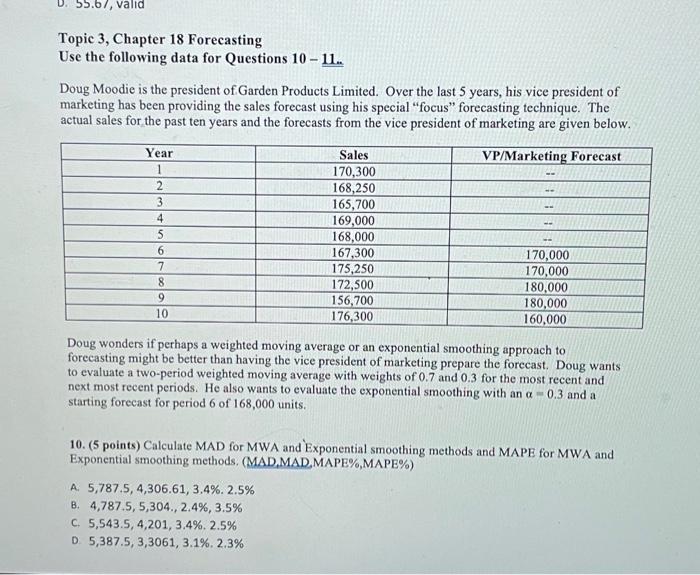
Question: 67, valid Topic 3, Chapter 18 Forecasting Use the following data for Questions 10 - 11. Doug Moodie is the president of Garden Products Limited.
67, valid Topic 3, Chapter 18 Forecasting Use the following data for Questions 10 - 11. Doug Moodie is the president of Garden Products Limited. Over the last 5 years, his vice president of marketing has been providing the sales forecast using his special "focus" forecasting technique. The actual sales for the past ten years and the forecasts from the vice president of marketing are given below. Year Sales VP/Marketing Forecast 1 170,300 2 168,250 3 165,700 4 169,000 5 168,000 6 167,300 170,000 7 175,250 170,000 8 172,500 180,000 9 156,700 180,000 10 176,300 160,000 Doug wonders if perhaps a weighted moving average or an exponential smoothing approach to forecasting might be better than having the vice president of marketing prepare the forecast. Doug wants to evaluate a two-period weighted moving average with weights of 0.7 and 0.3 for the most recent and next most recent periods. He also wants to evaluate the exponential smoothing with an a -0.3 and a starting forecast for period 6 of 168,000 units. 10. (5 points) Calculate MAD for MWA and Exponential smoothing methods and MAPE for MWA and Exponential smoothing methods, (MAD MAD MAPE%,MAPE%) A. 5,787.5, 4,306.61, 3.4%. 2.5% B. 4,787.5,5,304., 2.4%, 3.5% C. 5,543.5, 4,201, 3,4% 2.5% D 5,387.5, 3,3061, 3.1%. 2.3% 11. (5 points)_Which of the two methods (weighted moving average and exponential smoothing) provides the best forecasting method if you were to evaluate these methods for their forecasting accuracy for Years 9 through 10. Use MAD and MAPE evaluation methods we have discussed and used on homework assignments. A. MWA more accurate B. Exponential more accurate C. Both are equally accurate D. Neither is more accurate 12. (5 points) What would be the forecast for Year 11 using both the weighted moving average and the exponential smoothing methods? A. 150,320, 155,432 B. 170,420, 169,474 C. 168,410, 167,482 D. 171,521, 170,231 A builder has located a piece of property that she would like to buy and eventually build on. The land is currently zoned for four homes per acre, but she is planning to request new zoning. What she builds depends on approval of zoning requests and your analysis of this problem to advise her. With her input and your help, the decision process has been reduced to the following costs, alternatives, and probabilities: Cost of land: $2 million. Probability of rezoning:.60. If the land is rezoned, there will be additional costs of $1 million for new roads, lighting, and so on. If the land is rezoned, the contractor must decide whether to build a shopping center or 1,500 apartments that the tentative plan shows would be possible. If she builds a shopping center, there is a 70 percent chance that she can sell the shopping center to a large department store chain for $5 million over her construction cost, which excludes the land; and there is a 30 percent chance that she can sell it to an insurance company for $6 million over her construction cost (also excluding the land), If, instead of the shopping center, she decides to build the 1,500 apartments, she places probabilities on the profits as follows: There is a 60 percent chance that she can sell the apartments to a real estate investment corporation for $3,000 each over her construction cost; there is a 40 percent chance that she can get only $2,000 each over her construction cost. (Both exclude the land cost.) If the land is not rezoned, she will comply with the existing zoning restrictions and simply build 600 homes, on which she expects to make $4,000 over the construction cost on each one (excluding the cost of land). Draw a decision tree of the problem and determine the best solution. The network expected net profit (EV) is: A $4,300,000 B. $3,540,000 C. $1,540,000 D. $2,000,000