Question: (60pts) This class has static methods that will help us evaluate Lisp arithmetic expressions. Before a List expression is evaluated, we have to make

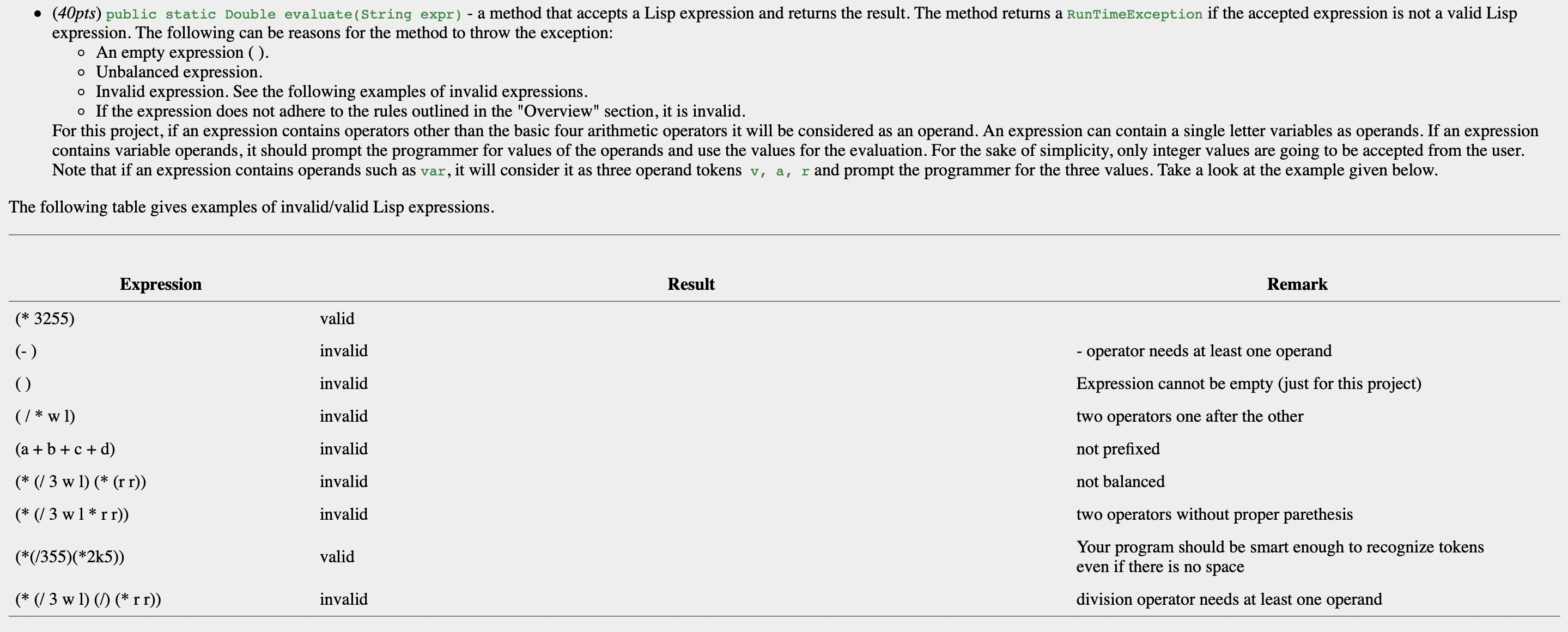
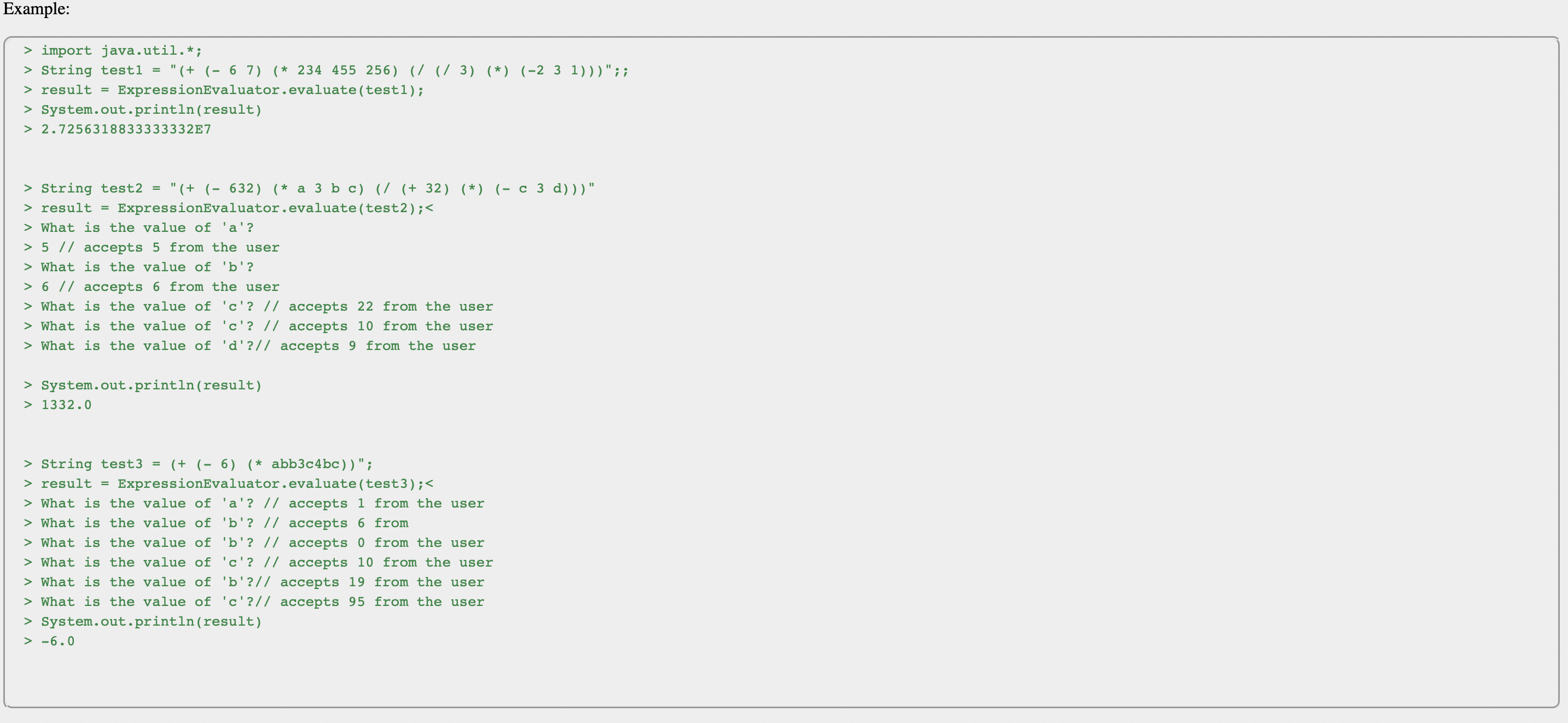
(60pts) This class has static methods that will help us evaluate Lisp arithmetic expressions. Before a List expression is evaluated, we have to make sure that it is a valid expression. The following expressions show valid and invalid Lisp arithmetic expressions. Valid Expression (+ (-5) ) (* 4 4 5) (322) (* 4 4) Invalid Expressions (+ (-) ) (* 4 4 5) (/3 8 11) (* 4 4) (+ (-9) (* 4 4 5) (* (/ 3 6 7) (* 1 1) (+ (-2) (* 4 4 5) (/ 3 2 1)) (* c 6) (+ (-2) (* 3 3 4) ((* (/ 3 1 1) (* a b) ) (40pts) public static Double evaluate(String expr) - a method that accepts a Lisp expression and returns the result. The method returns a RunTimeException if the accepted expression is not a valid Lisp expression. The following can be reasons for the method to throw the exception: o An empty expression (). o Unbalanced expression. o Invalid expression. See the following examples of invalid expressions. o If the expression does not adhere to the rules outlined in the "Overview" section, it is invalid. For this project, if an expression contains operators other than the basic four arithmetic operators it will be considered as an operand. An expression can contain a single letter variables as operands. If an expression contains variable operands, it should prompt the programmer for values of the operands and use the values for the evaluation. For the sake of simplicity, only integer values are going to be accepted from the user. Note that if an expression contains operands such as var, it will consider it as three operand tokens v, a, r and prompt the programmer for the three values. Take a look at the example given below. The following table gives examples of invalid/valid Lisp expressions. Expression (* 3255) (-) () (/* w 1) (a + b + c + d) (* (/ 3 w 1) (* (r r)) (* (/ 3 w 1* rr)) (*(/355)(*2k5)) (* (/ 3 w 1) (/) (* r r)) valid invalid invalid invalid invalid invalid invalid valid invalid Result Remark - operator needs at least one operand Expression cannot be empty (just for this project) two operators one after the other not prefixed not balanced two operators without proper parethesis Your program should be smart enough to recognize tokens even if there is no space division operator needs at least one operand Example: > import java.util.*; > String test1 = "(+ (- 6 7) (* 234 455 256) (/ (/3) (*) (-2 3 1)))";; > result = ExpressionEvaluator.evaluate (test1); > System.out.println(result) > 2.7256318833333332E7 > String test2 = "(+ (- 632) (* a 3 b c) (/ (+ 32) (*) (- c 3 d)))" > result = ExpressionEvaluator.evaluate (test2); < > What is the value of 'a'? > 5 // accepts 5 from the user > What is the value of 'b'? > 6 // accepts 6 from the user > What is the value of 'c'? // accepts 22 from the user > What is the value of 'c'? // accepts 10 from the user > What is the value of 'd'?// accepts 9 from the user > > 1332.0 System.out.println(result) > String test3 = (+ (-6) (* abb3c4bc))"; > result = ExpressionEvaluator.evaluate (test3); < > What is the value of 'a'? // accepts 1 from the user > What is the value of 'b'? // accepts 6 from > What is the value of 'b'? // accepts 0 from the user > What is the value of 'c'? // accepts 10 from the user > What is the value of 'b'?// accepts 19 from the user > What is the value of 'c'?// accepts 95 from the user > System.out.println(result) > -6.0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
This program checks if a given string is a valid JavaScript expression using the ScriptEngineManager import javaxscriptScriptEngine import javaxscript... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


