Question: 63 class M2TestArrayChallengel 64 { 65e eTest 66 void testContains() 67{ 68 int [] array 0={} ; 69 assertEquals (false, contains(arrayo, 1)); 71 int []
63 class M2TestArrayChallengel\ 64 {\ 65e eTest\ 66 void testContains()\ 67{\ 68 int [] array
0={};\ 69 assertEquals (false, contains(arrayo, 1));\ 71 int [] array
1={1};\ 72 assertEquals (true, contains(array1, 1));\ 73 assertEquals (false, contains(array1, 2));\ 74\ 75\ 76\ 77\ 78\ int [] array
2={1,2,3};\ assertEquals(true, contains(array2, 2));\ }\ assertEquals (false, contains(array2, 4));\ \ contains\ Let's start slowly by implementing a common code block for traversals! Recall a common traversal setup below for an array called data. Included is the enhanced for loop version (for-each loop in some programming language).\ for(int
i=0;
i data.length;
i++ Typical for loop traversal of a 1d array\ //any required logic\ }\ for(int element : data){ //
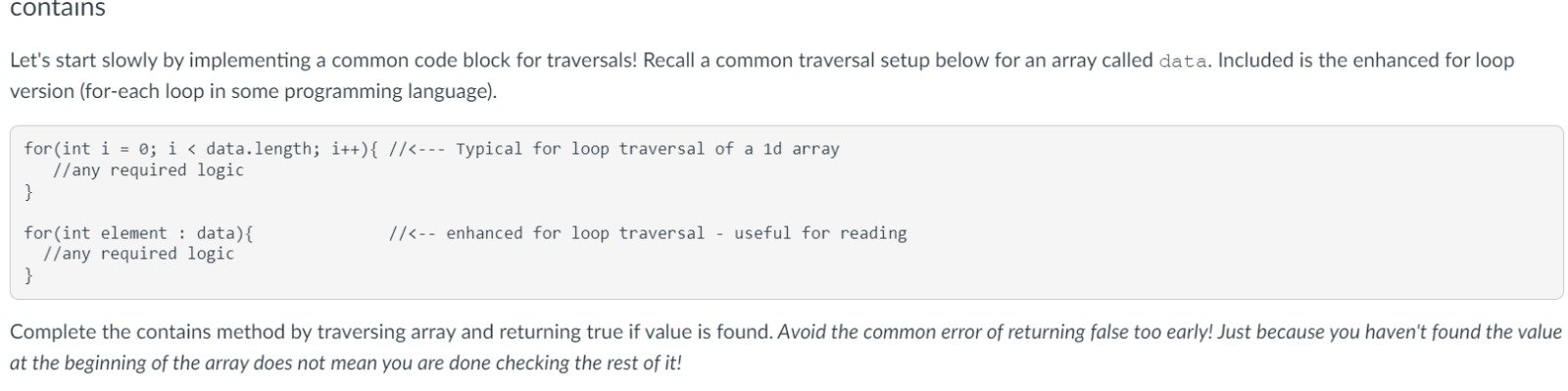
Let's start slowly by implementing a common code block for traversals! Recall a common traversal setup below for an array called data. Included is the enhanced for loop version (for-each loop in some programming language). for(int i=0; i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


