Question: 7:21 & Device Interface IP address Mask in dotted Default Gateway decimal form (e.g. 255.255.0.0 for /16) R1 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0 R2 Fa0/0 Fa0/1

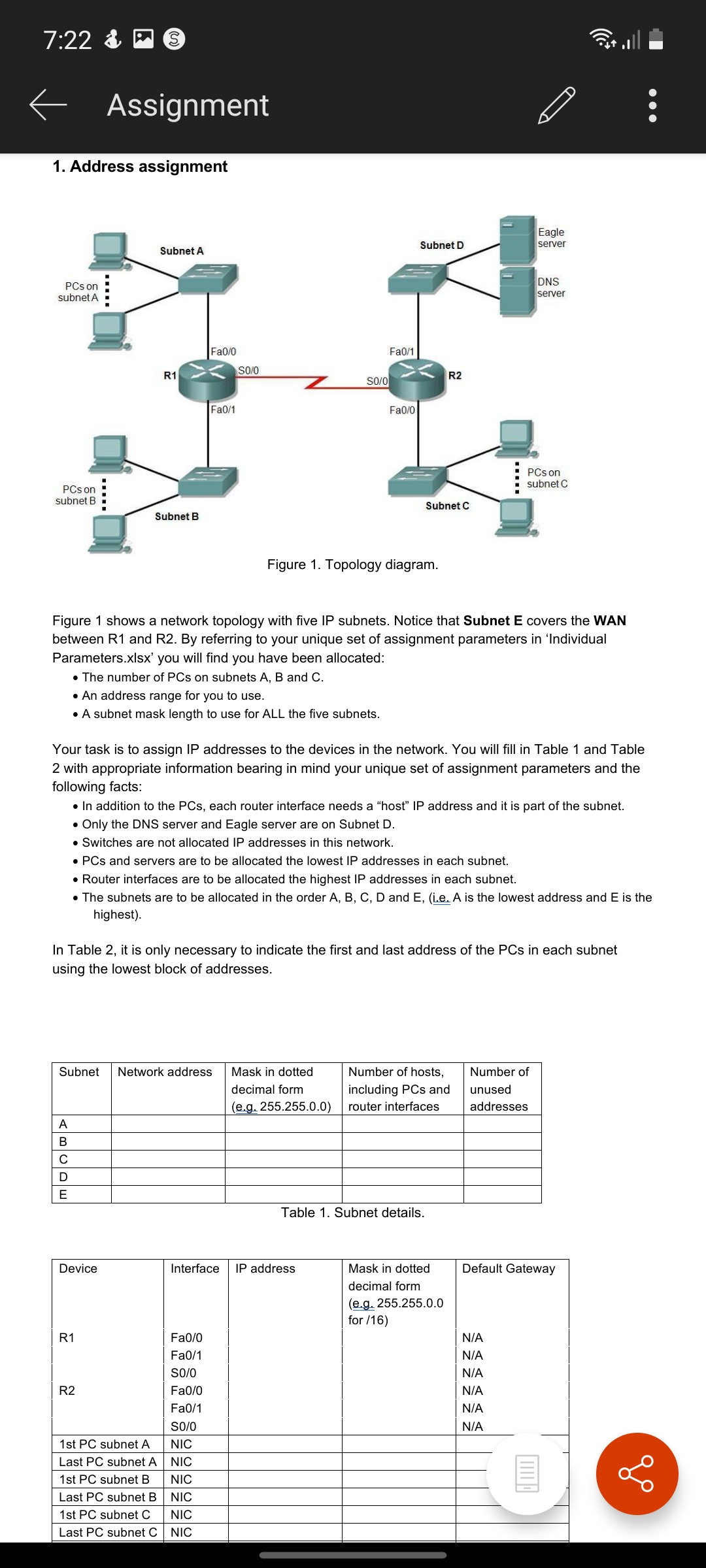
7:21 & Device Interface IP address Mask in dotted Default Gateway decimal form (e.g. 255.255.0.0 for /16) R1 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0 R2 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0 1st PC subnet A NIC Last PC subnet A NIC 1st PC subnet B NIC Last PC subnet B NIC 1st PC subnet C NIC Last PC subnet C NIC 1st PC subnet D NIC Last PC subnet D NIC DNS server NIC Eagle server NIC Table 2. Addressing table. N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 2. Analysis of address space usage You will submit an explanation encompassing: A statement on how many further subnets are available using the address range and mask that you have been allocated. A comment on how efficiently the address space you have been allocated has been used. Calculate the two ratios of: o used addresses to total number of usable addresses, and o unused addresses to total number of usable addresses A brief description of how the address space you have been allocated could be utilised more efficiently to leave a maximum number of addresses free for future subnets. You should not state any actual addresses but rather provide a general description of the process used. A comment on the trade-off between efficient utilisation of the address space and the prospects of future expansion within a subnet A comment on how you would address this trade-off if you had complete freedom in allocating the address range. 3. Application layer services In the 'Individual Parameters.xlsx' file you have been allocated two application layer services. The first of the above is described in the Cisco ITN courseware, to find out about the second you will have to look elsewhere. In most cases the name is given as an abbreviation. For each one, provide: The full title of the protocol if it is given in abbreviated form (e.g. HTTP is hypertext transfer protocol) A brief description of the purpose of the application The transport layer protocol (or protocols) usually used to transport the application protocol The normal (well known) transport layer port(s) that the protocol uses (some may use more than one) A brief description of how the protocol works, for example the key messages sent by the protocol. You are free to include visual illustrations such as (but not limited to) message sequence diagrams. A selection of references to either: a book, published article, or standards document that describes the protocol. Each reference should be included (i.e. cited) at a suitable point in your description of the protocol. A web reference (except to a standards document) is unacceptable. For example, HTTP is defined in RFC 2626 [1], described in a journal paper by Janssen [2] and also described by Tanenbaum [3]. Note how a recognised reference standard, the IEEE, is used below in Section 4 as an example to a standards document, a scholarly article and finally a well-known textbook. Address range - 192.168.113.0-192.168.114.255 Number of PC on Subnet A-20 Number of PC on Subnet B-4 Number of PC on Subnet C - 23 Subnet mask - /26 Application. Layer Protocol 1 - telnet Application. Layer Protocol 2 - SNMP || 7:22 & Assignment 1. Address assignment PCs on subnet A Eagle Subnet D server Subnet A Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0 R1 R2 S0/0 Fa0/1 Fa0/0 PCs on subnet B Subnet B Subnet C Figure 1. Topology diagram. DNS server PCs on subnet C Figure 1 shows a network topology with five IP subnets. Notice that Subnet E covers the WAN between R1 and R2. By referring to your unique set of assignment parameters in 'Individual Parameters.xlsx' you will find you have been allocated: The number of PCs on subnets A, B and C. An address range for you to use. A subnet mask length to use for ALL the five subnets. Your task is to assign IP addresses to the devices in the network. You will fill in Table 1 and Table 2 with appropriate information bearing in mind your unique set of assignment parameters and the following facts: In addition to the PCs, each router interface needs a "host" IP address and it is part of the subnet. Only the DNS server and Eagle server are on Subnet D. Switches are not allocated IP addresses in this network. PCs and servers are to be allocated the lowest IP addresses in each subnet. Router interfaces are to be allocated the highest IP addresses in each subnet. The subnets are to be allocated in the order A, B, C, D and E, (i.e. A is the lowest address and E is the highest). In Table 2, it is only necessary to indicate the first and last address of the PCs in each subnet using the lowest block of addresses. Subnet Network address Mask in dotted Number of hosts, decimal form including PCs and (e.g. 255.255.0.0) router interfaces Number of unused addresses ABCDE Table 1. Subnet details. Device Interface IP address R1 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0 R2 P2 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 S0/0 NIC 1st PC subnet A Last PC subnet A NIC 1st PC subnet B NIC Last PC subnet B NIC 1st PC subnet C NIC Last PC subnet C NIC Mask in dotted decimal form (e.g. 255.255.0.0 for /16) Default Gateway N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A go
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


