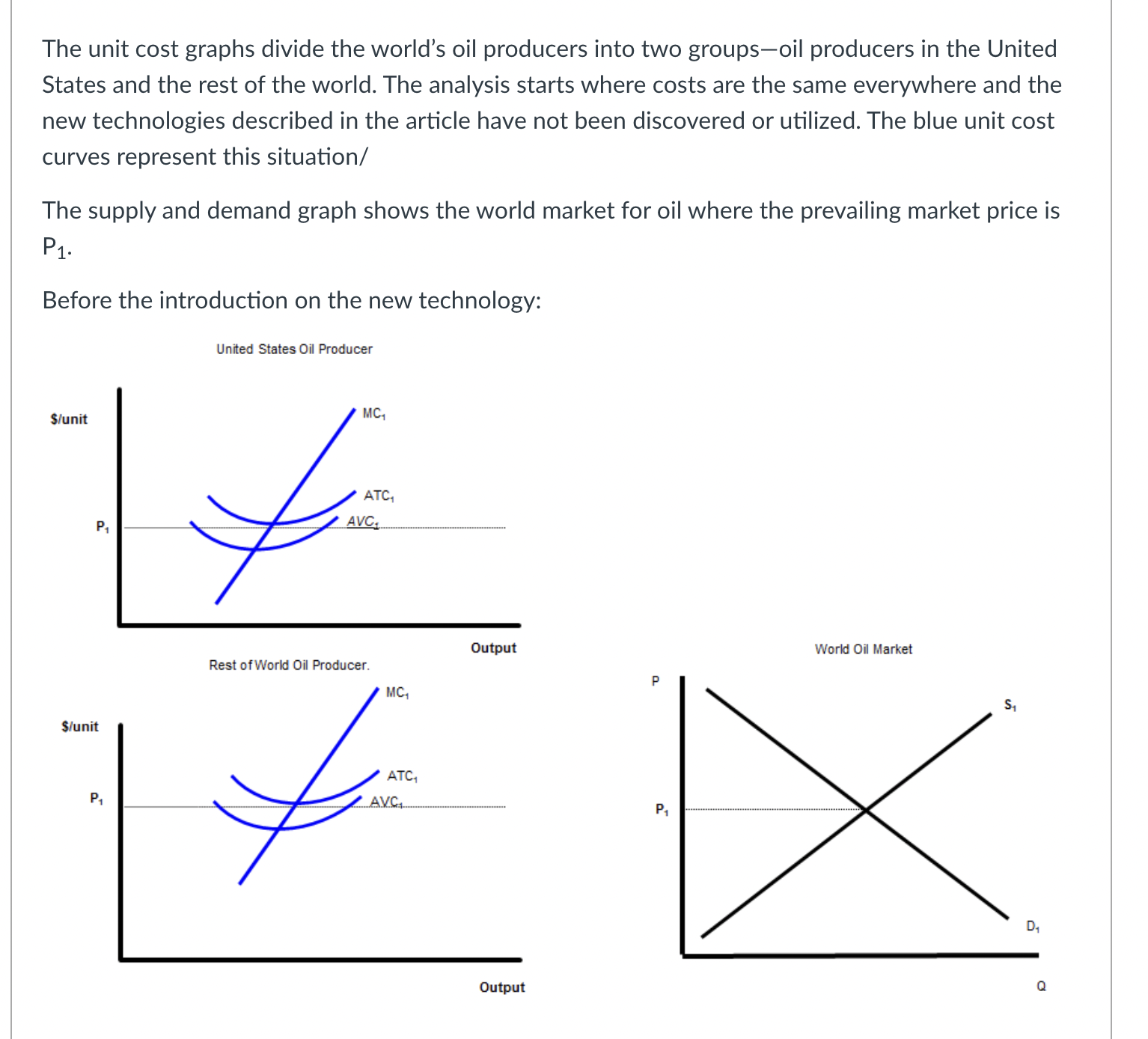
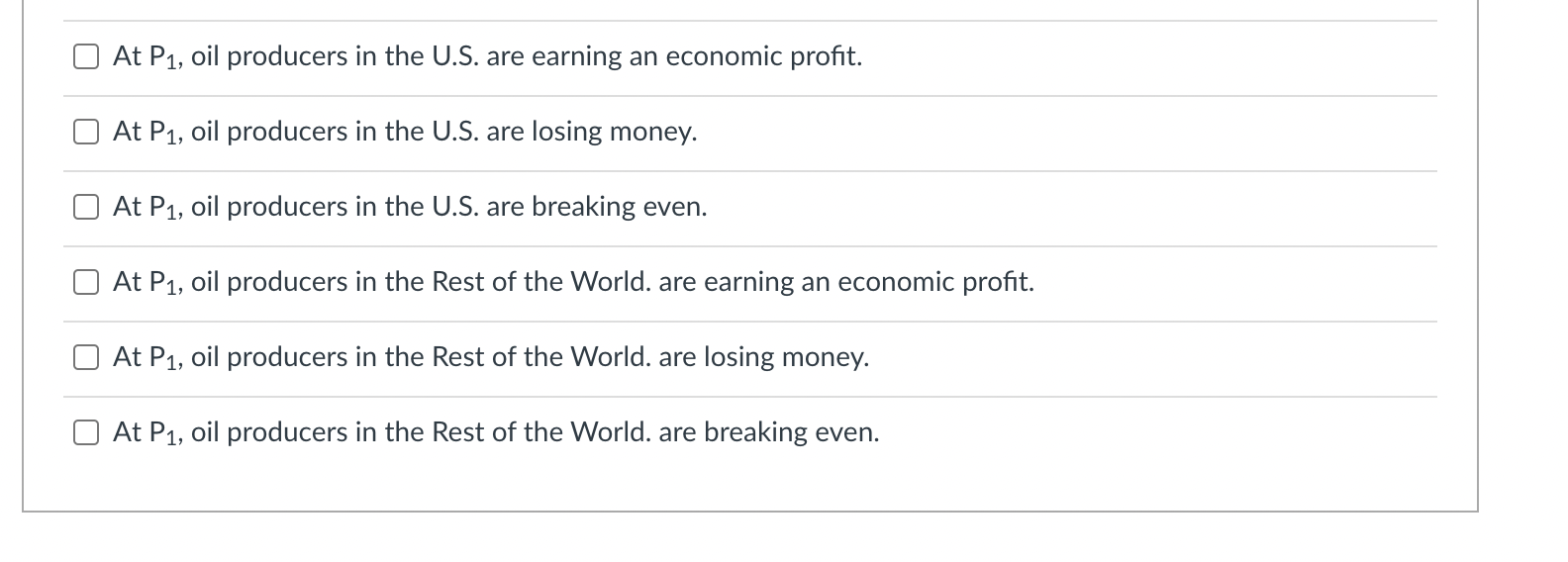
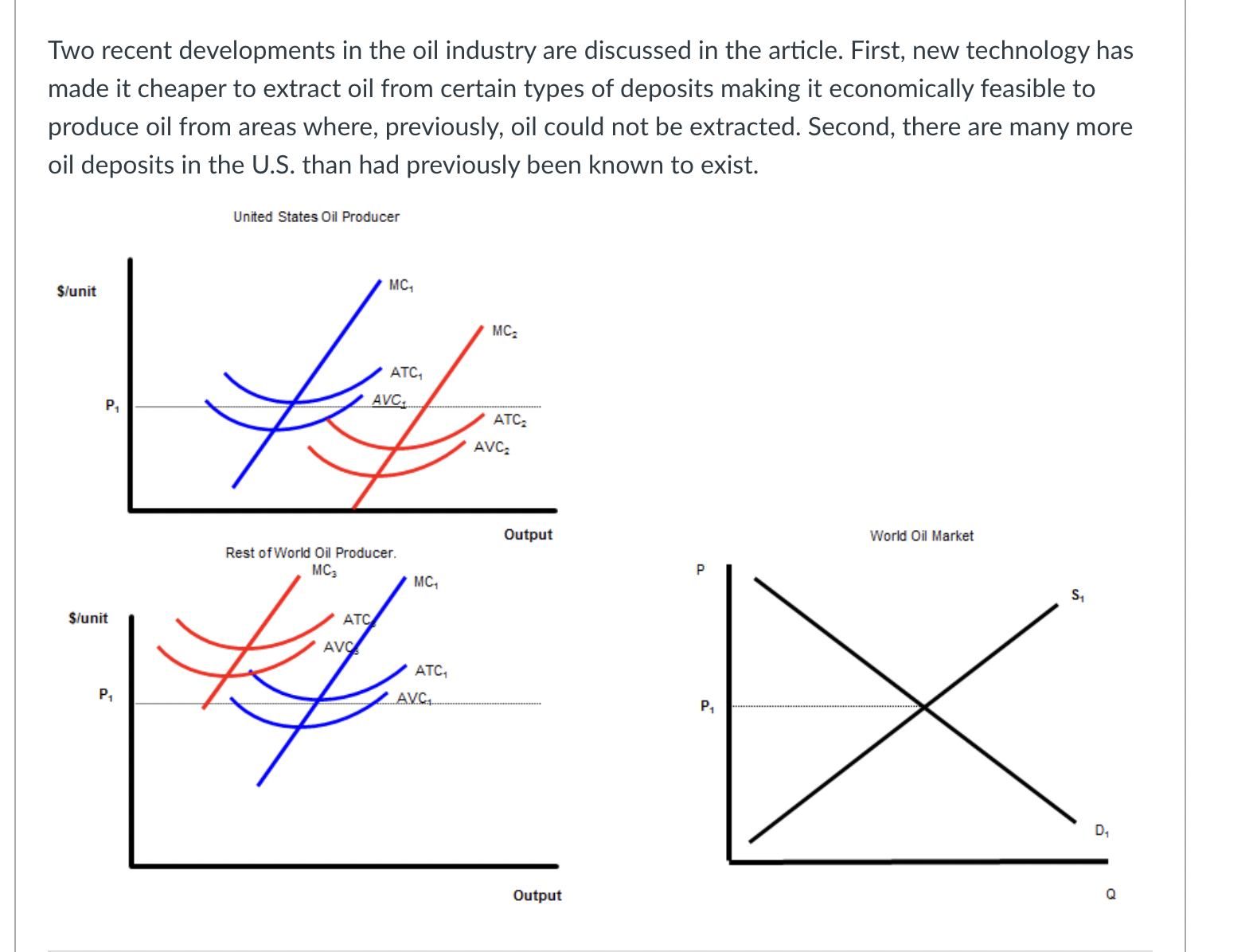
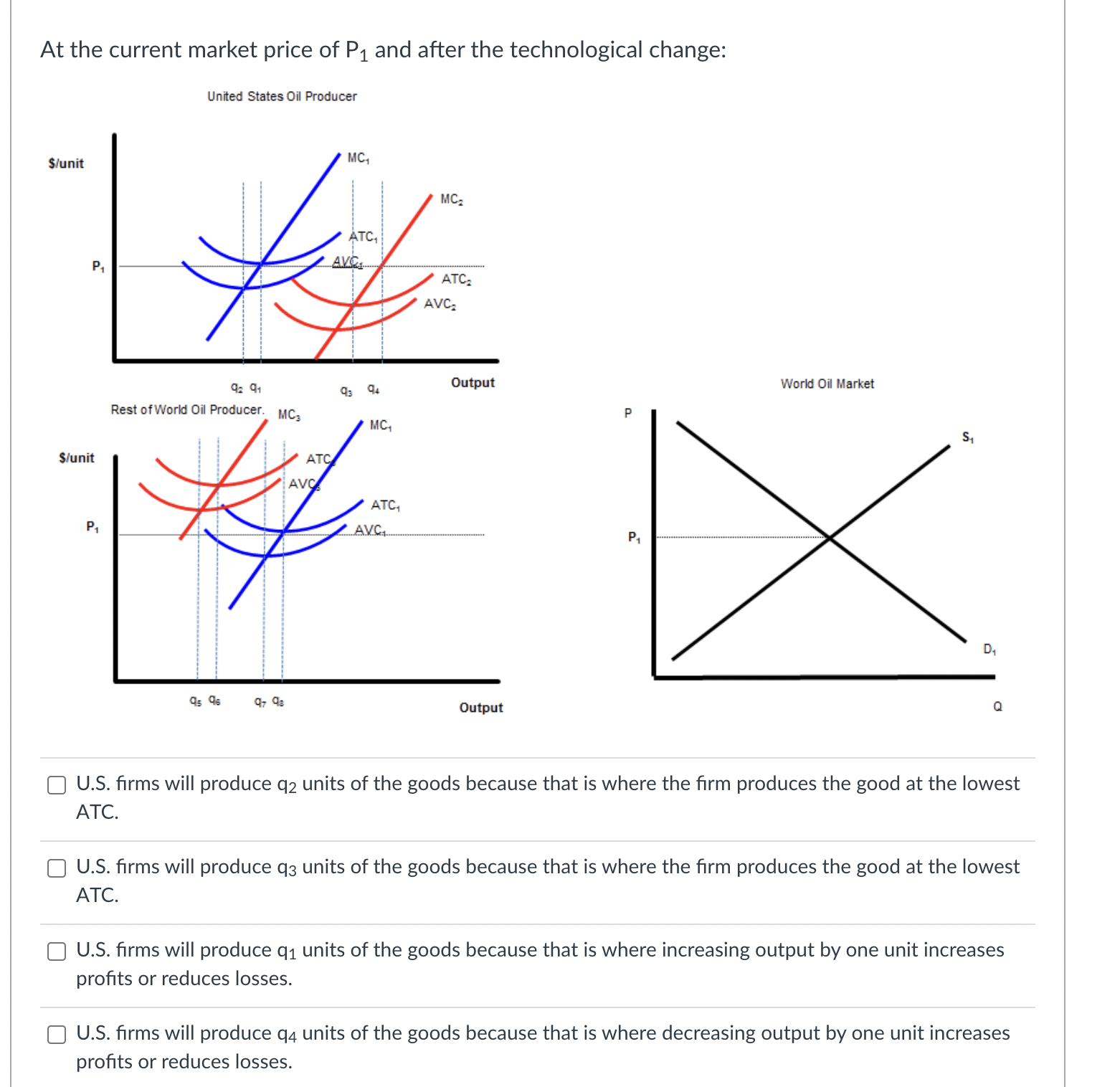
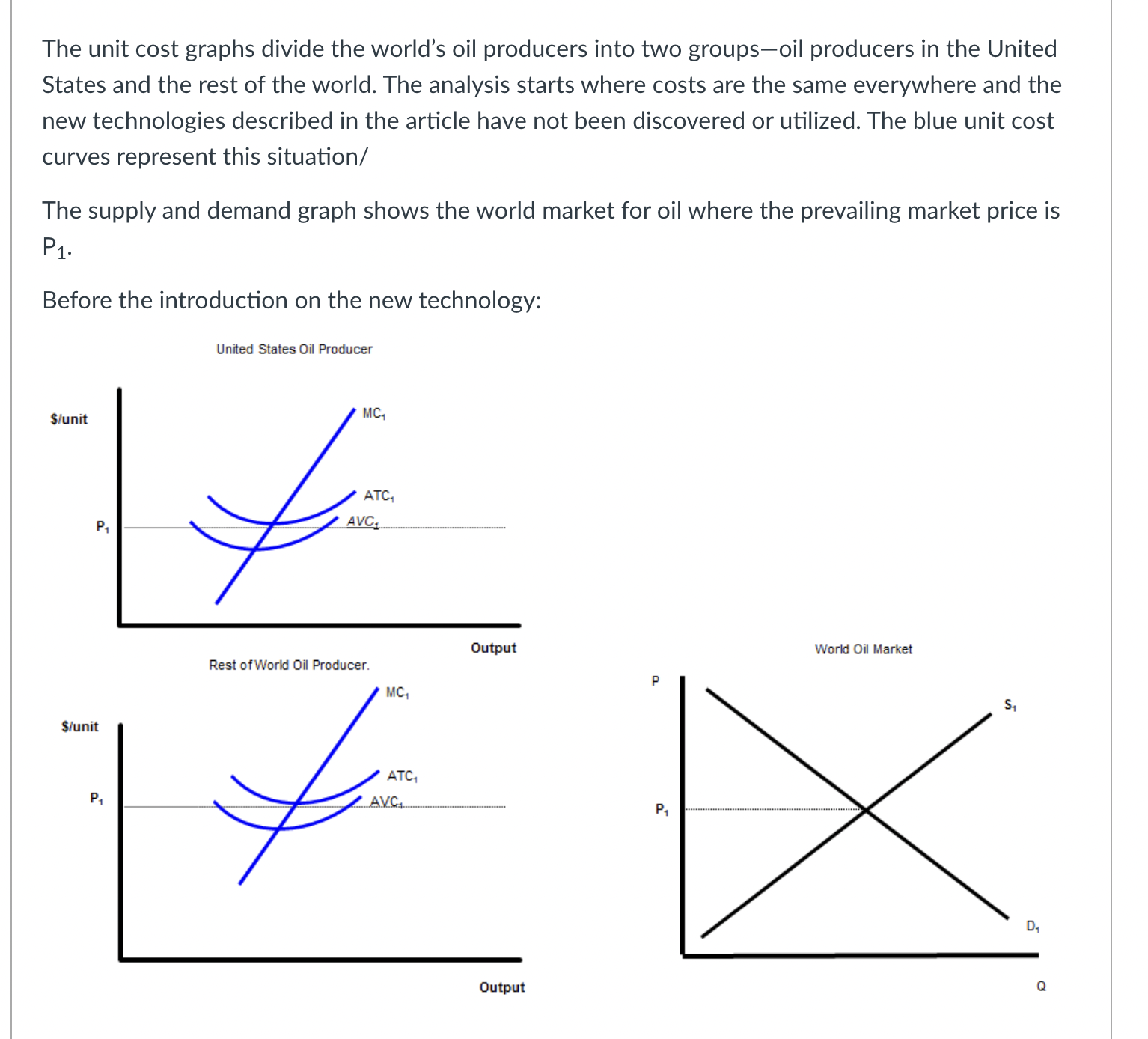
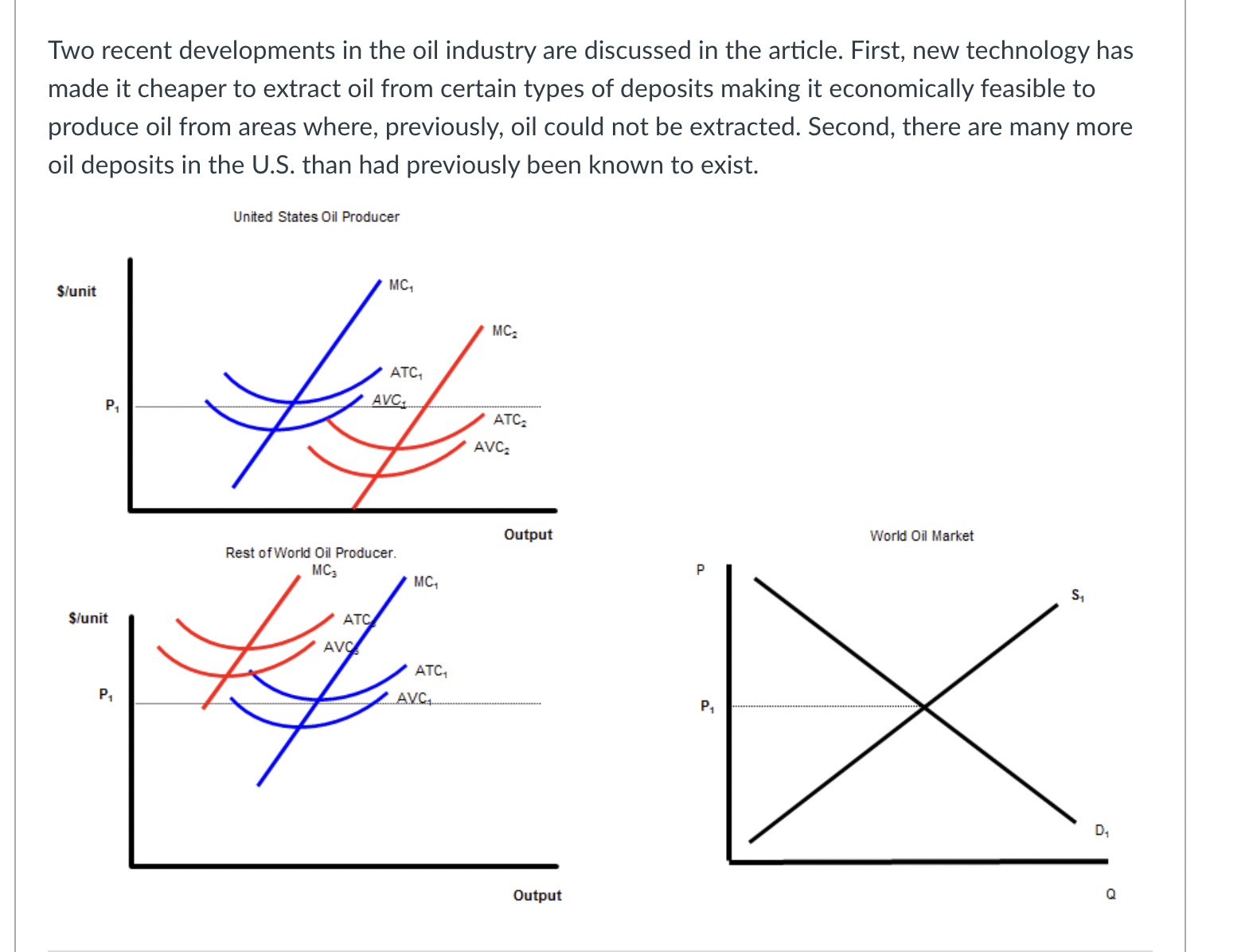
The black lines on the graph show the unit cost curves of a representative rm in a constant cost competitive industry. The black supply and demand curve shows the market for the good in equilibrium at a price P1. Suppose there price of a complement decreased or income fell and the good is inferior. Unit Cost Curves of a Representative Firm $per unit Market Supply and Demand p P1 .......................................... 5100 m :21 -' ...................... ............... ...... 5150mm P3 consensus-I-uu-uo-uu-uuu noun-cou-uo-uuuuu D2 '11 '11 Q C] After the change in demand, the price will drop from P1 to P3. C] After the change in demand, the price will rise from P1 to P2. C] After the change in price, the rm will increase output to q2 because given the change in price that is the quantity where price equals MC. C] After the change in price, ql is no longer the prot maximizing quantity because producing one more unit produces less additional revenue than the additional cost incurred to produce that extra unit. C] In the short run after the change in price, each rm in the industry will produce more output at any given price. This will shift the Short Industry Supply Curve from black to blue. C] In the short run after the change in price, each rm in the industry will produce more output at any given price. This will shift the Short Industry Supply Curve from black to green. C] In the short run after the change in price, each rm in the industry will earn a prot. C] In the short run after the change in price, each rm in the industry will break even. C] In the short run after the change in price, each rm in the industry will lose money. O In the long run, new firms will enter the industry shifting the Short Run Supply Curve from blue to green. O In the long run, new firms will enter the industry shifting the Short Run Supply Curve from black to green. O In the long run, new firms will exit the industry shifting the Short Run Supply Curve from black to green. O In the long run firms will continue to enter the industry, shifting the demand curve to the left until the price has fallen to the minimum of ATC1. O In the long run firms will continue to enter the industry, shifting the demand curve to the right until the price has fallen to the minimum of ATC1. O In the long run firms will continue to enter the industry, shifting the demand curve to the left until the price has fallen to the minimum of ATC2. O In the long run firms will continue to enter the industry, shifting the demand curve to the right until the price has fallen to the minimum of ATC2. O In the short run, existing firms benefit from the change in demand because their profits increase. In the short run, existing firms don't benefit from the change in demand because their profits stay the same. O In the long run, existing firms benefit from the change in demand because their profits increase. O In the long run, existing firms don't benefit from the change in demand because their profits stay the same. The increase in the price in the short run acts a signal to producers to produce more of the good because it is more highly desired by consumers. O The increase in the price in the short run acts a signal to producers to produce less of the good because it is less highly desired by consumers. Allowing the price to move in response to a change in demand triggers a reallocation of productive resources from less highly valued use to more highly valued use. Allowing the price to move in response to a change in demand triggers a reallocation of productive resources from more highly valued use to less highly valued use.The unit cost graphs divide the world's oil producers into two groups-oil producers in the United States and the rest of the world. The analysis starts where costs are the same everywhere and the new technologies described in the article have not been discovered or utilized. The blue unit cost curves represent this situation/ The supply and demand graph shows the world market for oil where the prevailing market price is P1 Before the introduction on the new technology: United States Oil Producer S/unit MC, ATC, AVC.. Output World Oil Market Rest of World Oil Producer. P S/unit PA DA OutputC] At P1, oil producers in the U.S. are earning an economic prot. C] At P1, oil producers in the U.S. are losing money. C] At P1, oil producers in the U.S. are breaking even. C] At P1, oil producers in the Rest of the World. are earning an economic prot. C] At P1, oil producers in the Rest of the World. are losing money. C] At P1, oil producers in the Rest of the World. are breaking even. Two recent developments in the oil industry are discussed in the article. First, new technology has made it cheaper to extract oil from certain types of deposits making it economically feasible to produce oil from areas where, previously, oil could not be extracted. Second, there are many more oil deposits in the U.S. than had previously been known to exist. United States Oil Producer S/unit MC, PA World Oil Market Rest of World Oil Producer. MC3 P S/unit P1 OutputThe shift to MC3, ATC3, and AVC3, represent the improvement in technology discussed in the article. The shift to MC3, ATC3, and AVC3, represent the degredation in technology discussed in the article. The shift to MC3, ATC3, and AVC3, represent the lowering of costs described in the article. The shift to MC3, ATC3, and AVC3, represent the increase in costs described in the article. The shift to MC2, ATC2, and AVC2, represent the improvement in technology discussed in the article. The shift to MC2, ATC2, and AVC2, represent the degredation in technology discussed in the article. The shift to MC2, ATC2, and AVC2, represent the increase in costs described in the article. The shift to MC2, ATC2, and AVC2, represent the decrease in costs described in the article.At the current market price of P1 and after the technological change: Unied States Oil Producer \"unit World 0i Market Rest DfWorld Oil Producer. MC; Stunit as\": chh output a [3 US. rms will produce q2 units of the goods because that is where the rm produces the good at the lowest ATC. E] US. rms will produce q3 units of the goods because that is where the rm produces the good at the lowest ATC. E] US. rms will produce q1 units of the goods because that is where increasing output by one unit increases prots or reduces losses. E] US. rms will produce q4 units of the goods because that is where decreasing output by one unit increases prots or reduces losses. C] U.S. rms will produce q1 units of the goods because that is where increasing output by one unit reduces prots or reduces losses. [3 US. rms will produce ql units of the goods because that is where decreasing output by one unit reduces prots or reduces losses. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce q units of the goods because that is where the rm produces the good at the lowest ATC. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce Clg units of the goods because that is where the rm produces the good at the lowest ATC. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce q units of the goods because that is where increasing output by one unit increases prots or reduces losses. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce q units of the goods because that is where decreasing output by one unit increases prots or reduces losses. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce q units of the goods because that is where increasing output by one unit decreases prots or reduces losses. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce q units of the goods because that is where decreasing output by one unit decreases prots or reduces losses. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce qg units of the goods because that is where decreasing output by one unit increases prots or reduces losses. [3 Firms in the Rest of the World will produce qg units of the goods because that is where increasing output by one unit increases prots or reduces losses. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce Clg units of the goods because that is where decreasing output by one unit decreases prots or reduces losses. C] Firms in the Rest of the World will produce qg units of the goods because that is where increasing output by one unit increases prots or reduces losses
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


