Question: 6.26 LAB: ASCII table In the previous lab, Convert to Binary, the algorithm to convert an integer to binary was given and the lab involved
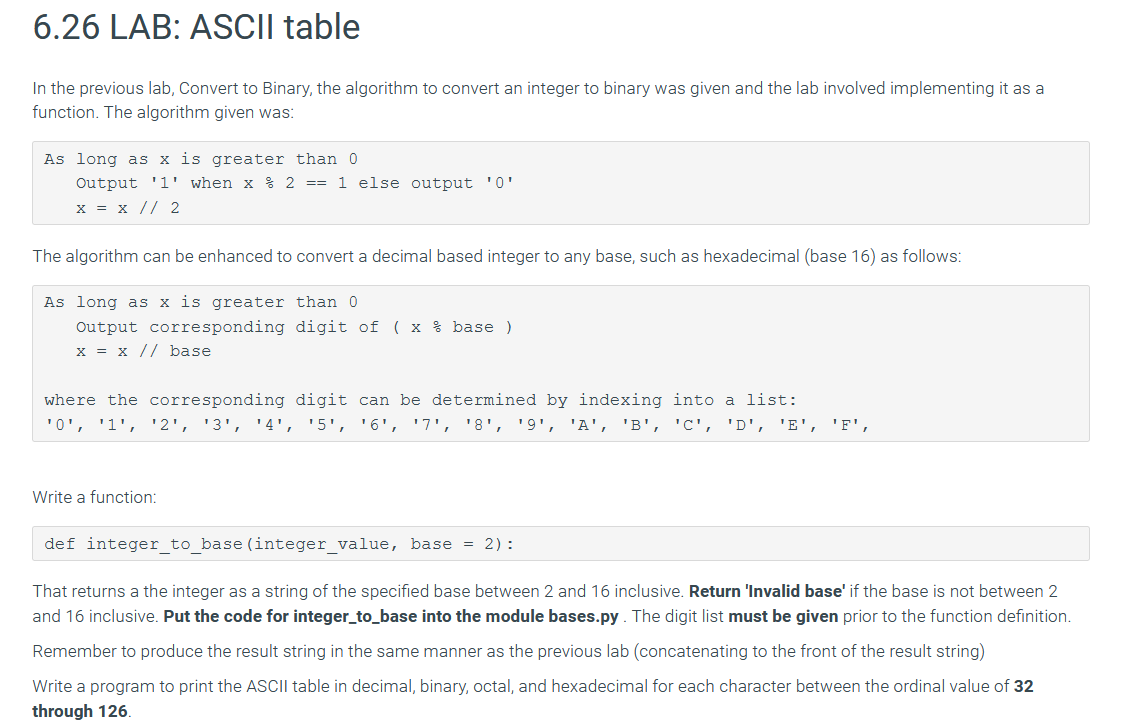

6.26 LAB: ASCII table In the previous lab, Convert to Binary, the algorithm to convert an integer to binary was given and the lab involved implementing it as a function. The algorithm given was: As long as x is greater than 0 Output 'l' when x % 2 == 1 else output '0' x = x // 2 The algorithm can be enhanced to convert a decimal based integer to any base, such as hexadecimal (base 16) as follows: As long as x is greater than 0 Output corresponding digit of ( x % base ) x = x // base where the corresponding digit can be determined by indexing into a list: '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', Write a function: def integer_to_base (integer_value, base = 2): That returns a the integer as a string of the specified base between 2 and 16 inclusive. Return 'Invalid base' if the base is not between 2 and 16 inclusive. Put the code for integer_to_base into the module bases.py. The digit list must be given prior to the function definition Remember to produce the result string in the same manner as the previous lab (concatenating to the front of the result string) Write a program to print the ASCII table in decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal for each character between the ordinal value of 32 through 126. through 126. ASCII Octal 40 Hex 20 21 ! 41 42 Decimal 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 Binary 100000 100001 100010 100011 100100 100101 100110 # 43 44 $ 22 23 24 25 26 45 & 46 Define the program in script main.py. The program must use the integer_to_base function to determine the binary, octal and hexadecimal values. To print the ASCII character corresponding to an integer value, use the function chr()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


